Abstract
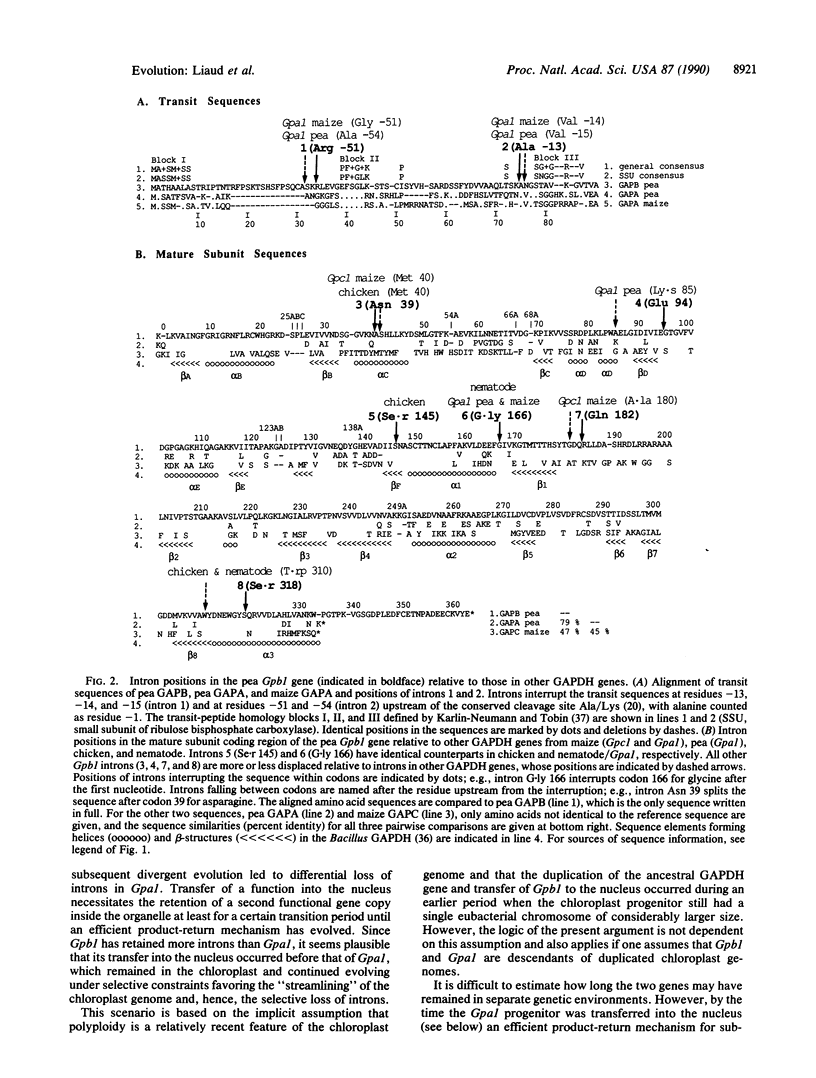
Chloroplast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) is composed of two different subunits, GAPA and GAPB, which are encoded in the nucleus by two related genes of eubacterial origin. In the present work the genes encoding chloroplast GAPA and GAPB from pea have been cloned and sequenced. The gene for GAPB is split by eight introns. Two introns interrupt the region encoding the transit peptide and six are found within the region encoding the mature subunit, four of which are in identical or similar positions relative to genes for cytosolic GAPDH of eukaryotic organisms. As opposed to this, the gene encoding pea GAPA has only two introns in the region encoding the mature subunit. These findings strongly support the "intron early" hypothesis and suggest that the low number of introns in the gene for chloroplast GAPA is due to differential loss of introns during the streamlining period of the chloroplast genome following the GAPB/GAPA separation. We deduce from this that eubacteria and chloroplasts contained GT-AG introns until relatively recently and that the duplication event leading to the genes encoding GAPB and GAPA and their respective transit peptides occurred in the chloroplast progenitor prior to the successive transfer and functional reintegration of these genes into the nuclear environment. These conclusions imply that GAPA/GAPB transit peptides are of eubacterial origin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldauf S. L., Palmer J. D. Evolutionary transfer of the chloroplast tufA gene to the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):262–265. doi: 10.1038/344262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker G., Harris J. I., Thierry J. C., Walker J. E., Wonacott A. J. Sequence and structure of D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Nature. 1977 Mar 24;266(5600):328–333. doi: 10.1038/266328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann H., Cerff R., Salomon M., Soll J. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNAs encoding the cytosolic precursors of subunits GapA and GapB of chloroplast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from pea and spinach. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Jul;13(1):81–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00027337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann H., Martinez P., Quigley F., Martin W., Cerff R. Endosymbiotic origin and codon bias of the nuclear gene for chloroplast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from maize. J Mol Evol. 1987;26(4):320–328. doi: 10.1007/BF02101150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W. A catalogue of splice junction and putative branch point sequences from plant introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9549–9559. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brändén C. I., Eklund H., Cambillau C., Pryor A. J. Correlation of exons with structural domains in alcohol dehydrogenase. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1307–1310. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01967.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. The generality of self-splicing RNA: relationship to nuclear mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90751-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerff R., Kloppstech K. Structural diversity and differential light control of mRNAs coding for angiosperm glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7624–7628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozens A. L., Walker J. E. The organization and sequence of the genes for ATP synthase subunits in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus 6301. Support for an endosymbiotic origin of chloroplasts. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):359–383. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90667-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik C. S., Rutter W. J., Fletterick R. Splice junctions: association with variation in protein structure. Science. 1983 Jun 10;220(4602):1125–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.6344214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duester G., Jörnvall H., Hatfield G. W. Intron-dependent evolution of the nucleotide-binding domains within alcohol dehydrogenase and related enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):1931–1941. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. The exon theory of genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:901–905. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., Turner S., Olsen G. J., Barns S., Lane D. J., Pace N. R. Evolutionary relationships among cyanobacteria and green chloroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3584–3592. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3584-3592.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W. The evolutionary origins of organelles. Trends Genet. 1989 Sep;5(9):294–299. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90111-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Mobile RNA catalysts. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):716–718. doi: 10.1038/336716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin-Neumann G. A., Tobin E. M. Transit peptides of nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins share a common amino acid framework. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):9–13. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04170.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegstra K. Transport and routing of proteins into chloroplasts. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90898-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B., Gingrich J. C., Stiegler G. L., Farley M. A., Delius H., Hallick R. B. Nine introns with conserved boundary sequences in the Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase gene. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):545–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90247-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Cerff R. Prokaryotic features of a nucleus-encoded enzyme. cDNA sequences for chloroplast and cytosolic glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases from mustard (Sinapis alba). Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 1;159(2):323–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez P., Martin W., Cerff R. Structure, evolution and anaerobic regulation of a nuclear gene encoding cytosolic glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from maize. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 20;208(4):551–565. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. D. Contrasting modes and tempos of genome evolution in land plant organelles. Trends Genet. 1990 Apr;6(4):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90125-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley F., Brinkmann H., Martin W. F., Cerff R. Strong functional GC pressure in a light-regulated maize gene encoding subunit GAPA of chloroplast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: implications for the evolution of GAPA pseudogenes. J Mol Evol. 1989 Nov;29(5):412–421. doi: 10.1007/BF02602911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley F., Martin W. F., Cerff R. Intron conservation across the prokaryote-eukaryote boundary: structure of the nuclear gene for chloroplast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2672–2676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. A., Sachs M. M. Differential expression and sequence analysis of the maize glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene family. Plant Cell. 1989 Aug;1(8):793–803. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.8.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. M., Dayhoff M. O. Origins of prokaryotes, eukaryotes, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. Science. 1978 Jan 27;199(4327):395–403. doi: 10.1126/science.202030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Gierl A., Klösgen R. B., Wienand U., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. The Spm (En) transposable element controls the excision of a 2-kb DNA insert at the wx allele of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1021–1028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. On the origin of RNA splicing and introns. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):397–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih M. C., Lazar G., Goodman H. M. Evidence in favor of the symbiotic origin of chloroplasts: primary structure and evolution of tobacco glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90367-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone E. M., Rothblum K. N., Schwartz R. J. Intron-dependent evolution of chicken glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase gene. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):498–500. doi: 10.1038/313498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tingey S. V., Walker E. L., Coruzzi G. M. Glutamine synthetase genes of pea encode distinct polypeptides which are differentially expressed in leaves, roots and nodules. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04710.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeden N. F. Genetic and biochemical implications of the endosymbiotic origin of the chloroplast. J Mol Evol. 1981;17(3):133–139. doi: 10.1007/BF01733906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarbrough P. O., Hayden M. A., Dunn L. A., Vermersch P. S., Klass M. R., Hecht R. M. The glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene family in the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans: isolation and characterization of one of the genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 28;908(1):21–33. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. A new method for predicting signal sequence cleavage sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4683–4690. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Steppuhn J., Herrmann R. G. Domain structure of mitochondrial and chloroplast targeting peptides. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 1;180(3):535–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



