Abstract
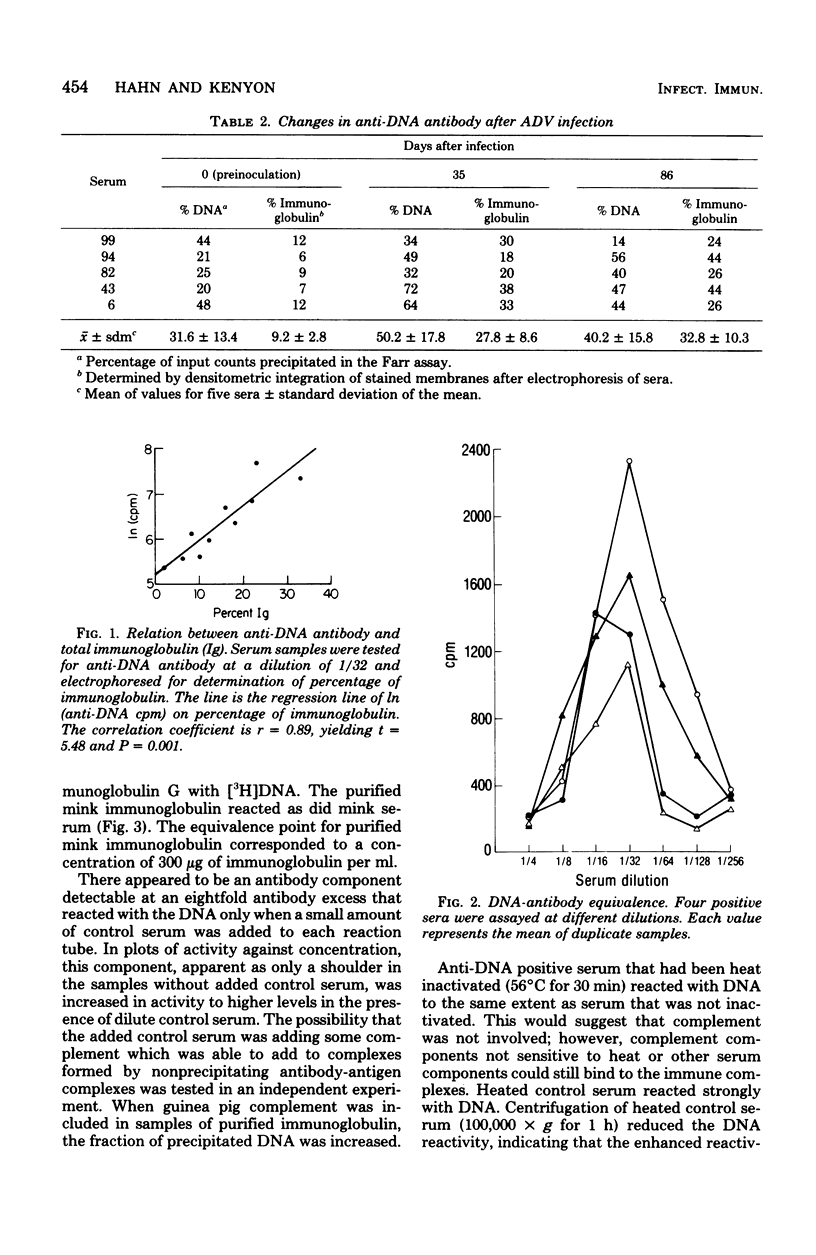
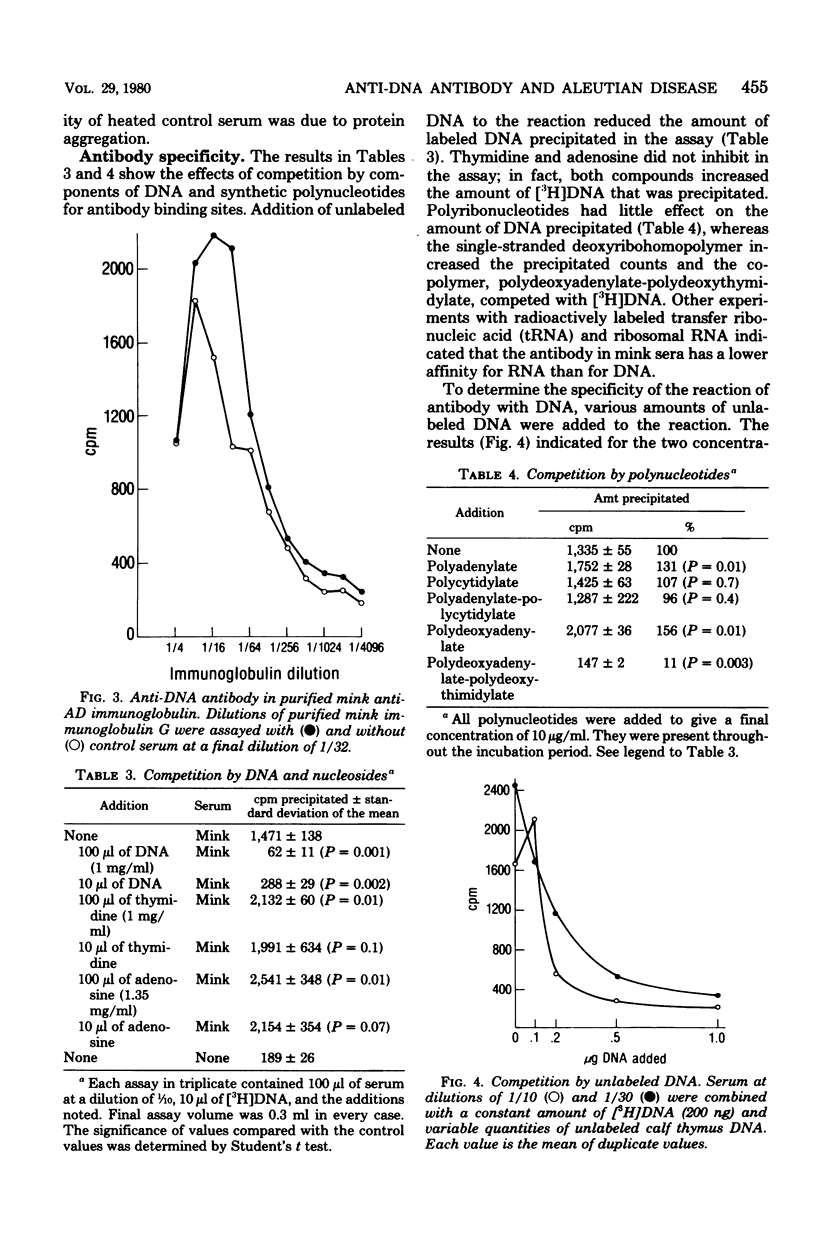
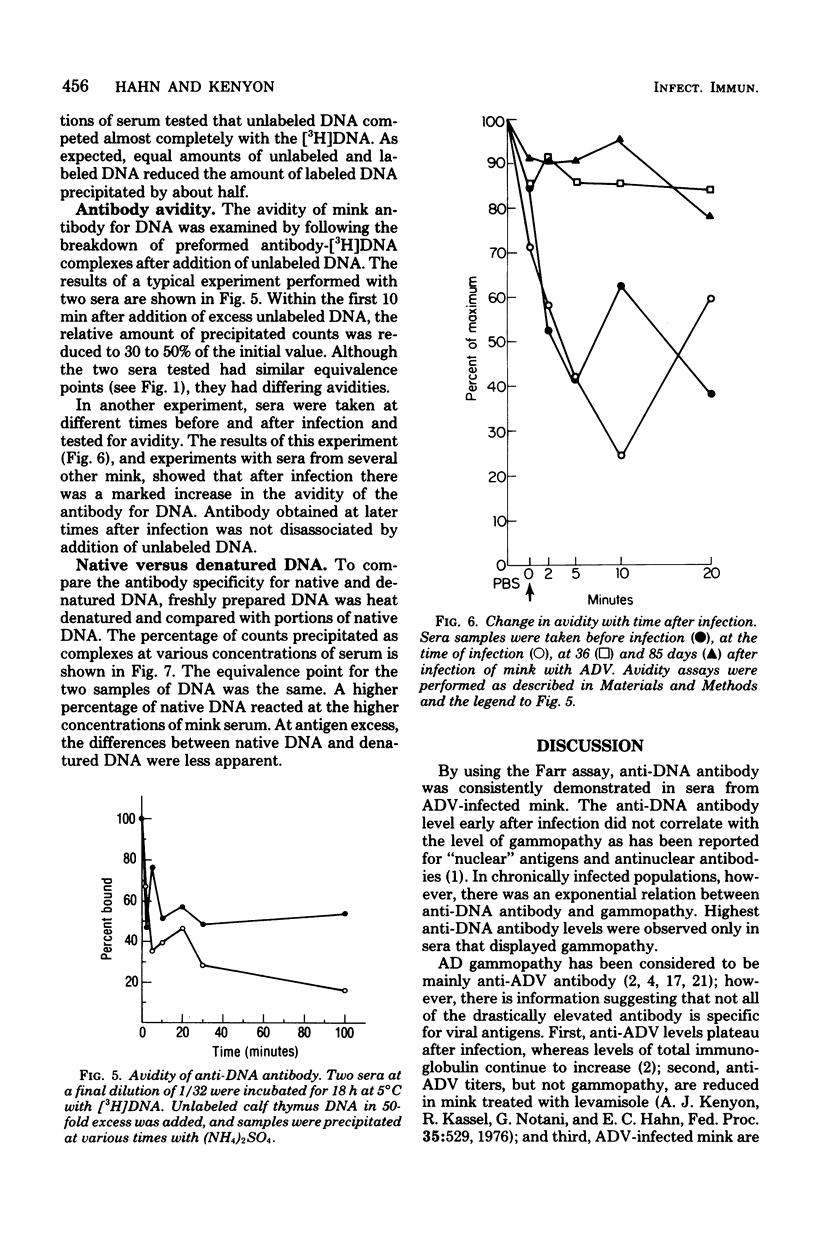
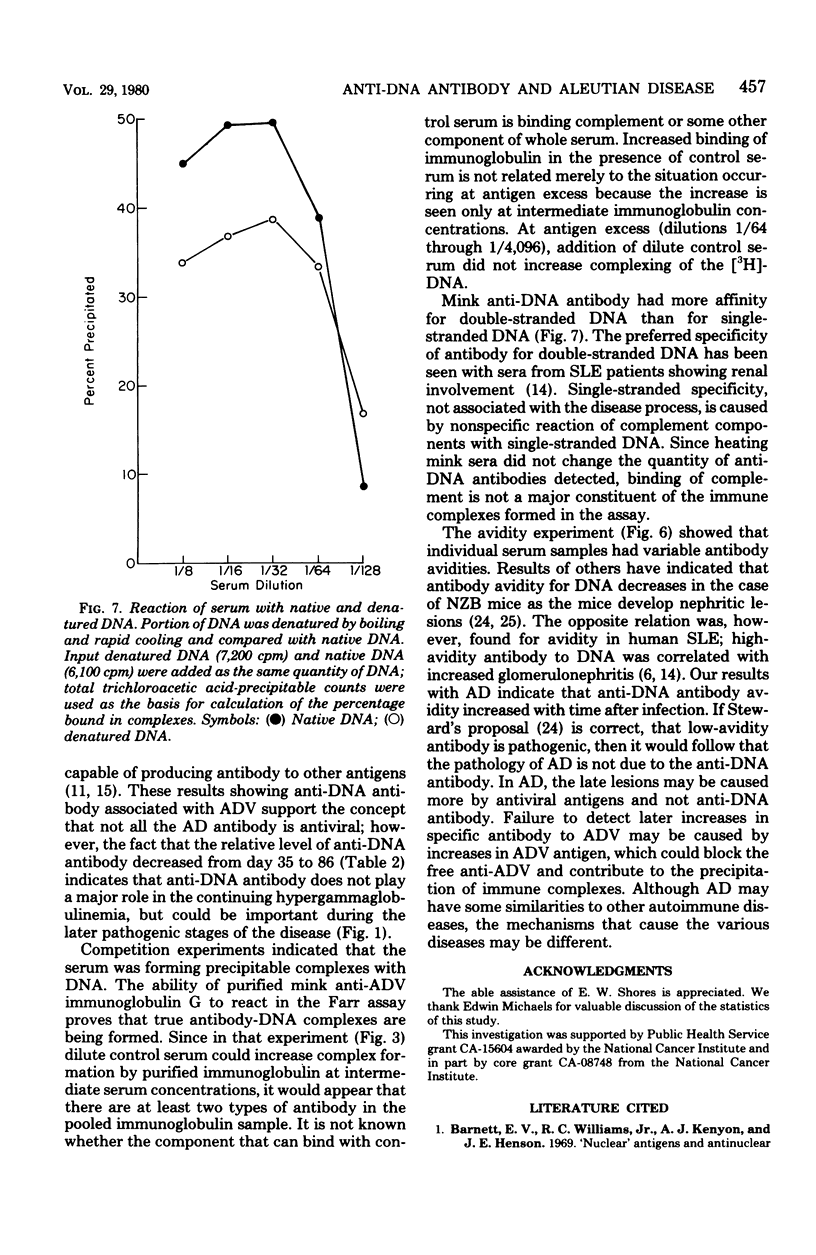
Anti-deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) antibody was quantitated in sera from mink infected with Aleutian disease virus (ADV). During the course of the disease after experimental infection, the amount of anti-DNA antibody increased 60% initially, but then decreased to an intermediate level when measured 2.5 months later. The percentage of serum immunoglobulin, however, steadily increased over 3.5-fold during this period, resulting in the characteristic gammopathy. Correlation between the level of anti-DNA antibody and hypergammaglobulinemia was demonstrated with sera from chronically infected mink. Competition experiments and use of labeled nucleic acids indicated that the immunoactivity was more specific for double-stranded DNA than single-stranded DNA or ribonucleic acid. Anti-DNA antibody was found in purified immunoglobulin from chronically infected mink. Differences in avidity of antibody to DNA among antisera that had the same equivalence point were found. Avidity of antibody for DNA increased during the course of the disease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Hadlow W. J., Chesebro B. Aleutian disease of mink: the antibody response of sapphire and pastel mink to Aleutian disease virus. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1034–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CEPPELLINI R., POLLI E., CELADA F. A DNA-reacting factor in serum of a patient with lupus erythematosus diffusus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Dec;96(3):572–574. doi: 10.3181/00379727-96-23544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J., Ingram D. G. Antigen and antibody in Aleutian disease in mink. I. Precipitation reaction by agar-gel electrophoresis. J Immunol. 