Abstract
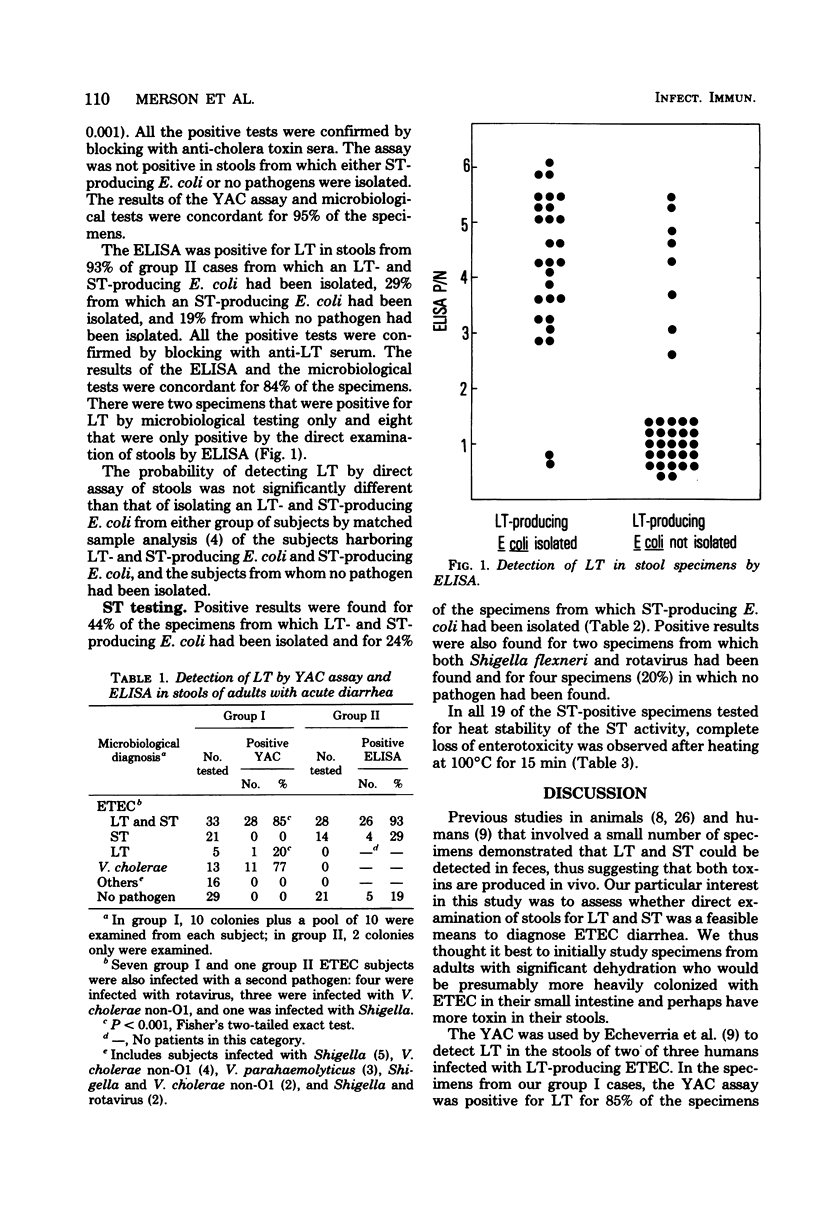
We determined whether enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhea could be diagnosed by direct examination of stools for heat-labile (LT) and heat-stable (ST) enterotoxins. The Y-1 adrenal cell and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) detected LT in 85 and 93%, respectively, of stool specimens obtained from adults with acute diarrhea from whom an LT- and ST-producing organism had been isolated. Furthermore, the ELISA assay detected LT in 8 of 35 stool specimens from which no LT-producing E. coli had been isolated. The infant mouse assay was utilized to detect ST in these stool specimens and was found to be an insensitive method, showing positive results in only 36% of the specimens from which an ST-producing organism was isolated. Further studies are warranted to determine the diagnostic value of direct detection of LT in stools, especially by the ELISA method.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Purification and chemical characterization of the heat-stable enterotoxin produced by porcine strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1021-1030.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertschinger H. U., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Association of Escherichia coli with the small intestinal epithelium. II. Variations in association index and the relationship between association index and enterosorption in pigs. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):606–611. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.606-611.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill B. M., Wasilauskas B. L., Richardson S. H. Adaptation of the staphylococcal coagglutination technique for detection of heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):49–55. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.49-55.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCHRAN W. G. The comparison of percentages in matched samples. Biometrika. 1950 Dec;37(3-4):256–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Affinity chromatography. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:259–278. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C., Skartvedt S. M. In vitro production and inactivation of Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Gastroenterology. 1974 Nov;67(5):983–990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Verheart L., Ulyanco C. V., Santiago L. T. Detection of heat-labile enterotoxin-like activity in stools of patients with cholera and Escherichia coli diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):343–344. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.343-344.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G. Direct serological assay for the heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli, using passive immune hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1977 May;16(2):604–609. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.2.604-609.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg H. B., Levine M. M., Merson M. H., Sack R. B., Sack D. A., Valdesuso J. R., Nalin D., Hoover D., Chanock R. M., Kapikian A. Z. Solid-phase microtiter radioimmunoassay blocking test for detection of antibodies to Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):60–64. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.60-64.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T. M., Wu B. J. Biochemical properties of Escherichia coli low-molecular-weight, heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1974 Feb;9(2):342–347. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.2.342-347.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Robertson D. C. Factors affecting release of heat-labile enterotoxin by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):652–659. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.652-659.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kétyi I., Vertényi A., Málovics I., Kontrohr T., Pácsa S. Unique features of heat-stable enterotoxin of Shigella flexneri. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1978;25(3):219–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merson M. H., Orskov F., Orskov I., Sack R. B., Huq I., Koster F. T. Relationship between enterotoxin production and serotype in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):325–329. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.325-329.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merson M. H., Sack R. B., Kibriya A. K., Al-Mahmood A., Adamed Q. S., Huq I. Use of colony pools for diagnosis of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Apr;9(4):493–497. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.4.493-497.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Mors V., Toma S. Prevalence of enterotoxigenicity in human and nonhuman isolates of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):334–338. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.334-338.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Wallace C. K. Stimulation of jejunal secretion by a crude Escherichia coli enterotixin. Gastroenterology. 1972 Sep;63(6):439–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Sack R. B. Test for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli using Y-1 adrenal cells in miniculture. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.334-336.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Halls S. Studies on Escherichia coli enterotoxin. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):531–543. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. W., Sack R. B. Immunologic cross-reactions of enterotoxins from Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Feb;127(2):164–170. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.2.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whipp S. C., Moon H. W., Lyon N. C. Heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin production in vivo. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):240–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.240-244.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yolken R. H., Greenberg H. B., Merson M. H., Sack R. B., Kapikian A. Z. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Nov;6(5):439–444. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.5.439-444.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


