Abstract
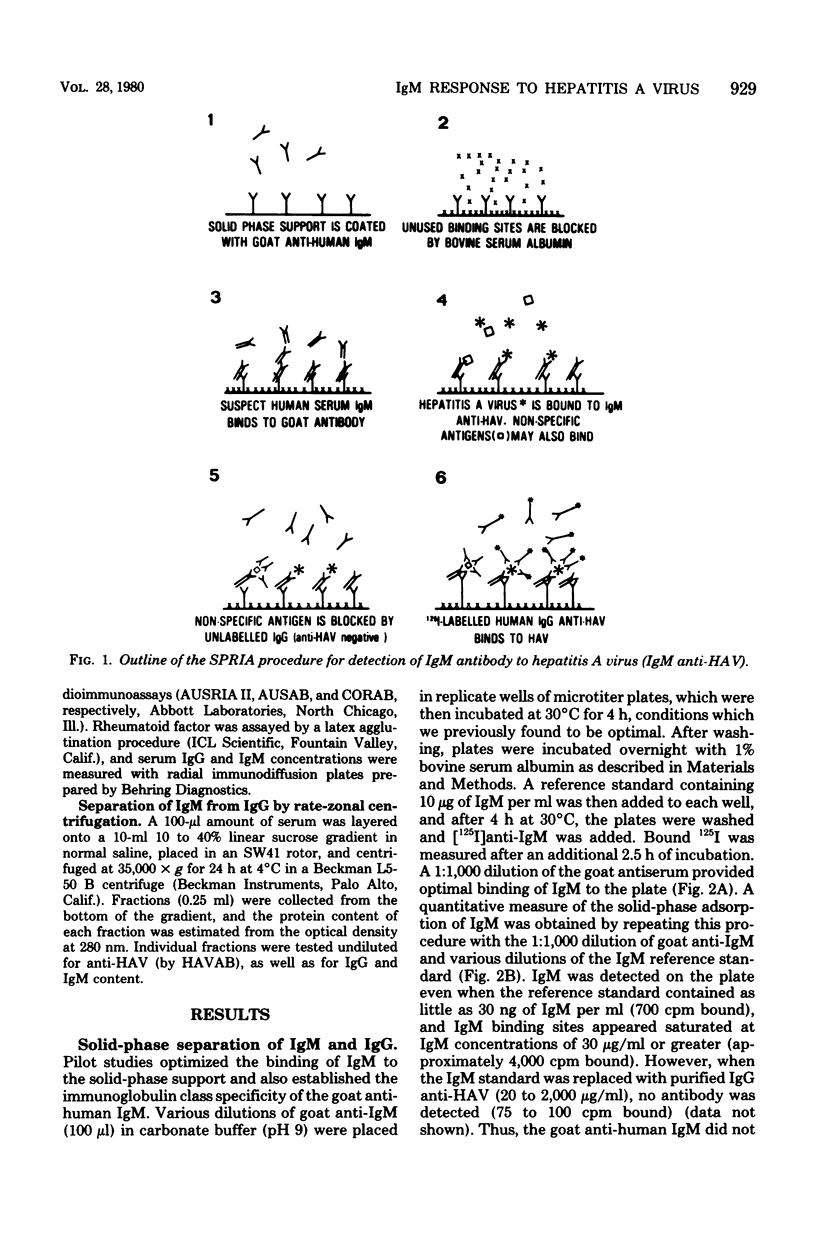
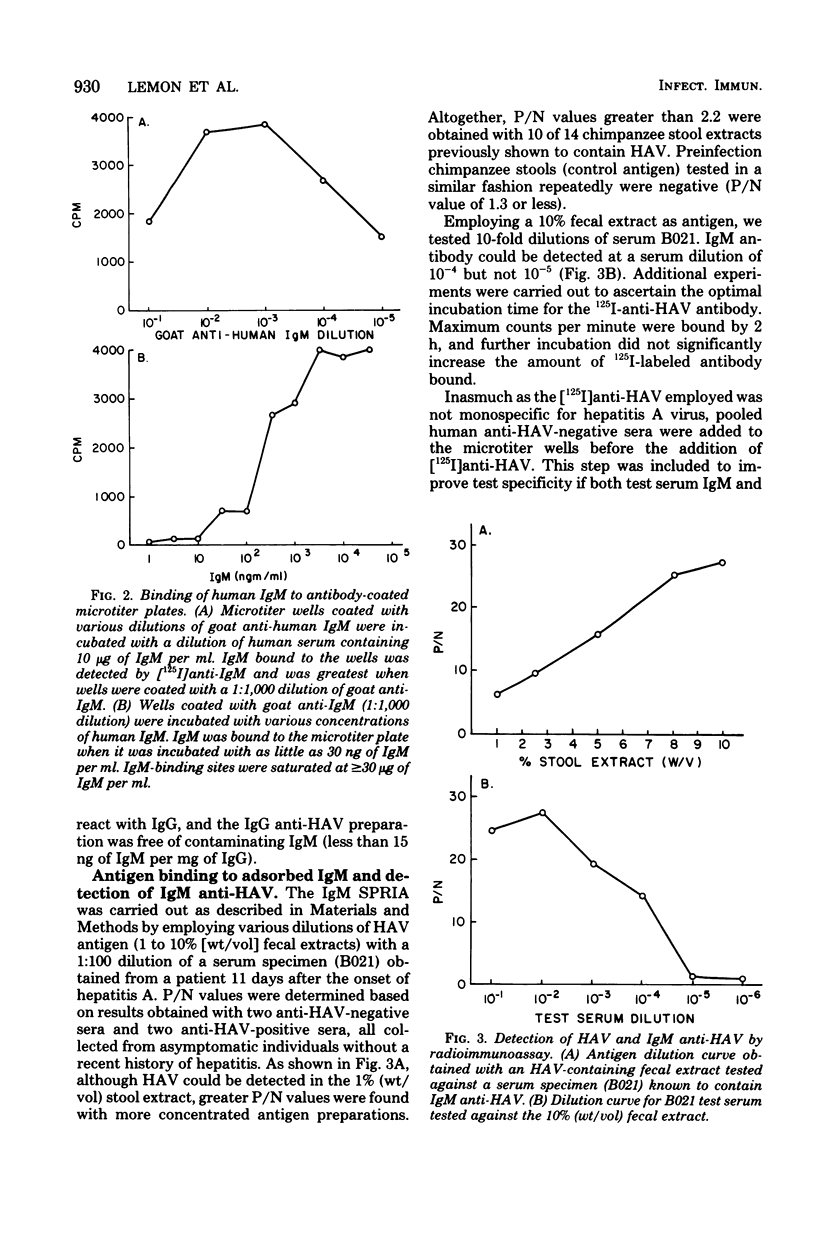
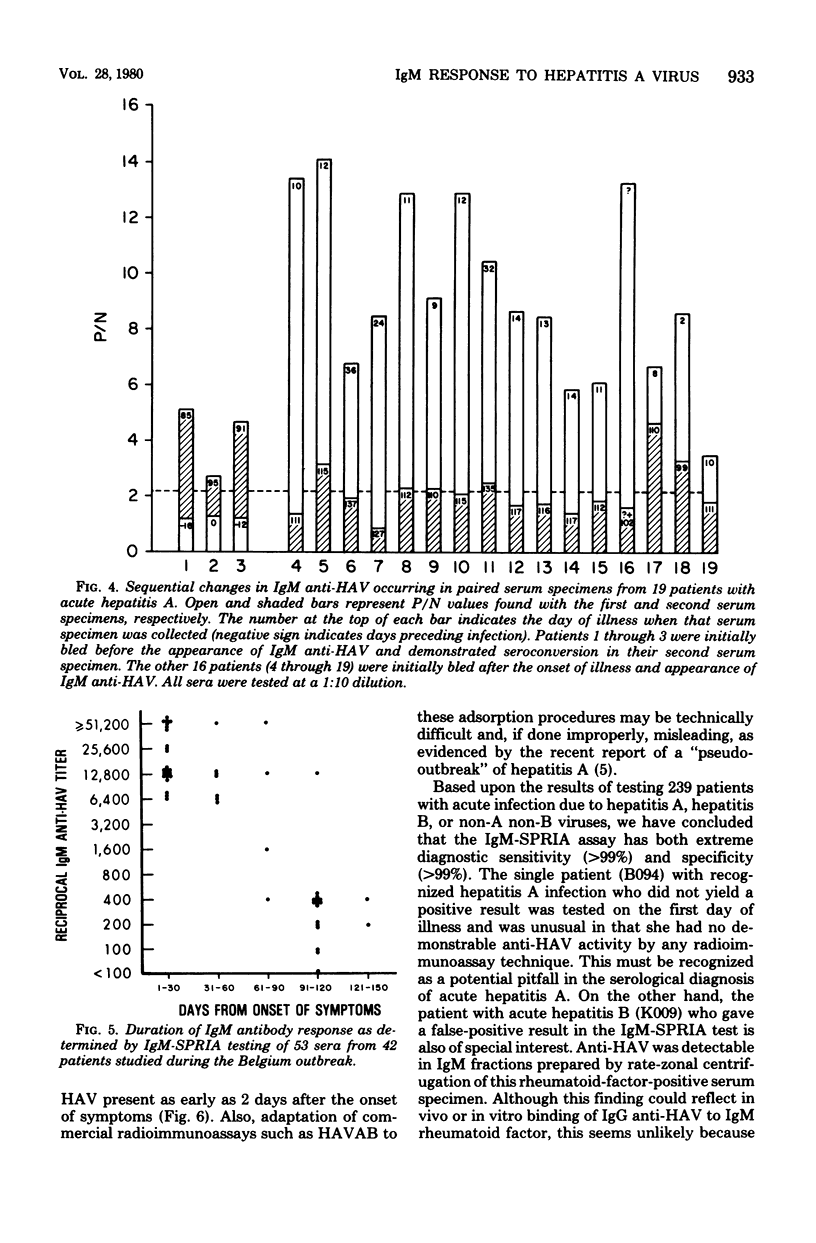
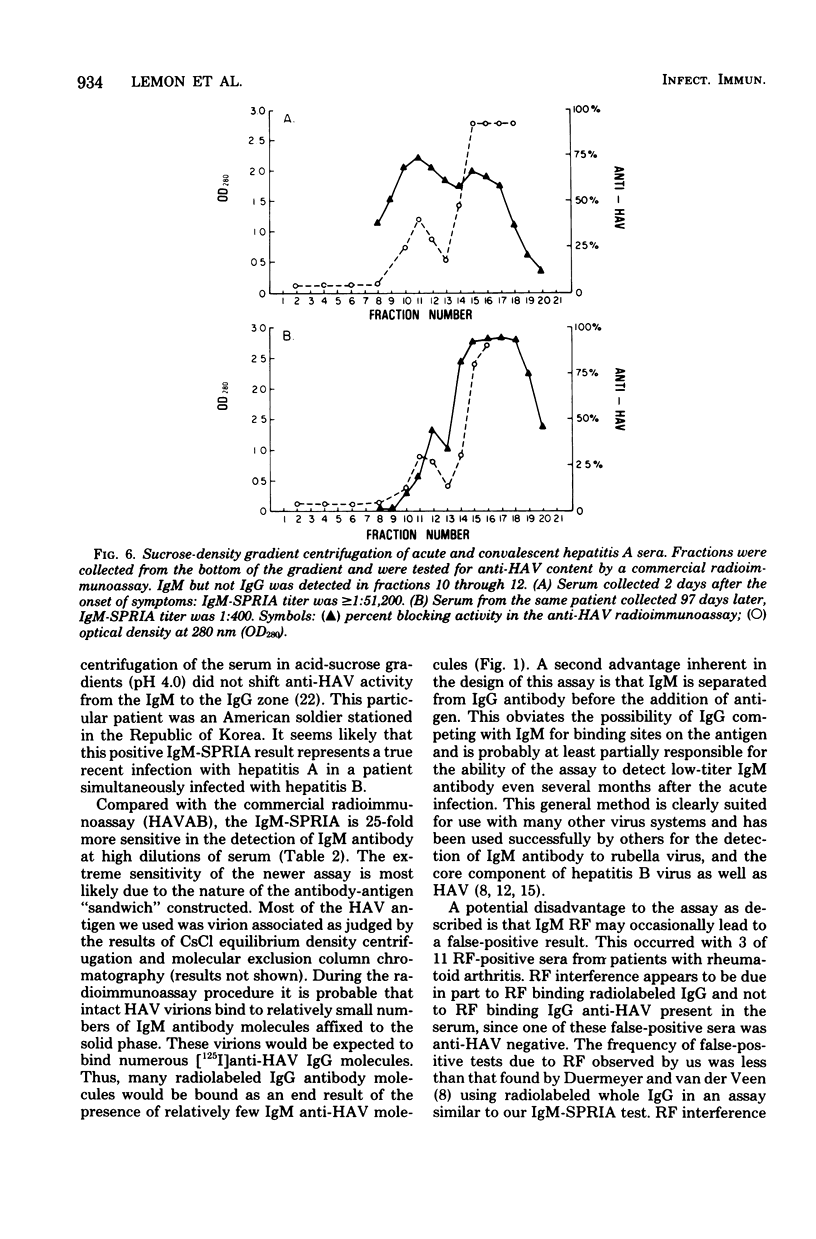
Immunoglobulin M antibody to hepatitis A virus (IgM anti-HAV) is found in most patients with acute type A hepatitis. To determine the duration of this IgM response as well as to confirm that IgM anti-HAV is a specific marker for acute infection, we developed a solid-phase radioimmunoassay for IgM anti-HAV. This new assay is 25-fold more sensitive than a conventional blocking radioimmunoassay for anti-HAV, and interference due to rheumatoid factor was eliminated by simultaneously testing sera against virus-free control antigen. Maximum IgM anti-HAV titers (1:6,400 to greater than or equal to 1:51,200) were detected during the first 30 days after the onset of illness. Although the IgM anti-HAV titer subsequently declined 64-fold over the ensuing 90 days, low-titer IgM anti-HAV (1:100 to 1:400) persisted in many sera for 90 to 150 days. Acute sera having an IgM anti-HAV titer of greater than or equal to 1:25,600 possessed a significantly higher mean IgM concentration (492 mg/dl) than acute sera with an IgM anti-HAV titer of less than or equal to 1:12,800 (344 mg/dl; P < 0.05). IgM anti-HAV titers did not correlate with other clinical or laboratory measures of disease severity. Detection of IgM anti-HAV proved to be both a highly specific (>99%) and a sensitive (>99%) method for the diagnosis of type A hepatitis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker W. Determination of antisera titres ing the single radial immunodiffusion method. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jul;6(4):539–546. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90193-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs J. D., Melnick J. L., Conrad M. E., Felsher B. F. Viral hepatitis. Clinical and tissue culture studies. JAMA. 1970 Nov 9;214(6):1041–1046. doi: 10.1001/jama.214.6.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W., Fields H. A., McCaustland K. A., Maynard J. E., Decker R. H., Whittington R., Overby L. R. Serodiagnosis of viral hepatitis A by a modified competitive binding radioimmunoassay for immunoglobulin M anti-hepatitis A virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):120–127. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.120-127.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W., Maynard J. E., Hindman S. H., Hornbeck C. L., Fields H. A., McCaustland K. A., Cook E. H., Jr Serodiagnosis of viral hepatitis A: detection of acute-phase immunoglobulin M anti-hepatitis A virus by radioimmunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 May;5(5):521–530. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.5.521-530.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstag J. L., Feinstone S. M., Purcell R. H., Hoofnagle J. H., Barker L. F., London W. T., Popper H., Peterson J. M., Kapikian A. Z. Experimental infection of chimpanzees with hepatitis A virus. J Infect Dis. 1975 Nov;132(5):532–545. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.5.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duermeyer W., Wielaard F., van der Veen J. A new principle for the detection of specific IgM antibodies applied in an ELISA for hepatitis A. J Med Virol. 1979;4(1):25–32. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duermeyer W., van der Veen J. Specific detection of IgM-antibodies by ELISA, applied in hepatitis-A. Lancet. 1978 Sep 23;2(8091):684–685. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92802-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstone S. M., Kapikian A. Z., Purceli R. H. Hepatitis A: detection by immune electron microscopy of a viruslike antigen associated with acute illness. Science. 1973 Dec 7;182(4116):1026–1028. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4116.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flehmig B., Ranke M., Berthold H., Gerth H. J. A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detection of IgM antibodies to hepatitis A virus. J Infect Dis. 1979 Aug;140(2):169–175. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frösner G. G., Scheid R., Wolf H., Deinhardt F. Immunoglobulin M anti-hepatitis A virus determination reorienting gradient centrifugation for diagnosis of Acute Hepatitis A. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):476–478. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.476-478.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlich W. H., Lüer W. Selective detection of IgM-antibody against core antigen of the hepatitis B virus by a modified enzyme immune assay. J Med Virol. 