Abstract
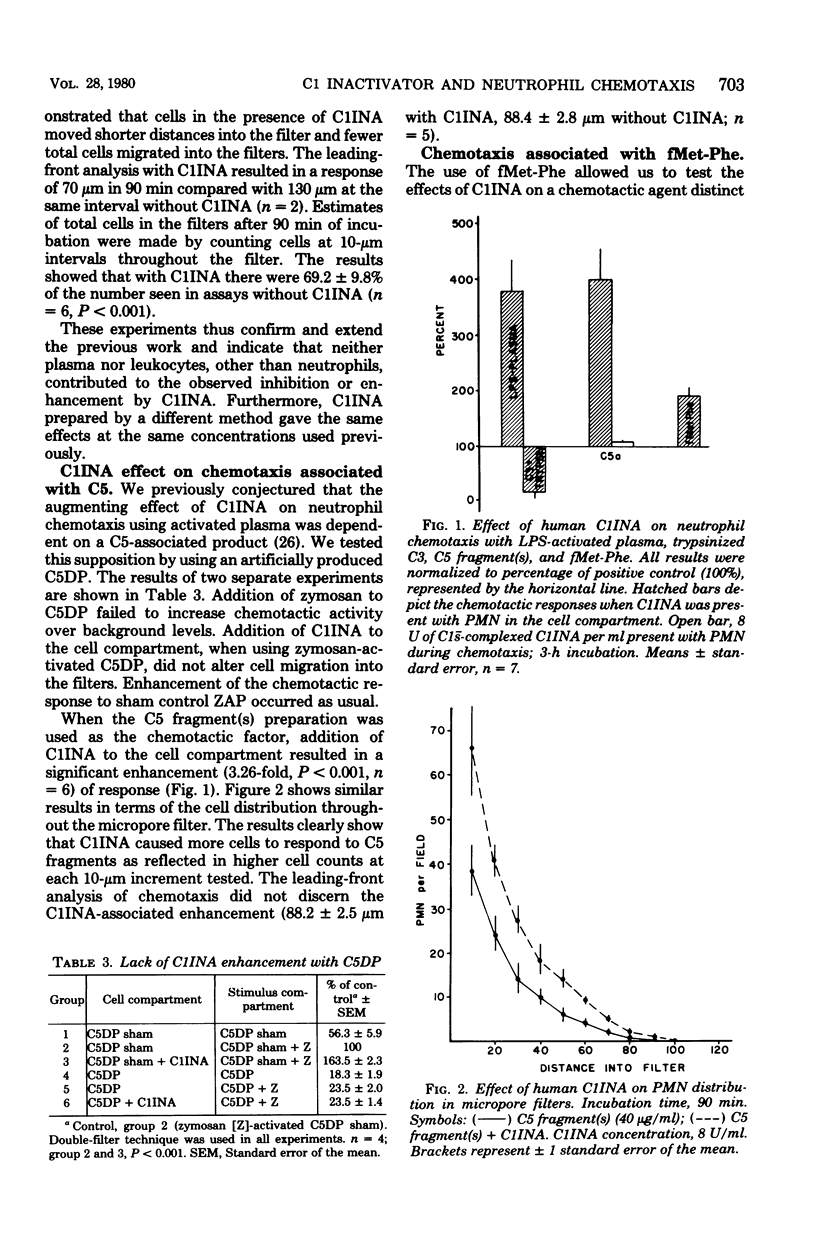
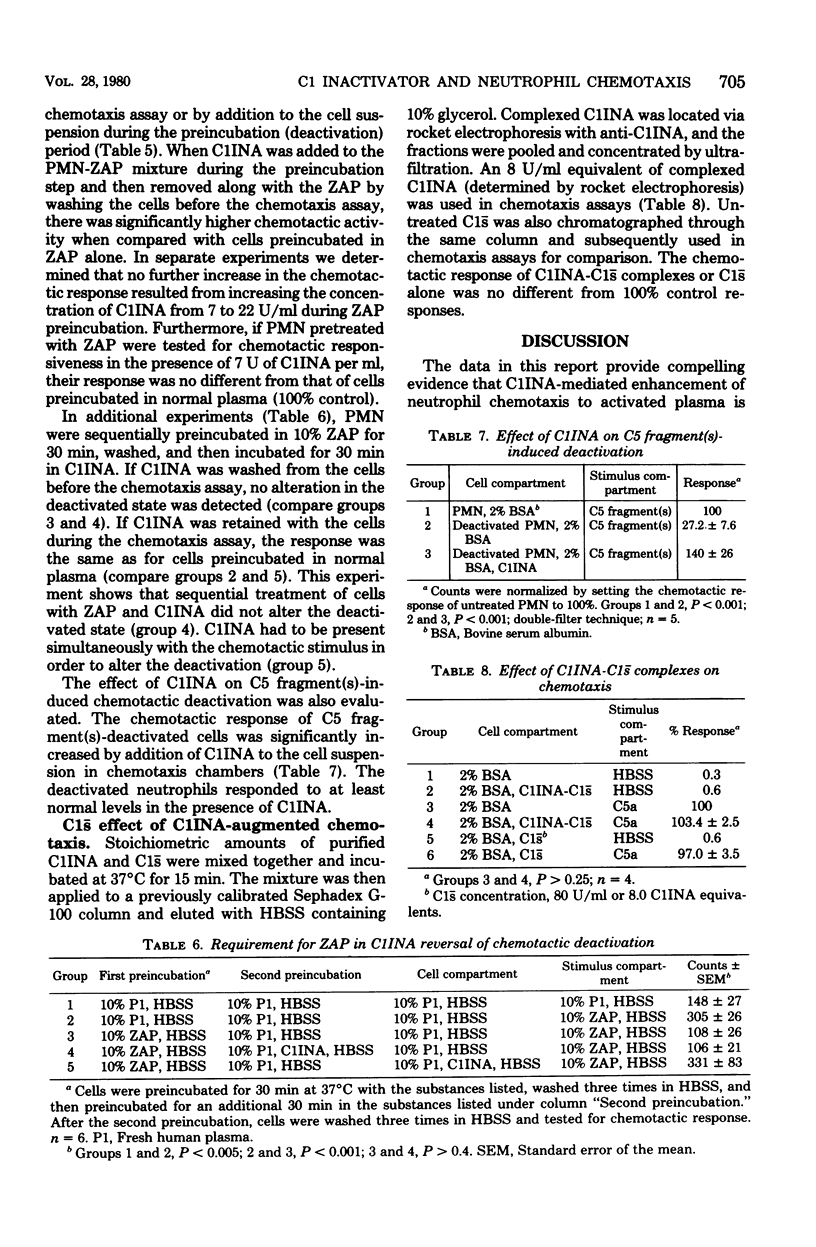
This study was undertaken to ascertain the relationship between complement-derived chemotactic factors and complement component 1 inactivator (C1INA) enhancement of neutrophil chemotaxis. Studies were also designed to determine whether the C1s- reactive or binding site on C1INA was functional in altering chemotactic responsiveness of neutrophilic leukocyes. Chemotaxis was assessed by determining cell migration in micropore filters. C1INA was found to enhance the chemotactic response to zymosan-activated plasma, C5a, and N-formyl-L-methionyl-L-phenylalanine and to bring the response of chemotactically deactivated cells to normal. In contrast, C1INA inhibited the chemotactic response to trypsin and EAC4oxy2-activated C3. Complexes of C1INA and C1s- failed to mediate the usual C1INA-enhanced response. Artificially produced C5-deficient plasma, when treated with zymosan, failed to support chemotaxis or to produce chemotactic deactivation. C1INA was without effect when this activated plasma was used as a source of chemotactic factors. We conclude from these data that C1INA enhancement of neutrophil chemotaxis to activated plasma is associated with C5-derived chemotactic fragments. The effects of C1INA are apparently related to the C1s- reactive or binding site(s) on the C1INA molecule. We suggest that C1INA may play a homeostatic role in neutrophil chemotaxis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Donaldson V. H. Serum inhibitor of C'1-esterase in health and disease. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Sep;68(3):369–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English D., Andersen B. R. Single-step separation of red blood cells. Granulocytes and mononuclear leukocytes on discontinuous density gradients of Ficoll-Hypaque. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehr J., Dahinden C. Modulating influence of chemotactic factor-induced cell adhesiveness on granulocyte function. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jul;64(1):8–16. doi: 10.1172/JCI109466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Henson P. M., Otani A., Hugli T. E. Chemotactic response to human C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins. I. Evaluation of C3a and C5a leukotaxis in vitro and under stimulated in vivo conditions. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):109–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Rosenthal A. S. The regulatory role of divalent cations in human granulocyte chemotaxis. Evidence for an association between calcium exchanges and microtubule assembly. J Cell Biol. 1974 Sep;62(3):594–609. