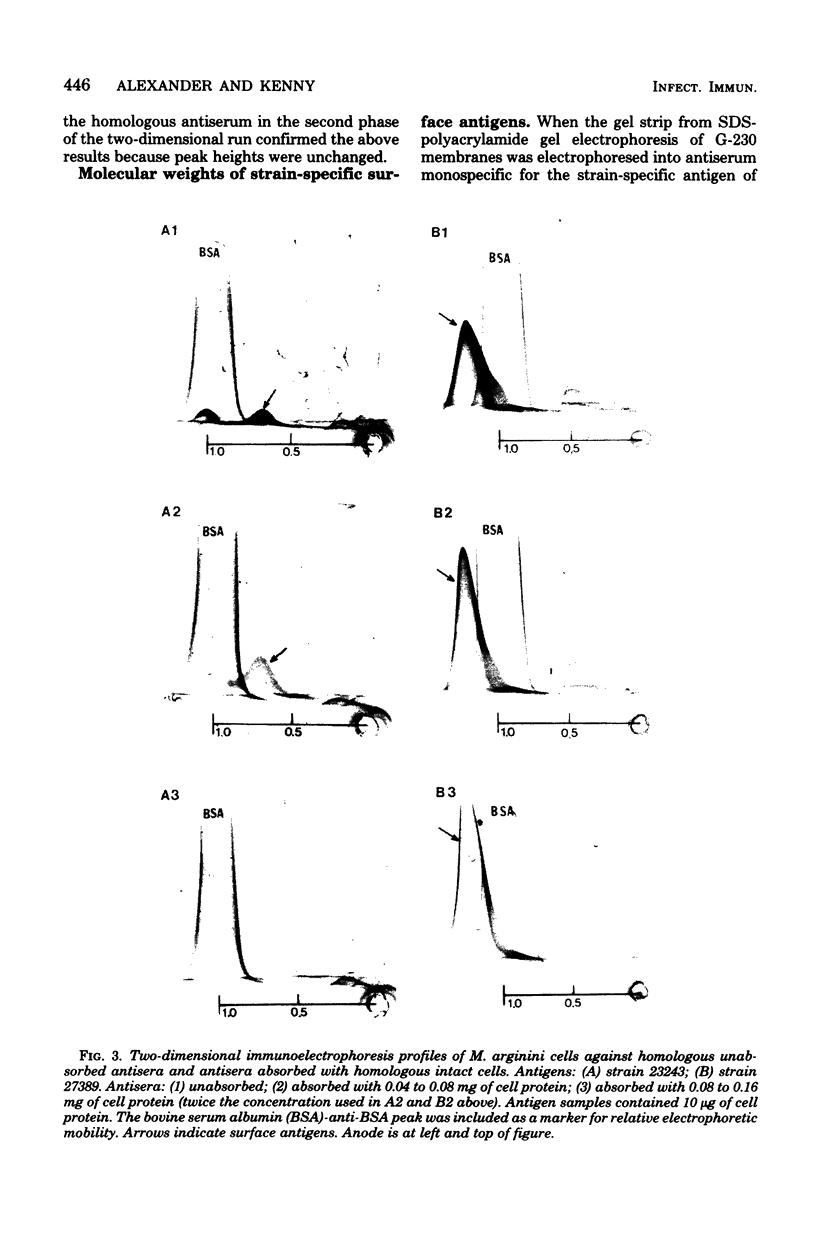
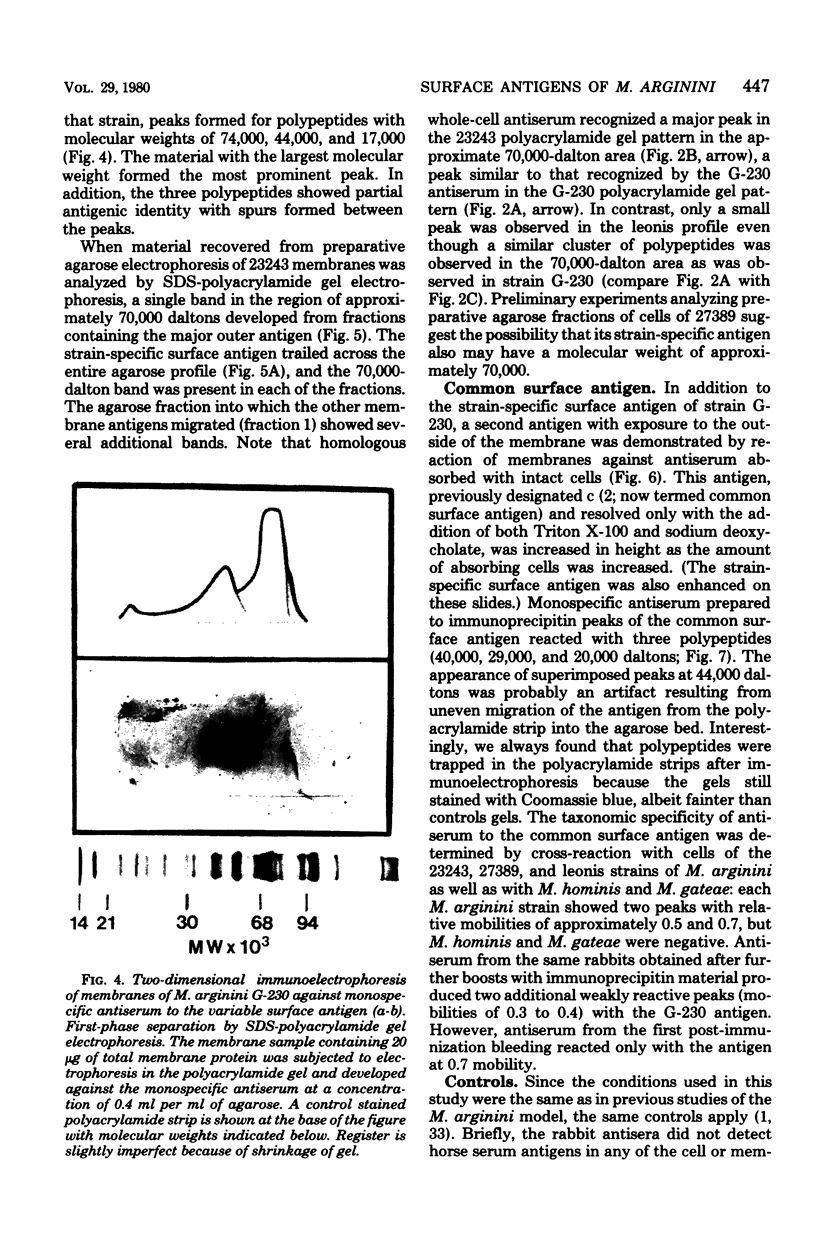
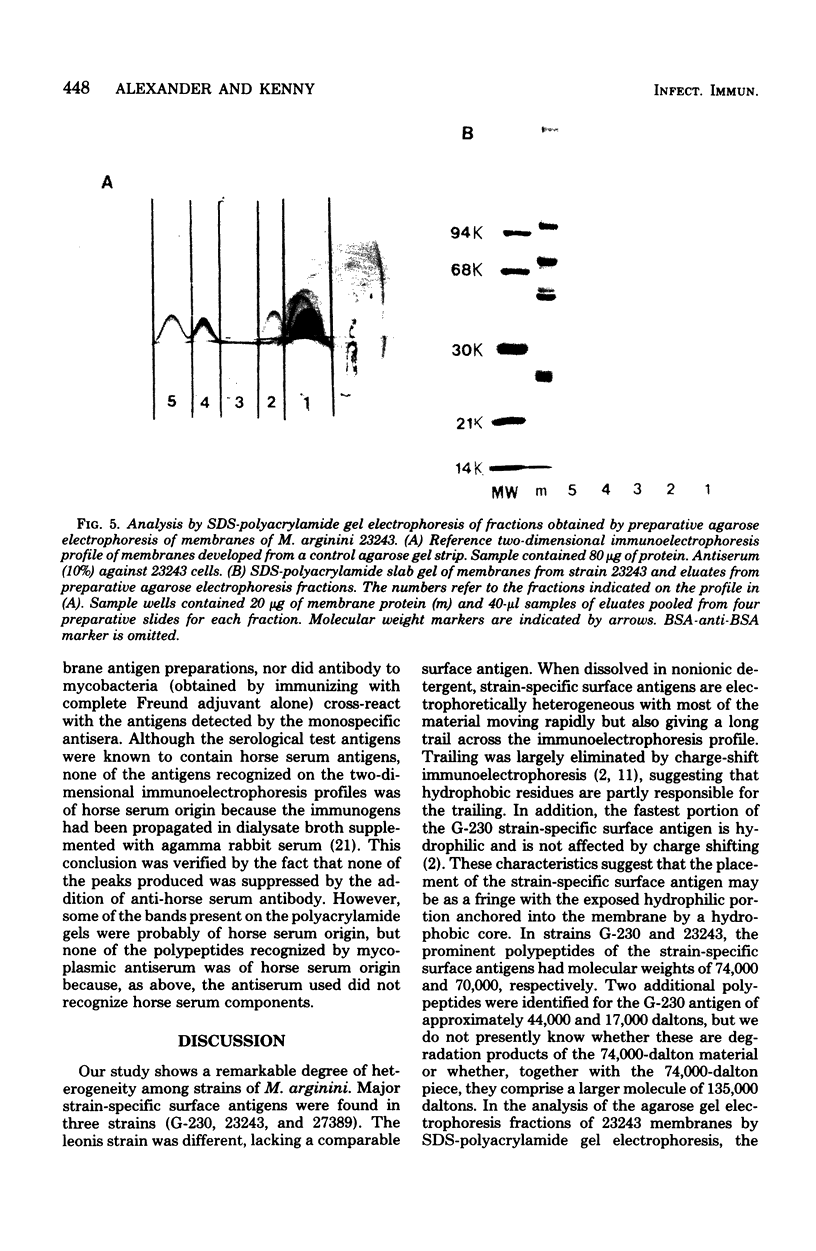
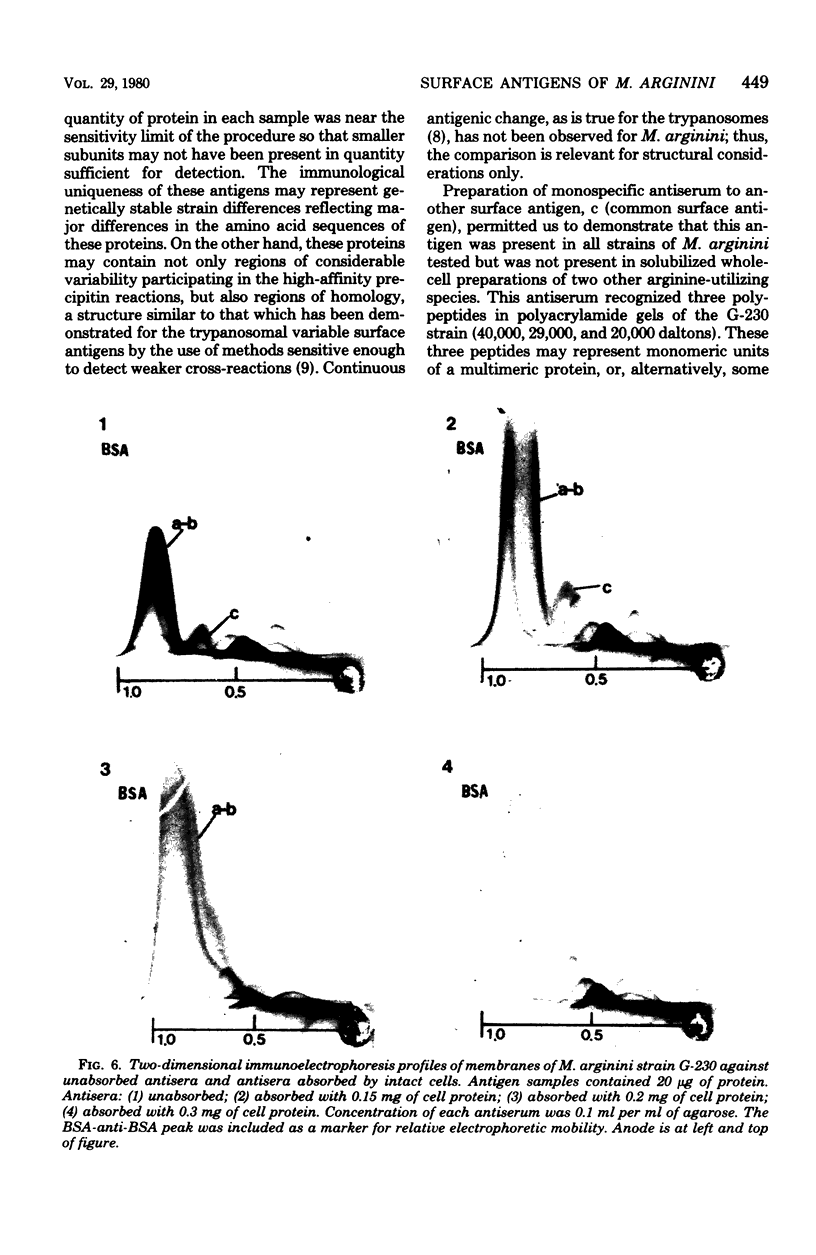
Abstract
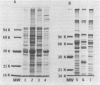
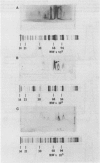
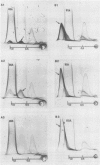
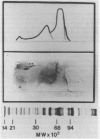
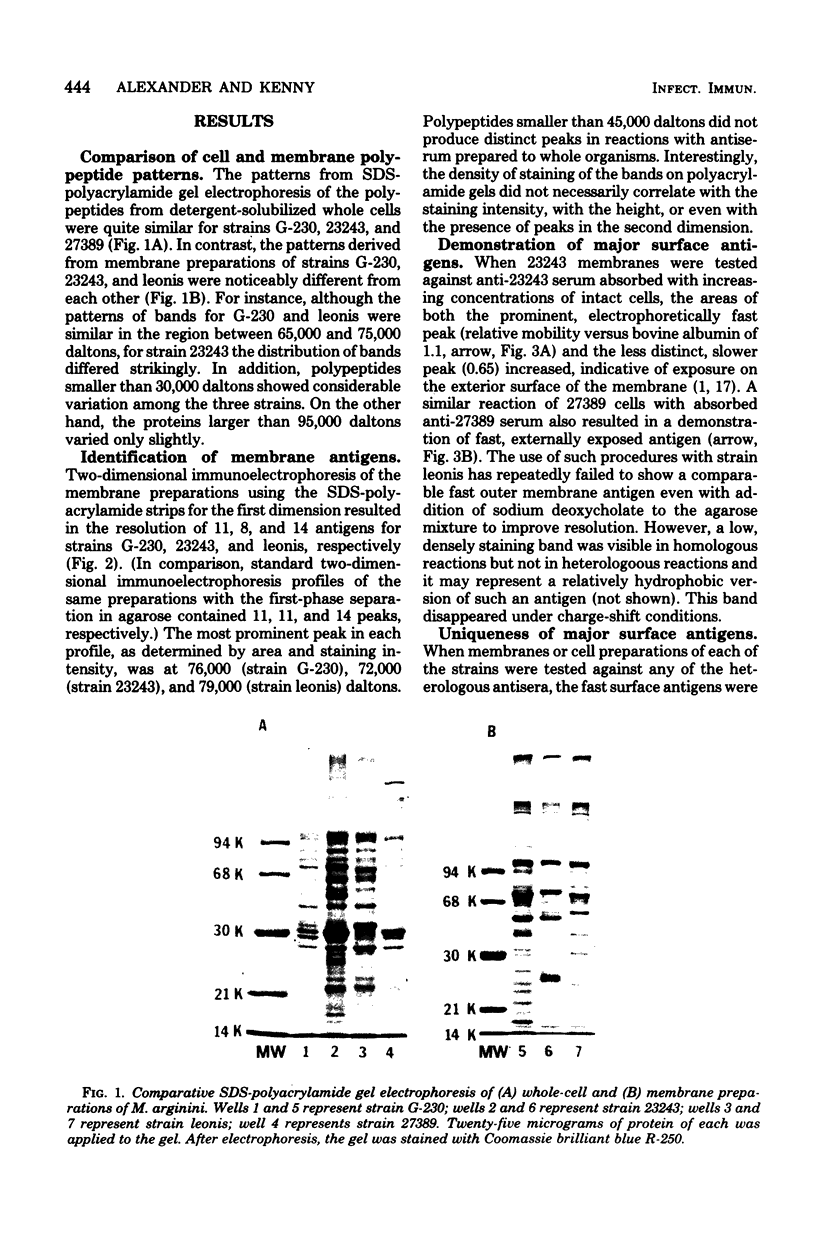
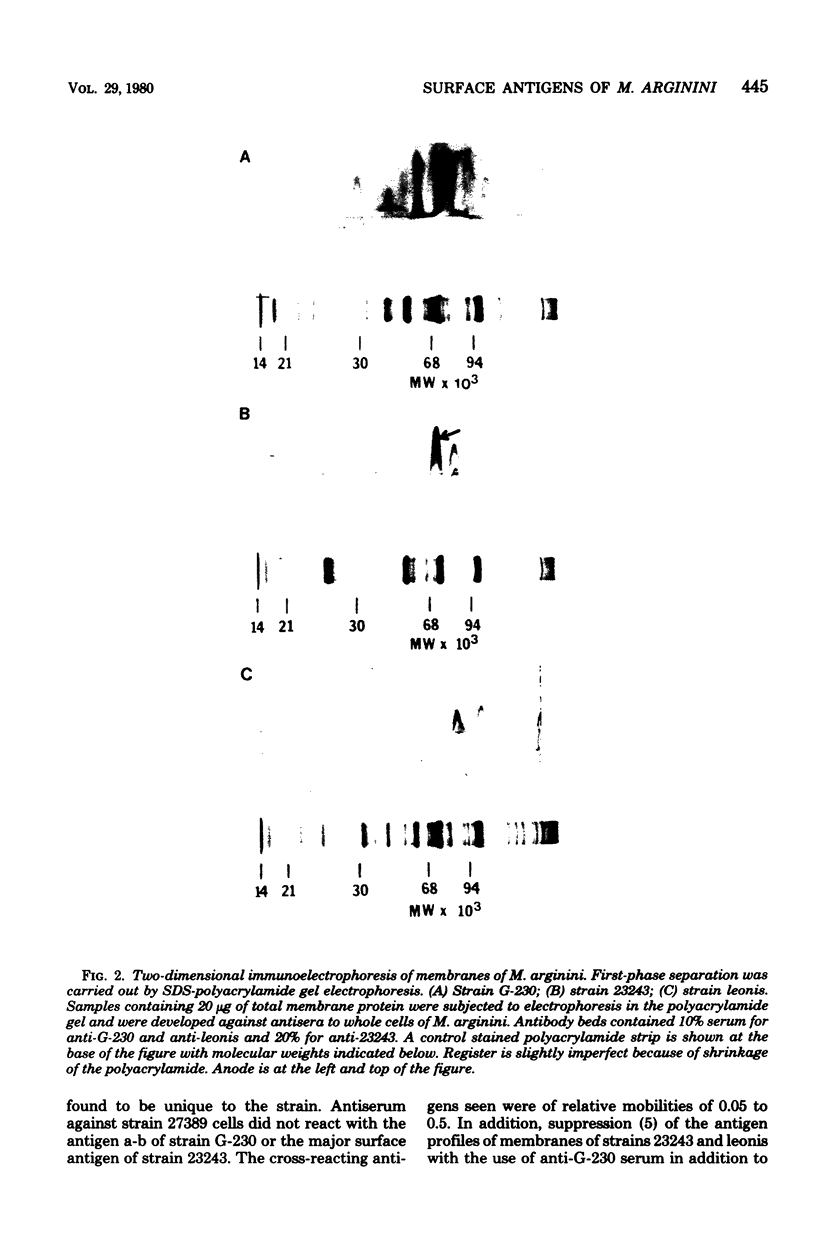
A combination of quantitative immunoelectrophoresis and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis was used to determine location and molecular weights of surface membrane antigens of four strains of Mycoplasma arginini. Two major surface antigens were identified for M. arginini by absorption of antiserum with whole cells: one surface antigen was strain specific, electrophoretically fast, and prominently located on the surface, whereas the other surface antigen was common to the four strains and of intermediate electrophoretic mobility. Three of the four strains of M. arginini (G-230, 23243, and 27389) possessed immunologically strain-specific antigens which did not cross-react, whereas the leonis strain lacked an immunologically detectable unique surface antigen. A monospecific antiserum prepared against immune precipitates of the strain-specific antigen of strain G-230 detected three polypeptides of 74,000, 44,000, and 17,000 daltons in SDS-polyacrylamide gels of membrane preparations. All four strains shared the common surface antigen which appeared considerably more hydrophobic