Abstract
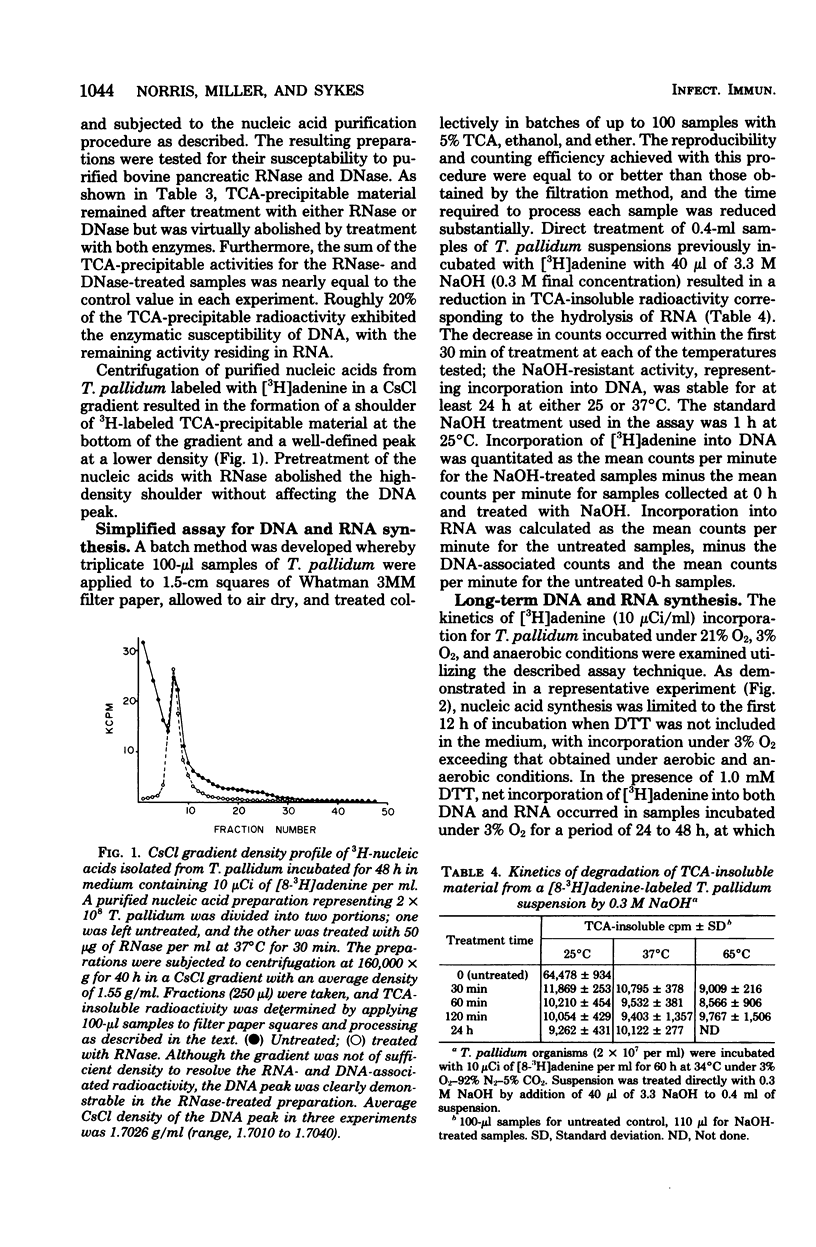
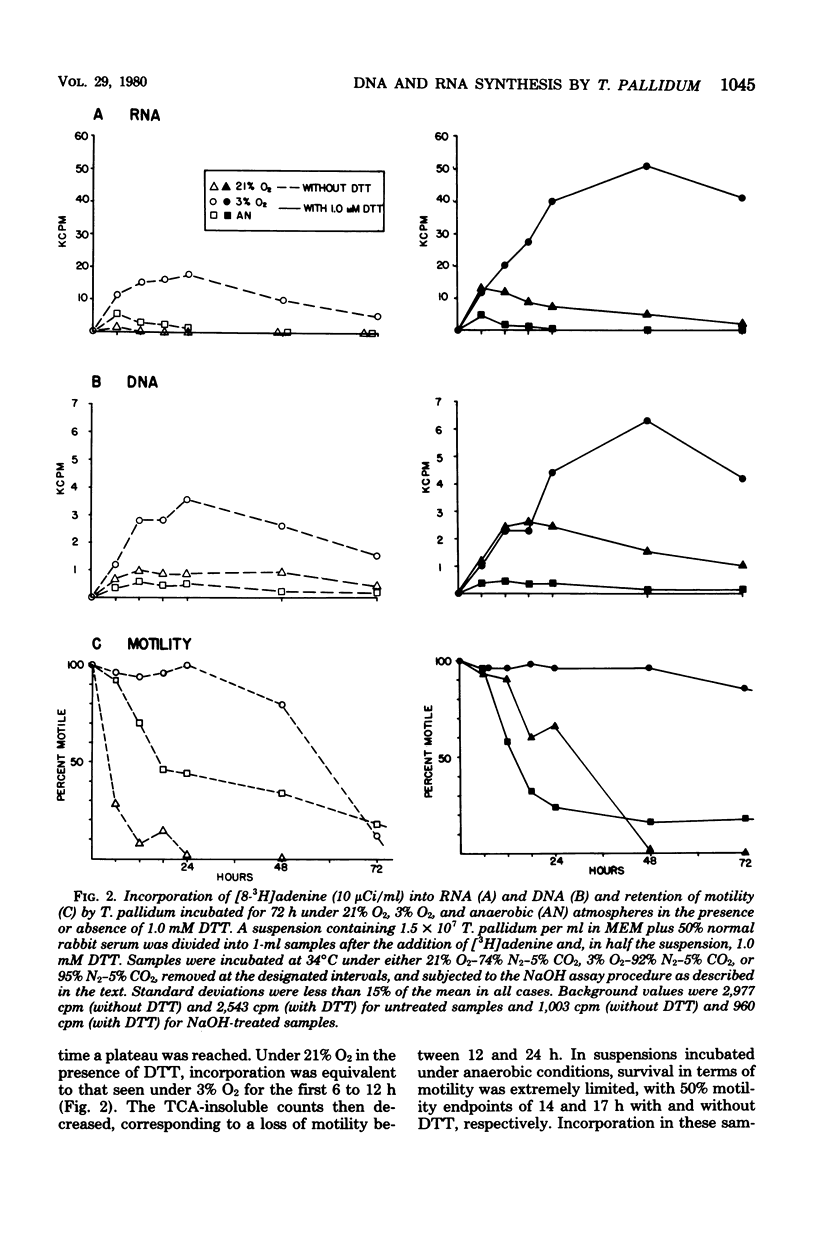
Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain), extracted in medium containing Eagle minimal essential medium 50% fresh, heat-inactivated normal rabbit serum, and 1.0 mM dithiothreitol, was incubated under 3% oxygen in the presence of tritiated nucleic acid precursors. [8-3H]adenine was incorporated with high efficiency into trichloroacetic acid-insoluble material; 2'-deoxyadenosine and uridine were incorporated in lower quantities, and thymine and thymidine were not incorporated. Incorporation of [3H]adenine was inhibited by penicillin G, mitomycin C, actinomycin D, and erythromycin, but was not affected by cycloheximide. Partial purification of nucleic acids from T. pallidum incubated with [8-3H]adenine for 36 to 72 h and subsequent treatment with ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease revealed that 15 to 20% of the trichloroacetic acid-precipitable counts were resistant to ribonuclease but susceptible to deoxyribonuclease. A simple assay was developed in which NaOH treatment was used to distinguish incorporation into ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid. Both ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis continued for 6 days of incubation under 3% O2, whereas incorporation was limited to the first day of incubation in samples incubated under aerobic or anaerobic conditions. T. pallidum thus appears to be capable of significant de novo deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid synthesis under microaerobic conditions.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baseman J. B., Hayes N. S. Protein synthesis by Treponema pallidum extracted from infected rabbit tissue. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1350–1355. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1350-1355.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Nichols J. C., Hayes N. C. Virulent Treponema pallidum: aerobe or anaerobe. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):704–711. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.704-711.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Nichols J. C., Mogerley S. Capacity of virulent Treponema pallidum (Nichols) for deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. Infect Immun. 1979 Feb;23(2):392–397. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.2.392-397.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton K. Transport of adenine, hypoxanthine and uracil into Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1977 Nov 15;168(2):195–204. doi: 10.1042/bj1680195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers W. S., Taylor-Robinson D. The effect of reducing and other agents on the motility of Treponema pallidum in an acellular culture medium. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Oct;114(2):443–447. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-2-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D., Barber M. K. Oxygen uptake by Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):123–127. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.123-127.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fangman W. L. Specificity and efficiency of thymidine incorporation in Escherichia coli lacking thymidine phosphorylase. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):681–687. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.681-687.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieldsteel A. H., Becker F. A., Stout J. G. Prolonged survival of virulent Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in cell-free and tissue culture systems. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):173–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.173-182.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieldsteel A. H., Stout J. G., Becker F. A. Comparative behavior of virulent strains of Treponema pallidum and Treponema pertenue in gradient cultures of various mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):337–345. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.337-345.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C., Sykes J. A., Miller J. N. Interaction of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) with cultured mammalian cells: effects of oxygen, reducing agents, serum supplements, and different cell types. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):444–452. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.444-452.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstadt-Ozer J., Stadtman E. R. The regulation of purine utilization in bacteria. II. Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase in isolated membrane preparations and its role in transport of adenine across the membrane. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5304–5311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jyssum S. Labelling of DNA and RNA from thymine and thymidine in Neisseria meningitidis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(2):325–334. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb00166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIMM G. E., ALLEN R. H., MORTON H. J., MORGAN J. F. Enhancement of survival in vitro of Treponema pallidum by addition of glucose and magnesium. J Bacteriol. 1960 Nov;80:726–727. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.5.726-727.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. T., Duncan J. F. Use of exogenous adenine to label the nucleic acids of wild-type Neisseria meningitidis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1262–1263. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1262-1263.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysko P. G., Cox C. D. Respiration and oxidative phosphorylation in Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):462–473. