Abstract
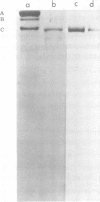
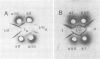
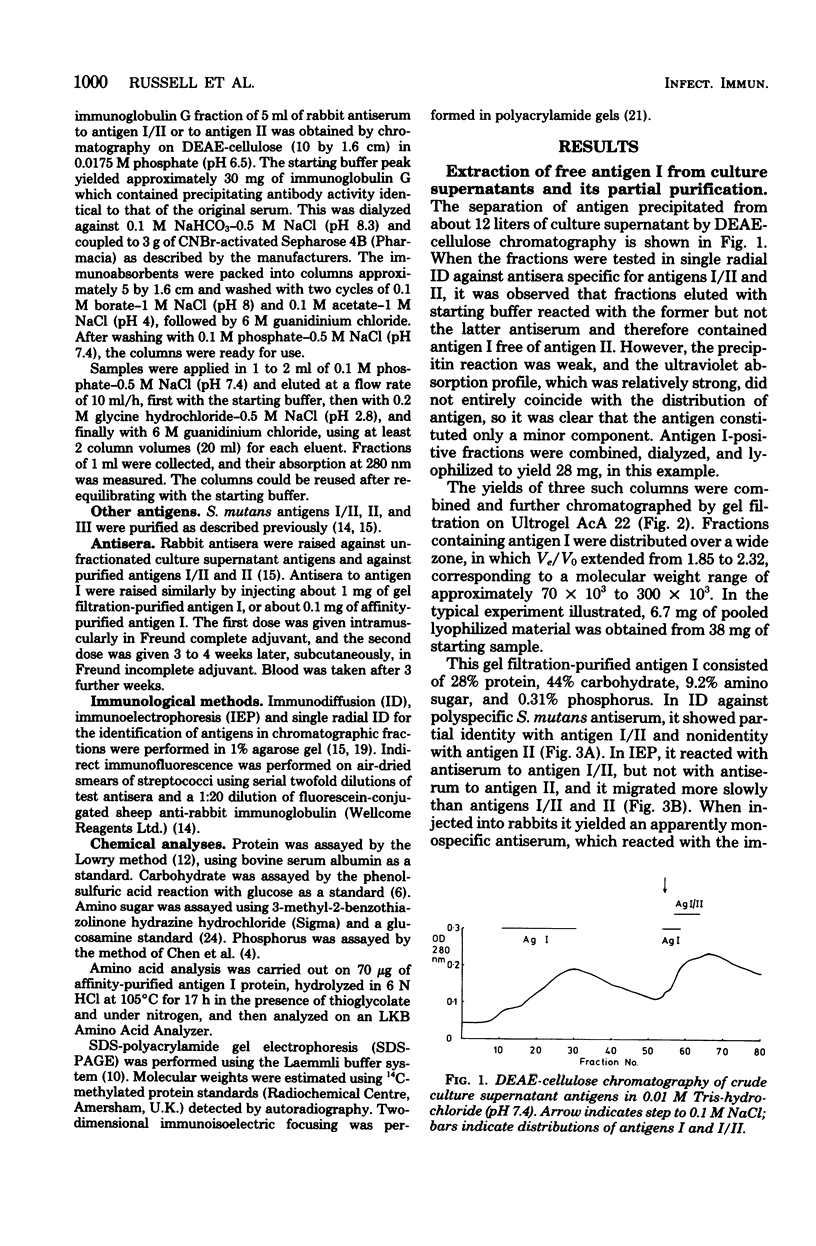
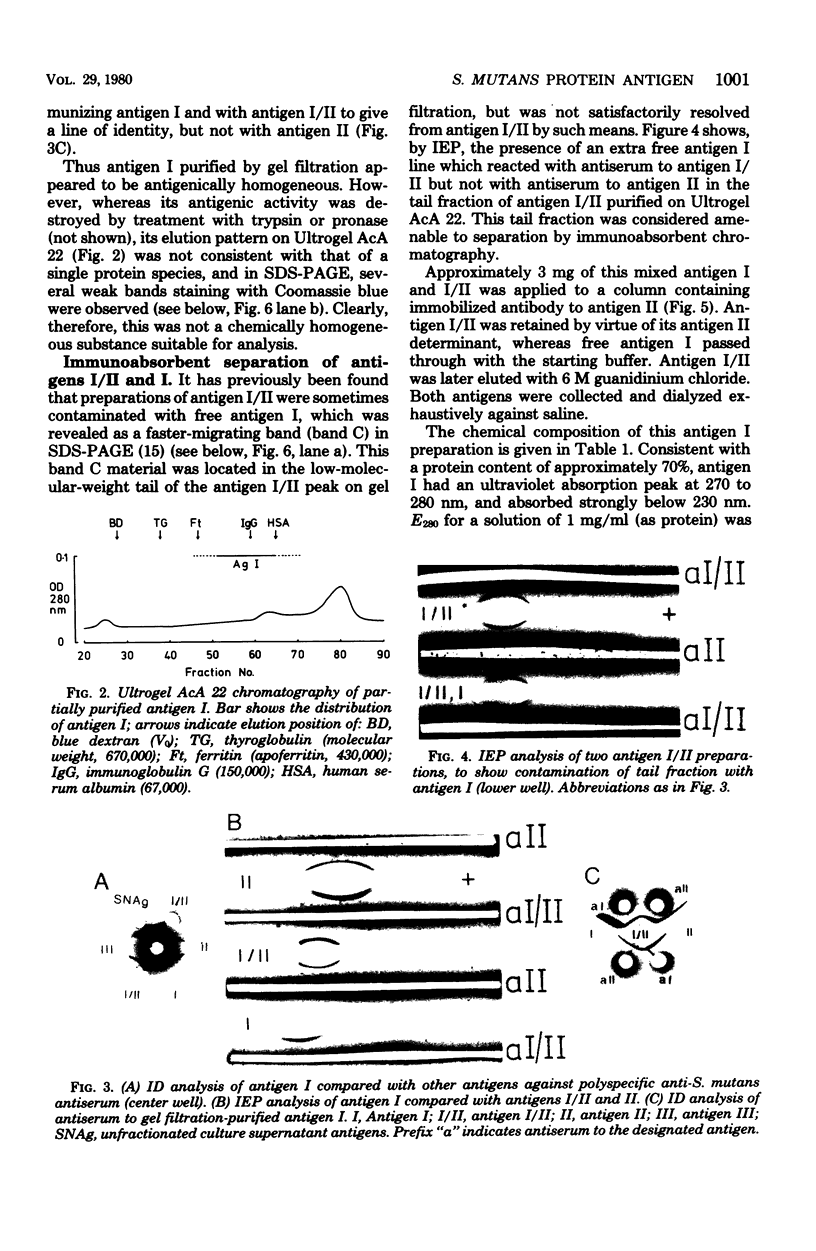
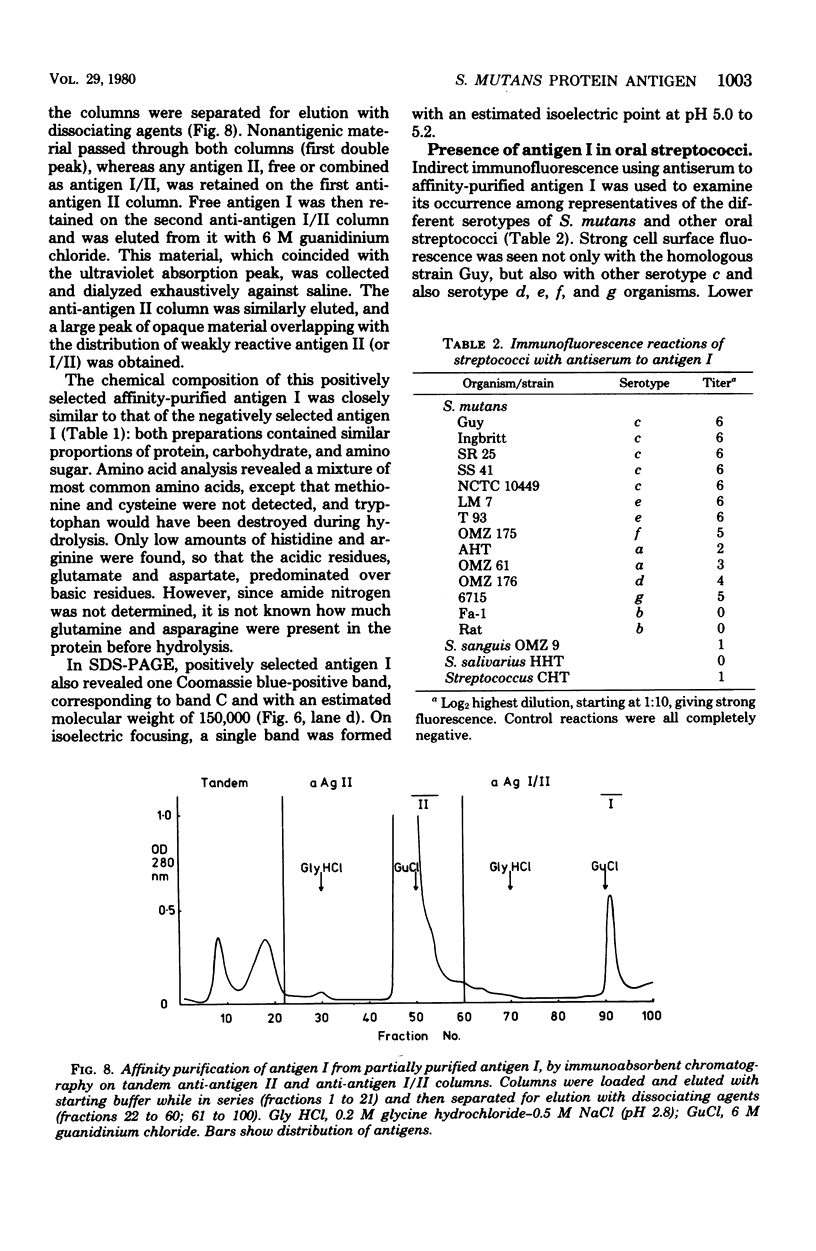
An antigenic component (antigen I) of the cell surface of Streptococcus mutans has been purified from culture supernatants and shown to be immunologically identical to the protease-susceptible moiety of antigen I/II. Ion-exchange and gel filtration chromatography failed to yield a physicochemically homogeneous product. Immunoasbsorbent chromatography on single and tandem columns containing immobilized antibodies to antigens I/II and II yielded identical products which were homogeneous in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and which when injected into rabbits induced monospecific antisera to antigen I. This antigen consisted of approximately 70% protein. Its molecular weight was estimated as 150,000, and the isoelectric point was estimated to be 5.1. Immunofluorescence microscopy using monospecific antiserum to antigen I showed that a similar antigen was present on cells of S. mutans serotypes a, c, d, e, f, and g, but not b.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowden G. H., Hardie J. M., Fillery E. D. Antigens from Actinomyces species and their value in identification. J Dent Res. 1976 Jan;55:A192–A204. doi: 10.1177/002203457605500112011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. A., Bleiweis A. S. Chemical, immunochemical, and structural studies of the cross-reactive antigens of Streptococcus mutans AHT and B13. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):326–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.326-336.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chorpenning F. W., Cooper H. R., Rosen S. Cross-reactions of Streptococcus mutans due to cell wall teichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):586–591. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.586-591.