Abstract
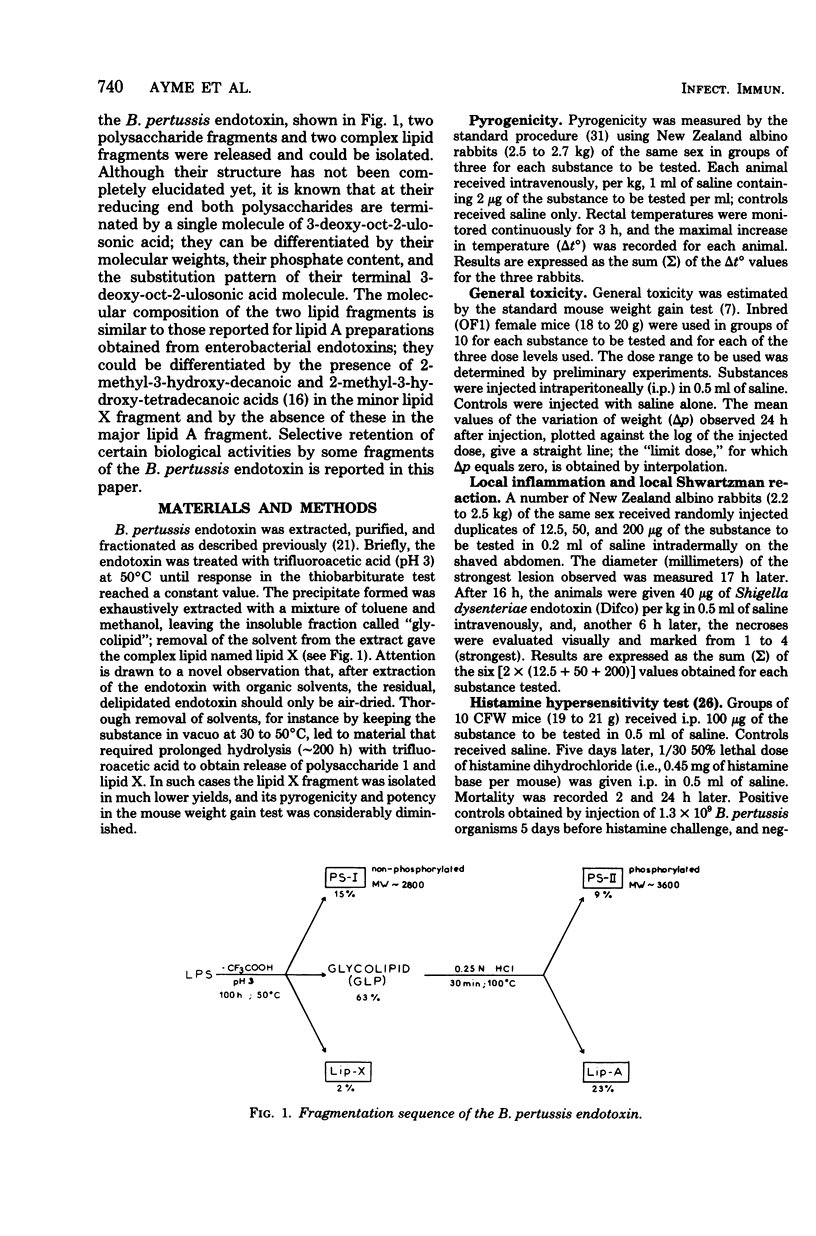
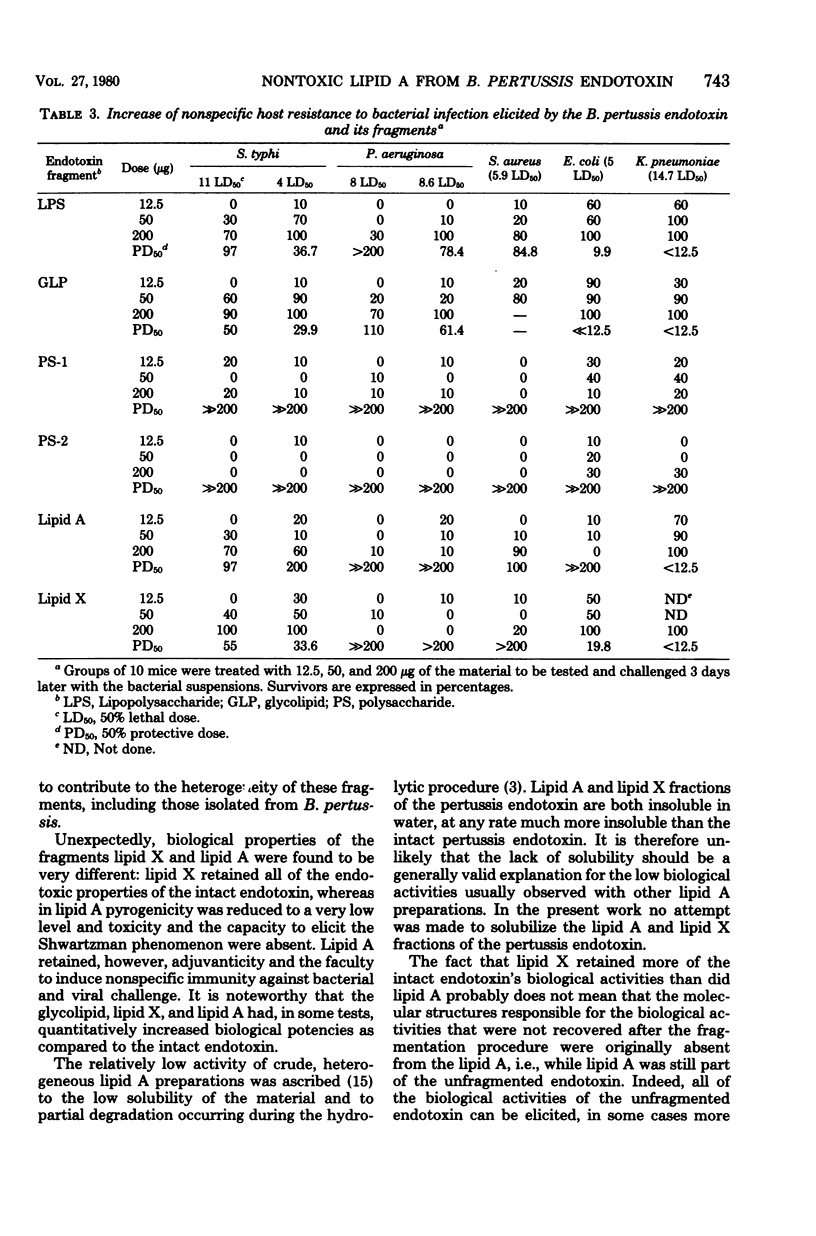
Endotoxin from fresly sedimented Bordetella pertussis cells, isolated by the phenol/water procedure when submitted to kinetically controlled, mild acidic hydrolysis released a polysaccharide (polysaccharide 1), a complex lipid (lipid X), and a glycolipid. When treated with somewhat stronger acid, the glycolipid yielded a second polysaccharide (polysaccharide 2) and another complex lipid (lipid A). The intact pertussis endotoxin had all the usual properties of endotoxins extracted from enteric bacteria. Lipid X and the intermediary glycolipid retained all the endotoxic properties of the unfractionated endotoxin. In lipid A, pyrogenicity was reduced to a very low level and toxicity and Shwartzman reactivity were absent; however, this fraction retained most of the endotoxin's antiviral activity, and its adjuvant power was considerably higher than that of the intact endotoxin. Lipid A elicited nonspecific resistance against challenge with certain bacteria, but not against others.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackers J. P., Dolby J. M. The antigen of Bordetella pertussis that induces bactericidal antibody and its relationship to protection of mice. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Apr;70(2):371–382. doi: 10.1099/00221287-70-2-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aprile M. A., Wardlaw A. C. Immunochemical studies on the lipopolysaccharides of Bordetella pertussis. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Feb;19(2):231–239. doi: 10.1139/m73-035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Nowotny Relation of structure to function in bacterial O-antigens--VII. Endotoxicity of 'lipid A'. Immunochemistry. 1975 Jan;12(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cundy K. R., Nowotny A. Comparisons of 5 toxicity parameters of Serratia marcescens endotoxins. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Apr;127(4):999–1003. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolby J. M., Dolby D. E., Bronne-Shanbury C. J. The effects of humoral, cellular and non-specific immunity on intracerebral Bordetella pertussis infections in mice. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Feb;74(1):85–102. doi: 10.1017/s002217240004674x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDMAN H. H., SULTZER B. M. Dissociation of the biological properties of bacterial endotoxin by chemical modification of the molecule. J Exp Med. 1962 Dec 1;116:929–942. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.6.