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Active site chemotactic factors and the regulation of the human neutrophil chemotactic response. Antibiot Chemother (1971) 1974;19:218–232. doi: 10.1159/000395433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Stimulation of human neutrophil leukocyte aerobic glucose metabolism by purified chemotactic factors. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):591–599. doi: 10.1172/JCI107594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J. Modulation of human neutrophil polymorphonuclear leucocyte migration by human plasma alpha-globulin inhibitors and synthetic esterase inhibitors. Immunology. 1975 Jul;29(1):163–174. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAINES A. L., LEPOW I. H. STUDIES ON HUMAN C'1-ESTERASE. I. PURIFICATION AND ENZYMATIC PROPERTIES. J Immunol. 1964 Mar;92:456–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpel P. C., Cooper N. R. Studies on human plasma C1 inactivator-enzyme interactions. I. Mechanisms of interaction with C1s, plasmin, and trypsin. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):593–604. doi: 10.1172/JCI107967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt H., Heimburger N., Kranz T., Schwick H. G. Ein Beitrag zur Isolierung und Charakterisierung des Cl-Inaktivators aus Humanplasma. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Dec;17(2):254–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Anaphylatoxins: C3a and C5a. Adv Immunol. 1978;26:1–53. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60228-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. The fibrinolytic pathway of human plasma. II. The generation of chemotactic activity by activation of plasminogen proactivator. J Clin Invest. 1973 Oct;52(10):2591–2595. doi: 10.1172/JCI107451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Kay A. B., Austen K. F. A prealbumin activator of prekallikrein. 3. Appearance of chemotactic activity for human neutrophils by the conversion of human prekallikrein to kallikrein. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):81–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY L. R., LEPOW I. H. Assay and properties of serum inhibitor of C'l-esterase. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Aug-Sep;101:608–611. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-25034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON U. R., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. ISOLATION OF BETA IF-GLOBULIN FROM HUMAN SERUM AND ITS CHARACTERIZATION AS THE FIFTH COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:277–298. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson U. R., Tomar R. H., Taylor F. B., Jr Additional studies on human C5: development of a modified purification method and characterization of the purified product by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Immunochemistry. 1972 Jul;9(7):709–723. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reboul A., Arlaud G. J., Sim R. B., Colomb M. G. A simplified procedure for the purification of C1-inactivator from human plasma. Interaction with complement subcomponents C1r and C1s. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 1;79(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80347-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remold H. G., Rosenberg R. D. Enhancement of migration inhibitory factor activity by plasma esterase inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 25;250(16):6608–6613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Austen K. F., Goetzl E. J. Chemotactic activity derived from interaction of factors D and B of the properdin pathway with cobra venom factor or C3B. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):587–592. doi: 10.1172/JCI107966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Hollers J. C., Bing D. H., Patrick R. A. Effects of human C 1 inhibitor on complement-mediated human leukocyte chemotaxis. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):216–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Hollers J. C., Patrick R. A., Hassett C. Motility and adhesiveness in human neutrophils. Effects of chemotactic factors. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):221–229. doi: 10.1172/JCI109293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbuch M., Audran R. The isolation of IgG from mammalian sera with the aid of caprylic acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Nov;134(2):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. D., Prahl J. W. Third component of human complement: purification from plasma and physicochemical characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4513–4521. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Becker E. L. Biochemical demonstration of the activatable esterase of the rabbit netrophil involved in the chemotactic response. J Immunol. 1970 Nov;105(5):1057–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Becker E. L. The deactivation of rabbit neutrophils by chemotactic factor and the nature of the activatable esterase. J Exp Med. 1968 Apr 1;127(4):693–709. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.4.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeke B. Rocket immunoelectrophoresis. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:37–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