than the strain-specific surface antigen because it could only be demonstrated by charge-shift immunoelectrophoretic conditions (addition of deoxycholate to the nonionic detergent). Monospecific antiserum to the common antigen of strain G-230 reacted with all four M. arginini strains, but did not react with two other arginine-utilizing species, and recognized three polypeptides of 40,000, 29,000, and 20,000 daltons in membranes of strain G-230. Whereas the common surface antigen is a likely target for conventional serological reactions used for identification of the species M. arginini, strain-specific antigen cannot fulfill this role but must participate in other surface reactions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander A. G., Kenny G. E. Application of charge shift electrophoresis to antigenic analysis of mycoplasmic membranes by two-dimensional (crossed) immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1978 Jun;20(3):861–863. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.3.861-863.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander A. G., Kenny G. E. Characterization of membrane and cytoplasmic antigens of Mycoplasma arginini by two-dimensional (crossed) immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):313–321. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.313-321.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amar A., Rottem S., Razin S. Characterization of the mycoplasma membrane proteins. IV. Disposition of proteins in the membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 13;352(2):228–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argaman M., Razin S. Antigenic properties of mycoplasma organisms and membranes. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Jan;55(1):45–58. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsen N. H., Bock E., Kroll J. Comparison of antigens: the reaction of 'identity'. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:91–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barile M. F., DelGiudice R. A., Carski T. R., Gibbs C. J., Morris J. A. Isolation and characterization of Mycoplasma arginini: spec. nov. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Nov;129(2):489–494. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Converse C. A., Papermaster D. S. Membrane protein analysis by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Science. 1975 Aug 8;189(4201):469–472. doi: 10.1126/science.1154021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Crossreacting determinants in the C-terminal region of trypanosome variant surface antigens. Nature. 1979 Jan 25;277(5694):310–312. doi: 10.1038/277310a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Identification, purification and properties of clone-specific glycoprotein antigens constituting the surface coat of Trypanosoma brucei. Parasitology. 1975 Dec;71(3):393–417. doi: 10.1017/s003118200004717x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowle A. J., Revis G. J., Jarrett K. Preparatory electroimmunodiffusion for making precipitins to selected native antigens. Immunol Commun. 