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.462-473.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysko P. G., Cox C. D. Terminal electron transport in Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):885–890. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.885-890.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews H. M., Jenkin H. M., Crilly K., Sandok P. L. Effects of fatty acids on motility retention by Treponema pallidum in vitro. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):814–821. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.814-821.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miao R., Fieldsteel A. H. Genetics of Treponema: relationship between Treponema pallidum and five cultivable treponemes. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):101–107. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.101-107.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. C., Baseman J. B. Carbon sources utilized by virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1044–1050. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1044-1050.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. C., Baseman J. B. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid synthesis by virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):854–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.854-860.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris S. J., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A., Fitzgerald T. J. Influence of oxygen tension, sulfhydryl compounds, and serum on the motility and virulence of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) in a cell-free system. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):689–697. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.689-697.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandok P. L., Jenkin H. M., Matthews H. M., Roberts M. S. Unsustained multiplication of treponema pallidum (nichols virulent strain) in vitro in the presence of oxygen. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):421–429. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.421-429.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandok P. L., Jenkin H. M. Radiolabeling of Treponema pallidum (Nichols virulent strain) in vitro with precursors for protein and RNA biosynthesis. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):22–28. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.22-28.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller N. L., Cox C. D. Catabolism of glucose and fatty acids by virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):60–68. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.60-68.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER M. M. Factors influencing the in vitro survival of Treponema pallidum. Am J Hyg. 1960 May;71:401–417. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