1972 Feb;108(2):555–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournie G. J., Izui S., Lambert P. H., Conte J. J. Genesis and pathogenicity of anti-DNA antibodies. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1976;6:47–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershwin M. E., Steinberg A. D. Qualitative characteristics of anti-DNA antibodies in lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1974 Nov-Dec;17(6):947–954. doi: 10.1002/art.1780170605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMAN H. R., KUNKEL H. G. Affinity between the lupus erythematosus serum factor and cell nuclei and nucleoprotein. Science. 1957 Jul 26;126(3265):162–163. doi: 10.1126/science.126.3265.162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn E. C., Ramos L., Kenyon A. J. Properties of Aleutian disease virus assayed with feline kidney cells. Arch Virol. 1977;55(4):315–326. doi: 10.1007/BF01315053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howie J. B., Helyer B. J. The immunology and pathology of NZB mice. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:215–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram D. G., Cho H. J. Aleutian disease in mink: virology, immunology and pathogenesis. J Rheumatol. 1974 Mar;1(1):74–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon A. J. Immunologic deficiency in Aleutian disease of mink. Am J Vet Res. 1966 Nov;27(121):1780–1782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D. Immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Annu Rev Med. 1974;25:149–164. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.25.020174.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koffler D., Schur P. H., Kunkel H. G. Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):607–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leon S. A., Green A., Ehrlich G. E., Poland M., Shapiro B. Avidity of antibodies in SLE: relation to severity of renal involvement. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jan-Feb;20(1):23–29. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodmell D. L., Bergman R. K., Hadlow W. J. Antibody-forming cells and serum hemolysin responses of pastel and sapphire mink inoculated with Aleutian disease virus. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):769–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.769-774.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIESCHER P., STRASSLE R. New serological methods for the detection of the L.E. factor. Vox Sang. 1957 Sep;2(4):283–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1957.tb03704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Crawford T. B., Henson J. B., Gorham J. R. Aleutian disease of mink: detection of large quantities of complement-fixing antibody to viral antigen. J Immunol. 1971 Nov;107(5):1481–1482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty R. E., Steward M. W. Relationship of antibody affinity to onset of immune complex disease in New Zealand mice. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Feb;36(1):39–43. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E. Aleutian disease of mink. Prog Med Virol. 1974;18(0):32–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. The pathogenesis of Aleutian disease of mink. I. In vivo viral replication and the host antibody response to viral antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):575–593. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELIGMANN M. Etudes immunologiques sur le lupus érythémateux disséminé. Rev Fr Etud Clin Biol. 1958 Jun;3(6):558–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Pincus T., Talal N. DNA-binding assay for detection of anti-DNA antibodies in NZB-NZW F1 mice. J Immunol. 1969 Mar;102(3):788–790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Katz F. E., West N. J. The role of low affinity antibody in immune complex disease. The quantity of anti-DNA antibodies in NZB/W F1 hybrid mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Jul;21(1):121–130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talal N., Steinberg A. D. The pathogenesis of autoimmunity in New Zealand black mice. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1974;64(0):79–103. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65848-8_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr, Kenyon A. J., Huntley C. C. Immunoglobulins, viruses, and speculation on their interrelationship in certain human and animal disease states. Blood. 1968 Apr;31(4):522–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold R. T., Young F. E., Tan E. M., Farr R. S. Deoxyribonucleic acid antibody: a method to detect its primary interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid. Science. 1968 Aug 23;161(3843):806–807. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3843.806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