1972;1(4):325–336. doi: 10.3109/08820137209022946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Simons K. Charge shift electrophoresis: simple method for distinguishing between amphiphilic and hydrophilic proteins in detergent solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):529–532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjertén S., Johansson K. E. Selective solubilization with Tween 20 of membrane proteins from Acholeplasma laidlawaii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 2;288(2):312–325. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Lemcke R. M. Antigenic differences within the species Mycoplasma hominis. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Sep;68(3):469–477. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Lemcke R. M. Membrane antigens of Mycoplasma hominis. J Hyg (Lond) 1972 Mar;70(1):85–98. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400022129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Lemcke R. M. The antigens of Mycoplasma hominis. J Hyg (Lond) 1969 Dec;67(4):585–602. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400042042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. G. Agarose gel electrophoresis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:7–19. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson K. E., Hjertén S. Localization of the Tween 20-soluble membrane proteins of Acholeplasma laidlawii by crossed immunoelectrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson K. E., Wróblewski H. Crossed immunoelectrophoresis, in the presence of tween 20 or sodium deoxycholate, of purified membrane proteins from Acholeplasma laidlawii. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):324–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.324-330.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Razin S. Immunological analysis of Mycoplasma membranes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):187–194. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.187-194.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Heat-lability and organic solvent-solubility of mycoplasma antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):676–681. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Immunogenicity of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):510–515. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.510-515.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levisohn S., Razin S. Isolation, ultrastructure and antigenicity of Mycoplasma gallisepticum membranes. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Dec;71(4):725–737. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400022981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ne'eman Z., Kahane I., Kovartovsky J., Razin S. Characterization of the myoplasma membrane proteins. 3. Gel filtration and immunological characterization of Acholeplasma laidlawii membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Apr 14;266(1):255–268. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. W. Polymerization of proteins with glutaraldehyde. Soluble molecular-weight markers. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;135(4):867–873. doi: 10.1042/bj1350867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Mycoplasma taxonomy studiedy electrophoresis of cell proteins. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):687–694. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.687-694.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Razin S. Electrophoretic patterns of membrane proteins of Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):359–364. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.359-364.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Razin S. Isolation of mycoplasma membranes by digitonin. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):699–705. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.699-705.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirkill C. E., Kenny G. E. Antigenic analysis of three strains of Mycoplasma arginini by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):1107–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirkill C. E., Kenny G. E. Serological comparison of five arginine-utilizing Mycoplasma species by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Infect Immun. 1974 Sep;10(3):624–632. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.3.624-632.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]