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDMAN H. H., SULTZER B. M. Dissociation of the biological properties of bacterial endotoxin by chemical modification of the molecule. J Exp Med. 1962 Dec 1;116:929–942. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.6.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger H., Heymer B., Hof H., Rietschel E., Schleifer K. H. Uber Struktur und biologische Aktivität von Bordetella pertussis-Endotoxin. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1976 Aug;235(1-3):56–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O. Electrodialysis of lipopolysaccharides and their conversion to uniform salt forms. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):603–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04172.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C. Physical state and biological activity of lipopolysaccharides. Toxicity and immunogenicity of the lipid A component. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Jul;149(2-4):214–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Interaction of lipopolysaccharides and lipid A with complement. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Mar 1;19(1):143–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O., Westphal O., Kim Y. B., Watson D. W. Biological activities of lipid A complexed with bovine-serum albumin. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 4;31(2):230–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASKINS W. T., LANDY M., MILNER K. C., RIBI E. Biological properties of parent endotoxins and lipoid fractions, with a kinetic study of acid-hydrolyzed endotoxin. J Exp Med. 1961 Nov 1;114:665–684. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.5.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeffner N., Chaby R., Szabó L. Identification of 2-methyl-3-hydroxydecanoic and 2-methyl-3-hydroxytetradecanoic acids in the 'lipid X' fraction of the Bordetella pertussis endotoxin. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Aug 1;77(3):535–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KITAGAWA M., HAZAMA H., MOTOMURA M., YAMAMURA Y., SAWADA K., NAGAI J. Chemical studies on cellular components of Hemophilus pertussis. II. Isolation of toxic lipopolysaccharide. J Biochem. 1961 Jun;49:477–480. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai N. Chemical studies on the lipid component of endotoxin, with special emphasis on its relation to biological activities. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):486–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima Y., Yoshida F., Nakase Y. Interferon production by Bordetella pertussis components in rabbits and in rabbit cell cultures. Jpn J Microbiol. 