1979;4(3):227–238. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890040308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles J. P., Krugman S. Viral hepatitis. Immunoglobulin response during the course of the disease. JAMA. 1969 Apr 21;208(3):497–503. doi: 10.1001/jama.208.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irwin G. R., Allen R. G., Segal H. G., Allen A. M., Putnak J. R., Cannon H. G., Top F. H., Jr Serodiagnosis of hepatitis B virus infection by antibody to core antigen. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jul;136(1):31–36. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krech U., Wilhelm J. A. A solid-phase immunosorbent technique for the rapid detection of rubella IgM by haemagglutination inhibition. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):281–286. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locarnini S. A., Coulepis A. G., Stratton A. M., Kaldor J., Gust I. D. Solid-phase enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of hepatitis A-specific immunoglobulin M. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):459–465. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.459-465.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locarnini S. A., Ferris A. A., Lehmann N. I., Gust I. D. The antibody response following hepatitis A infection. Intervirology. 1977;8(5):309–318. doi: 10.1159/000148905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathiesen L. R., Feinstone S. M., Wong D. C., Skinhoej P., Purcell R. H. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of hepatitis A antigen in stool and antibody to hepatitis A antigen in sera: comparison with solid-phase radioimmunoassay, immune electron microscopy, and immune adherence hemagglutination assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Feb;7(2):184–193. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.2.184-193.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. J., Provost P. J., McAleer W. J., Ittensohn O. L., Villarejos V. M., Hilleman M. R. Specific immune adherence assay for human hepatitis A antibody application to diagnostic and epidemiologic investigations. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 May;149(1):254–261. doi: 10.3181/00379727-149-38783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Moritsugu Y., Dienstag J. L., Routenberg J. A., Boggs J. D. A microtiter solid-phase radioimmunoassay for hepatitis A antigen and antibody. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):349–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakela J., Mosley J. W. Fecal excretion of hepatitis A virus in humans. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jun;135(6):933–938. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.6.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stagno S., Volanakis J. E., Reynolds D. W., Stroud R., Alford C. A. Immune complexes in congenital and natal cytomegalovirus infections of man. J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;60(4):838–845. doi: 10.1172/JCI108838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


