Abstract
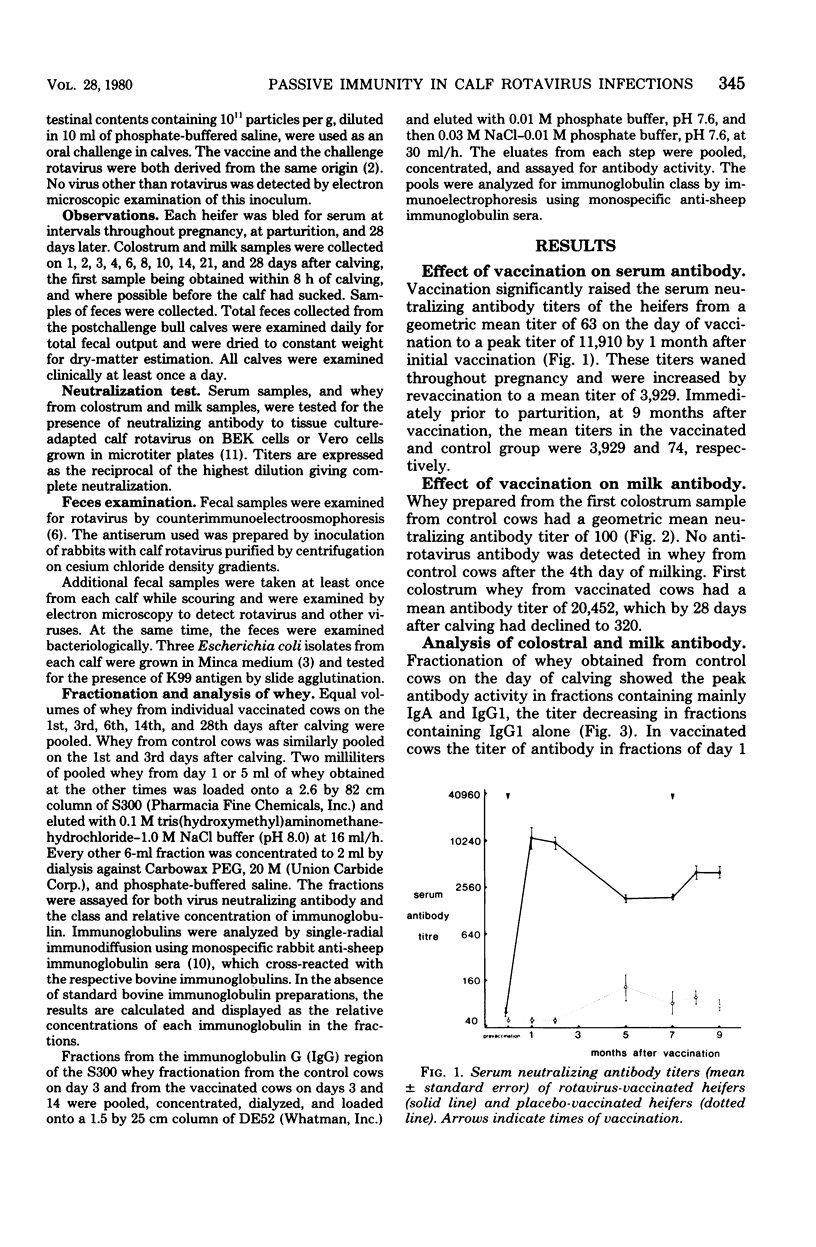
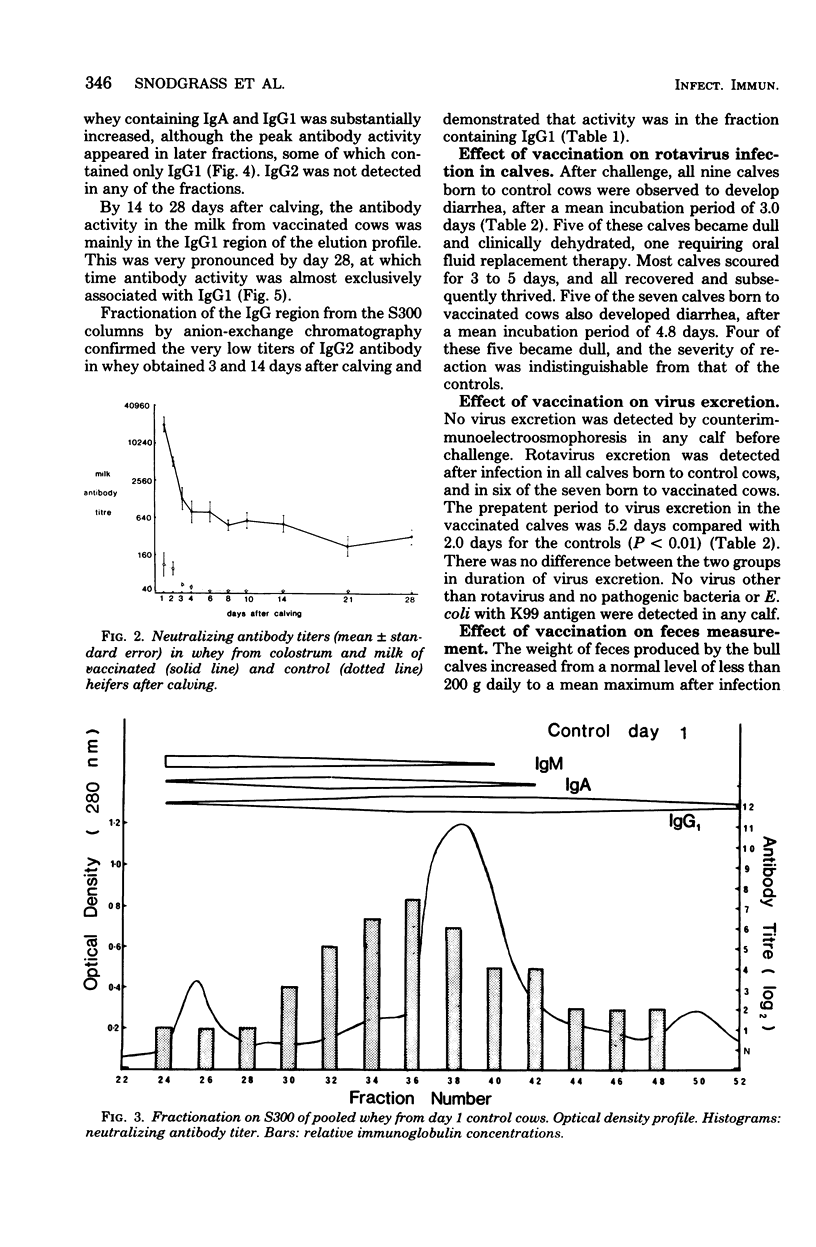
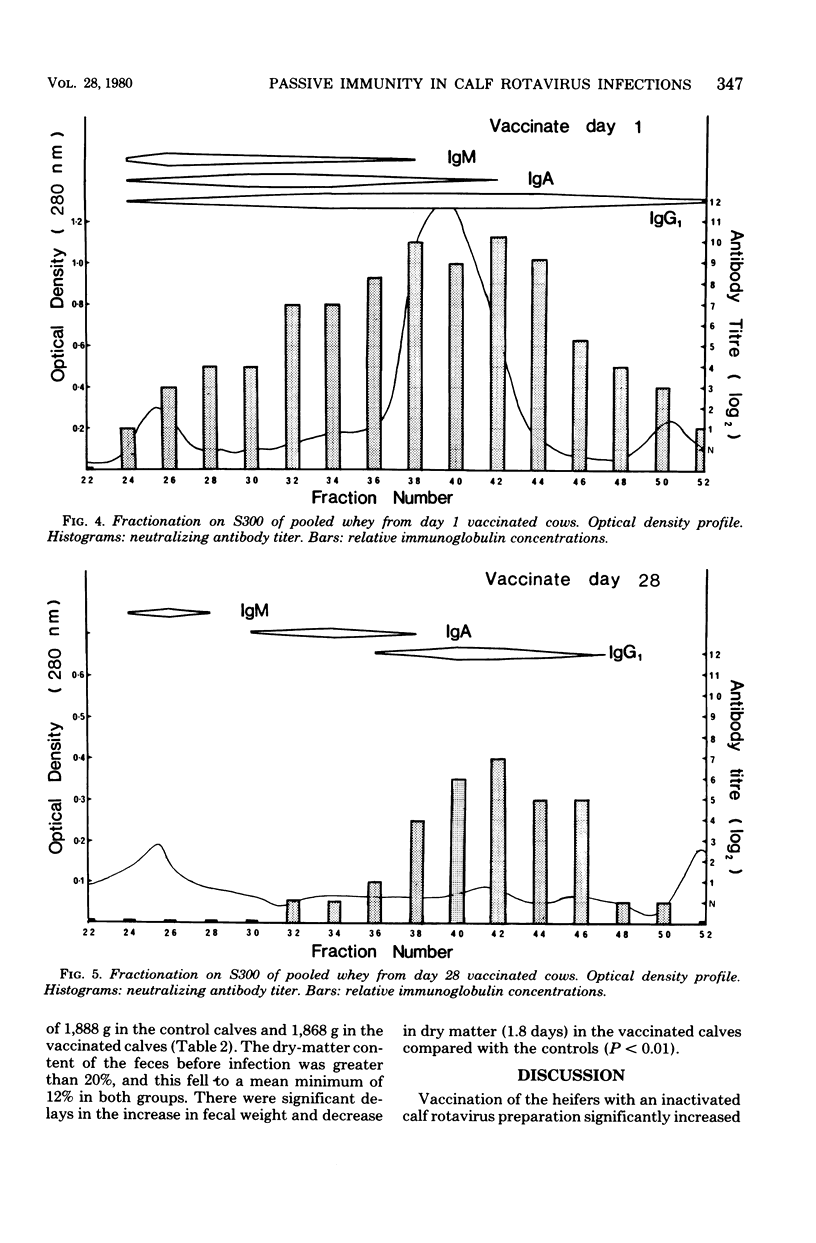
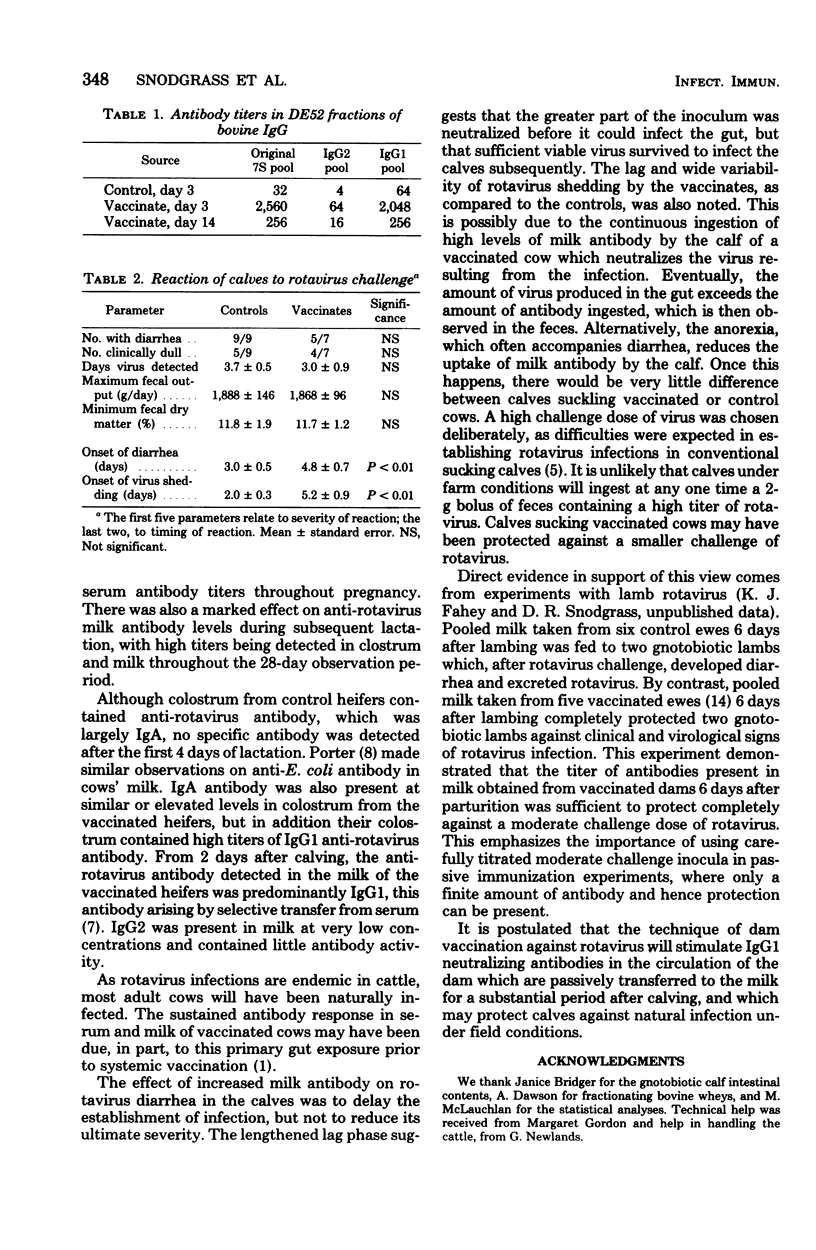
Ten heifers were inoculated on two occasions with an inactivated preparation of tissue culture-grown calf rotavirus, and a further ten heifers received a placebo vaccine. Serum anti-rotavirus antibody titers were significantly increased throughout pregnancy in the vaccinated group. After calving, the mean neutralizing antibody titer of colostral whey in control cows was 100, associated with immunoglobulins A and G1. No antibody was detected in the milk of these cows after the 4th day postpartum. The colostral whey from the vaccinated cows had a mean antibody titer of 20,452; 28 days after calving, the mean milk antibody titer was 320, associated mainly with immunoglobulin G1. Calves were challenged with a large oral inoculum of calf rotavirus at the 7th day of age. There was significant lengthening of the incubation and prepatent periods in calves born to vaccinated dams, but rotavirus-associated diarrhea of equal severity occurred in both groups. Evidence is presented which suggests that rotavirus antibody in milk can protect against a smaller challenge dose. Maternal immunization against rotavirus may be a practical proposition.