1973 Mar;17(2):160–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1973.tb00721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Dur A., Caroff M., Chaby R., Szabó L. A novel type of endotoxin structure present in Bordetella pertussis. Isolation of two different polysaccharides bound to lipid A. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):579–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLENNAN A. P. Specific lipopolysaccharides of Bordetella. Biochem J. 1960 Feb;74:398–409. doi: 10.1042/bj0740398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Verroust P., Weigle W. O. Anticomplementary activity of lipid A isolated from lipopolysaccharides. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Sep;143(4):1025–1030. doi: 10.3181/00379727-143-37462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munoz J., Bergman R. K. Histamine-sensitizing factors from microbial agents, with special reference to Bordetella pertussis. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Jun;32(2):103–126. doi: 10.1128/br.32.2.103-126.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E., WESTPHAL O., LUDERITZ O., GORZYNSKI E. A., EICHENBERGER E. Studies of enterobacterial lipopolysaccharides; effects of heat and chemicals on erythrocyte-modifying, antigenic, toxic and pyrogenic properties. J Immunol. 1956 May;76(5):377–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakase Y., Tateishi M., Sekiya K., Kasuga T. Chemical and biological properties of the purified O antigen of Bordetella pertussis. Jpn J Microbiol. 1970 Jan;14(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1970.tb00485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng A. K., Butler R. C., Chen C. L., Nowotny A. Relationship of structure to function in bacterial endotoxins. IX. Differences in the lipid moiety of endotoxic glycolipids. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):511–515. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.511-515.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowotny A., Radvany R., Neale N. E. Neutralization of toxic bacterial O-antigens with O-antibodies while maintaining their stimulus on non-specific resistance. Life Sci. 1965 May;4(10):1107–1114. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusztai Z., Csizér Z., Joó I. The role and specificity of bordetella lipopolysaccharide in immune reactions. Z Immunitatsforsch Allerg Klin Immunol. 1971;141(2):129–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


