Abstract
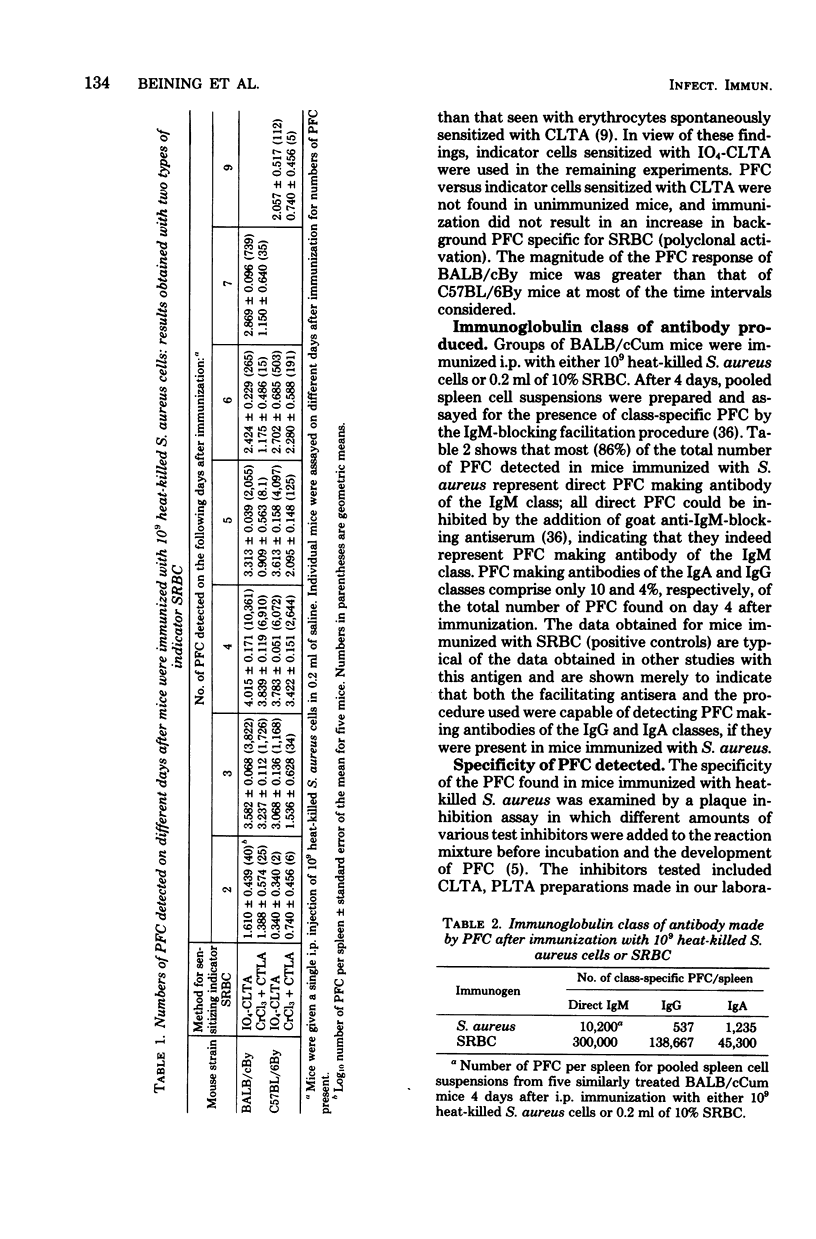
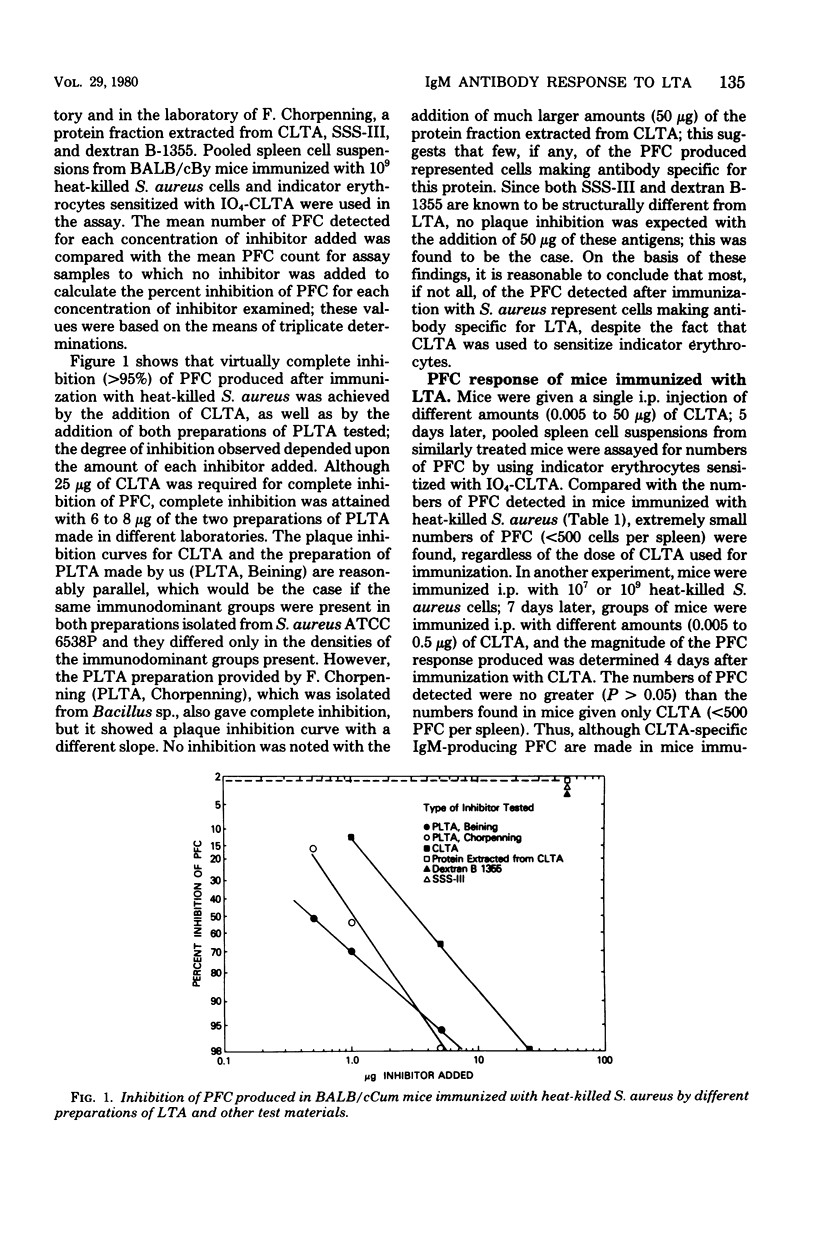
The immunoglobulin M antibody response to the lipoteichoic acid (LTA) of Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538P was examined by a procedure in which erythrocytes sensitized with periodate-activated LTA were used for the detection of immunoglobulin M-producing plaque-forming cells LTA-specific plaque-forming cells were first detected 2 days after immunization with heat-killed bacterial cells, and maximal numbers of plaque-forming cells, mostly of the immunoglobulin M class rather than the immunoblogulin G or immunoglobulin A class, were attained by day 4; specificity for LTA was affirmed by plaque inhibition tests. No plaque-forming cells were found in mice given isolated LTA over a 10,000-fold range of immunizing doses. Mice pretreated with a carrier known to activate thymus-derived helper lymphocytes produced a plaque-forming cell response to LTA only when immunized with LTA bound to the same carrier. This suggests that carrier-specific thymus-derived cells are needed to initiate an antibody response to poorly immunogenic LTA. Since an antibody response can be elicited in mice given heat-killed cells, other cell wall and/or cell membrane constituents may play an important role as immunologically active carriers for this antigen.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archibald A. R., Baddiley J., Blumsom N. L. The teichoic acids. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1968;30:223–253. doi: 10.1002/9780470122754.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald A. R., Baddiley J., Button D. The glycerol teichoic acid of walls of Staphylococcus lactis I3. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):543–557. doi: 10.1042/bj1100543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. The teichoic acids. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1966;21:323–375. doi: 10.1016/s0096-5332(08)60320-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGER M. M., GLASER L. THE SYNTHESIS OF TEICHOIC ACIDS. I. POLYGLYCEROPHOSPHATE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3168–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Prescott B., Stashak P. W., Amsbaugh D. F. Characterization of the antibody response to type 3 pneumococcal polysaccharide at the cellular level. 3. Studies on the average avidity of the antibody produced by specific plaque-forming cells. J Immunol. 1971 Sep;107(3):719–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Stashak P. W., Amsbaugh D. F., Prescott B. Characterization of the antibody response to type 3 pneumococcal polysaccharide at the cellular level. I. Dose-response studies and the effect of prior immunization on the magnitude of the antibody response. Immunology. 1971 Apr;20(4):469–480. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Stashak P. W., Amsbaugh D. F., Prescott B. Characterization of the antibody response to type 3 pneumococcal polysaccharide at the cellular level. II. Studies on the relative rate of antibody synthesis and release by antibody-producing cells. Immunology. 1971 Apr;20(4):481–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. J., Stashak P. W., Prescott B. Use of erythrocytes sensitized with purified pneumococcal polysaccharides for the assay of antibody and antibody-producing cells. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Mar;17(3):422–426. doi: 10.1128/am.17.3.422-426.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beining P. R., Flannery G. M., Caldes G., Prescott B., Baker P. J. Use of the periodate oxidation coupling method for the detection of antibody and antibody-producing cells specific for staphylococcal lipoteichoic acid. J Immunol Methods. 1980;32(2):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton R. W., Rozmiarek H., Chorpenning F. W. Cyclic antibody formation to polyglycerophosphate in normal and injected rats. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1154–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braley-Mullen H. Regulatory role of T cells in IgG antibody formation and immune memory to type III Pneumococcal polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1909–1920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braley-Mullen H., Sharp G. C. Conversion of type III pneumococcal polysaccharide low responders to high responders by immunization with a thymus-dependent form of antigen. Cell Immunol. 1974 Apr;12(1):49–60. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger M. M. Teichoic acids: antigenic determinants, chain separation, and their location in the cell wall. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):910–917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chorpenning F. W., Stamper H. B. Spontaneous adsorption of teichoic acid to erythrocytes. Immunochemistry. 1973 Jan;10(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90245-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coley J., Duckworth M., Baddiley J. Extraction and purification of lipoteichoic acids from Gram-positive bacteria. Carbohydr Res. 1975 Mar;40(1):41–52. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)82667-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedel B. A., Jackson R. W. Immunogenicity of a purified and carrier-complexed streptococcal lipoteichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1976 Jun;13(6):1585–1590. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.6.1585-1590.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb C. F. Application of transformations to normalize the distribution of plaque-forming cells. J Immunol. 1974 Jul;113(1):51–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOW M. J., BRIMACOMBE J. S., STACEY M. THE PNEUMOCOCCAL POLYSACCHARIDES. Adv Carbohydr Chem. 1964;19:303–358. doi: 10.1016/s0096-5332(08)60285-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewett M. J., Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Studies on the group F antigen of lactobacilli: detection of antibodies by haemagglutination. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Mar;60(3):315–322. doi: 10.1099/00221287-60-3-315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J. G., Courtenay B. M. Influence of molecular structure on the tolerogenicity of bacterial dextrans. II. The alpha1--3-linked epitope of dextran B1355. Immunology. 1975 Oct;29(4):599–610. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff E., Cole R. M., Theodore T. S. Lipoteichoic acid localization in mesosomal vesicles of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):273–281. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.273-281.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakawa W. W., Kane J. A. Immunochemical analysis of a galactosamine-rich teichoic acid of Staphylococcus aureus, phage type 187. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):900–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Immunological properties of teichoic acids. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Jun;37(2):215–257. doi: 10.1128/br.37.2.215-257.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox K. W., Wicken A. J. Serological studies on the teichoic acids of Lactobacillus plantarum. Infect Immun. 1972 Jul;6(1):43–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.1.43-49.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markham R. B., Stashak P. W., Prescott B., Amsbaugh D. F., Baker P. J. Selective sensitivity to hydrocortisone of regulatory functions that determine the magnitude of the antibody response to type III pneumococcal polysaccharide. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):829–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno T., Slade H. D. Group a streptococcal polysaccharide antigens. Infect Immun. 1971 Mar;3(3):385–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.3.385-389.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. A., Jackson R. W. The effect of a streptococcus pyogenes teichoic acid on the immune response of mice. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):148–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskowitz M. Separation and properties of a red cell sensitizing substance from streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2200–2204. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2200-2204.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasanen V. J., Asofsky R., Baker P. J. Synthesis of two classes of antibody, gammaM and gammaG or gammaM and gammaA, by identical cells. Amplification of the antibody response to pneumococcal polysaccharide type III. J Exp Med. 1979 May 1;149(5):1227–1237. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.5.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Wilson D. V. Methods for coupling protein or polysaccharide to red cells by periodate oxidation. Immunochemistry. 1971 Feb;8(2):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90236-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toon P., Brown P. E., Baddiley J. The lipid-teichoic acid complex in the cytoplasmic membrane of Streptococcus faecalis N.C.I.B. 8191. Biochem J. 1972 Apr;127(2):399–409. doi: 10.1042/bj1270399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Driel D., Wicken A. J., Dickson M. R., Knox K. W. Cellular location of the lipoteichoic acids of Lactobacillus fermenti NCTC 6991 and Lactobacillus casei NCTC 6375. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Jun;43(5):483–497. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Ekstedt R. D. Antibody response to Staphylococcus aureus in rabbits: sequence of immunoglobulin synthesis and its correlation with passive protection in mice. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1540–1545. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1540-1545.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