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui K., Fukui Y., Moriyama T. Purification and properties of dextransucrase and invertase from Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):796–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.796-804.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Purification and immunochemical characterization of type e polysaccharide antigen of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):68–76. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.68-76.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M., Machardy S. M., Sheppard A. J., Woods N. C. Evidence for an immunological relationship between Streptococcus mutans and human cardiac tissue. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):576–588. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.576-588.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Russell M. W., Caldwell J. Immunisation with a purified protein from Streptococcus mutans against dental caries in rhesus monkeys. Lancet. 1980 May 10;1(8176):995–996. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Slade H. D. Mechanism of adherence of Streptococcus mutans to smooth surfaces. I. Roles of insoluble dextran-levan synthetase enzymes and cell wall polysaccharide antigen in plaque formation. Infect Immun. 1973 Oct;8(4):555–562. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.4.555-562.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Bergmeier L. A., Zanders E. D., Lehner T. Protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans: purification and properties of a double antigen and its protease-resistant component. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):486–493. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.486-493.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Challacombe S. J., Lehner T. Serum glucosyltransferase-inhibiting antibodies and dental caries in rhesus monkeys immunized against Streptococcus mutans. Immunology. 1976 May;30(5):619–627. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Challacombe S. J., Lehner T. Specificity of antibodies induced by Streptococcus mutans during immunization against dental caries. Immunology. 1980 May;40(1):97–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W., Lehner T. Characterisation of antigens extracted from cells and culture fluids of Streptococcus mutans serotype c. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(1):7–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell M. W. Purification and properties of a protein surface antigen of Streptococcus mutants. Microbios. 1979;25(99):7–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell R. R. Wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus mutans. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):109–115. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Thompson W. S., Wallach D. F. Antigenic distinctions of glycoproteins in plasma and mitochondrial membranes of lymphoid cells neoplastically transformed by simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):643–647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. J., Taubman M. A., Ebersole J. L. Effects of local immunization with glucosyltransferase fractions from Streptococcus mutans on dental caries in hamsters caused by homologous and heterologous serotypes of Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):843–851. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.843-851.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Nisengard R. J., Bergey E. J. Binding of streptococcal antigens to muscle tissue in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):604–613. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.604-613.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Kinoshita T., Hoshino M. Analytical chemical studies on amino sugars. II. Determination of hexosamines using 3-methyl-2-benzothiazolone hydrazone hydrochloride. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1969 Jul;17(7):1505–1510. doi: 10.1248/cpb.17.1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]