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bohl E. H., Saif L. J. Passive immunity in transmissible gastroenteritis of swine: immunoglobulin characteristics of antibodies in milk after inoculating virus by different routes. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):23–32. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.23-32.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridger J. C., Woode G. N. Neonatal calf diarrhoea: identification of a reovirus-like (rotavirus) agent in faeces by immunofluorescence and immune electron microscopy. Br Vet J. 1975 Sep-Oct;131(5):528–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A., Jansen W. H., Agterberg C. M. Detection of the K99 antigen by means of agglutination and immunoelectrophoresis in Escherichia coli isolates from calves and its correlation with entertoxigenicity. Infect Immun. 1976 May;13(5):1369–1377. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.5.1369-1377.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecce J. G., King M. W., Mock R. Reovirus-like agent associated with fatal diarrhea in neonatal pigs. Infect Immun. 1976 Sep;14(3):816–825. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.3.816-825.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan E. F., Pearson G. R., McNulty M. S. Quantitative observations on experimental reo-like virus (rotavirus) infection in colostrum-deprived calves. Vet Rec. 1979 Mar 10;104(10):206–209. doi: 10.1136/vr.104.10.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton P. J., Petric M., Hewitt C. M., Szymanski M. T., Tam J. S. Counter-immunoelectro-osmophoresis for the detection of infantile gastroenteritis virus (orbi-group) antigen and antibody. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Mar;29(3):191–197. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.3.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newby T. J., Bourne J. The nature of the local immune system of the bovine mammary gland. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):461–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P. Immunoglobulins in bovine mammary secretions. Quantitative changes in early lactation and absorption by the neonatal calf. Immunology. 1972 Aug;23(2):225–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saif L. J., Bohl E. H. Passive immunity in transmissible gastroenteritis of swine: immunoglobulin classes of milk antibodies after oral-intranasal inoculation of sows with a live low cell culture-passaged virus. Am J Vet Res. 1979 Jan;40(1):115–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. D., Dawson A. M., Wells P. W., Burrells C. Immunoglobulin concentrations in ovine body fluids. Res Vet Sci. 1975 Sep;19(2):189–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Herring J. A. The action of disinfectants on lamb rotavirus. Vet Rec. 1977 Jul 23;101(4):81–81. doi: 10.1136/vr.101.4.81-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Wells P. W. Passive immunity in rotaviral infections. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Sep 1;173(5 Pt 2):565–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil K. W., Bohl E. H., Saif L. J. Techniques for rotaviral propagation. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Sep 1;173(5 Pt 2):548–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells P. W., Snodgrass D. R., Herring J. A., Dawson A. M. Antibody titres to lamb rotavirus in colostrum and milk of vaccinated ewes. Vet Rec. 1978 Jul 15;103(3):46–48. doi: 10.1136/vr.103.3.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



