Abstract
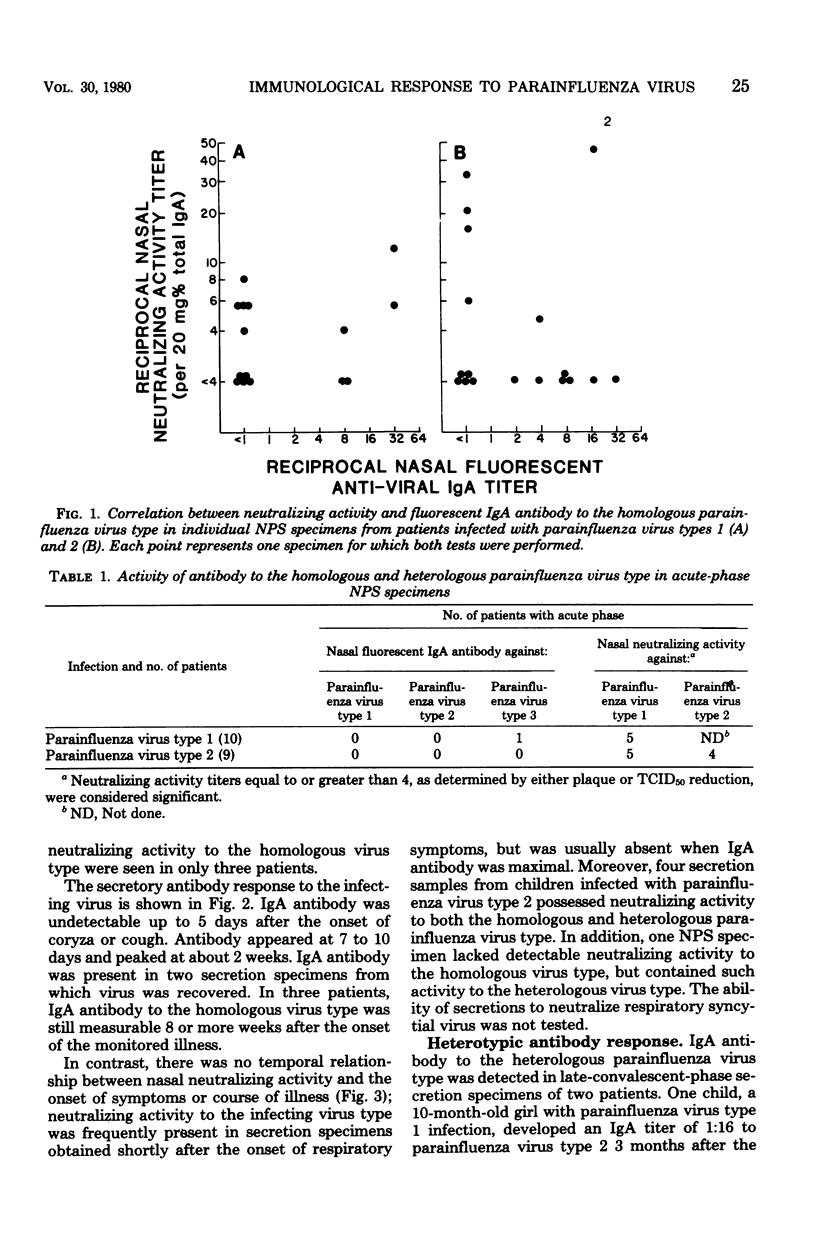
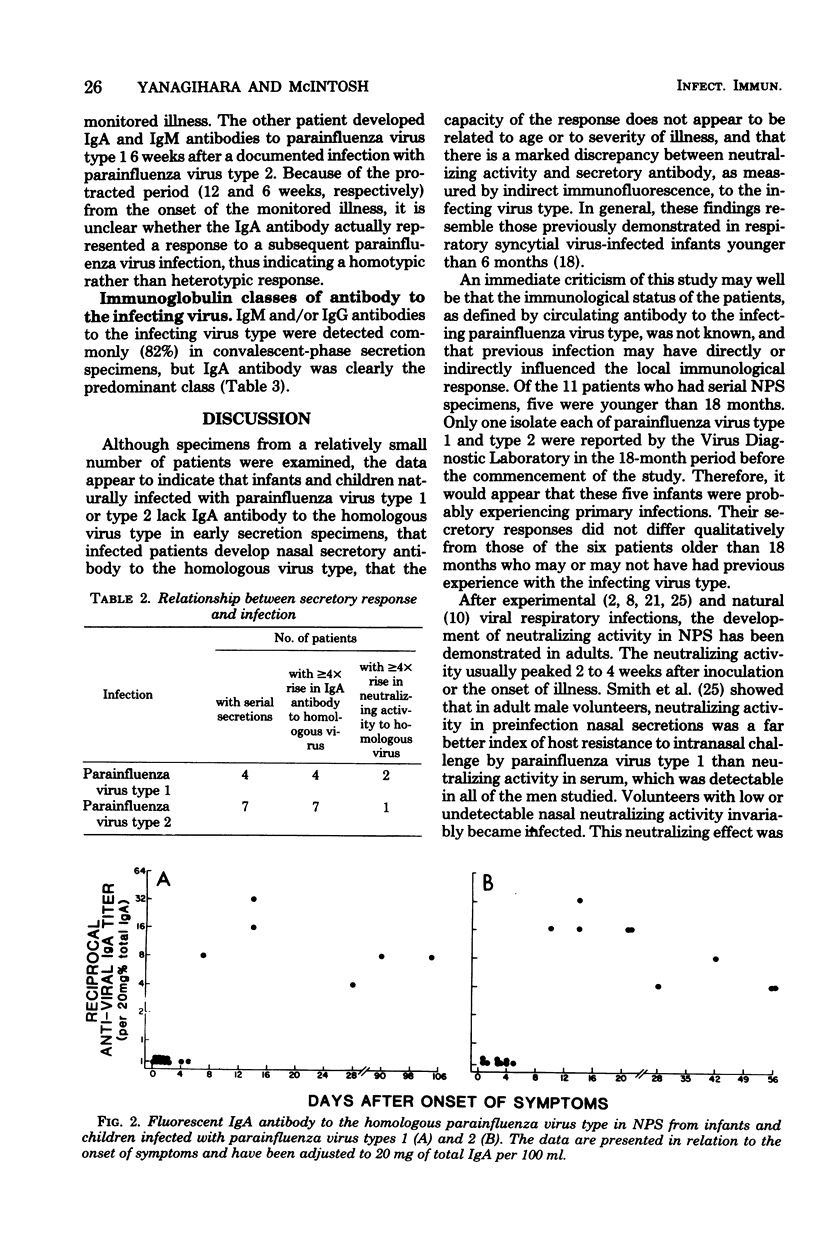
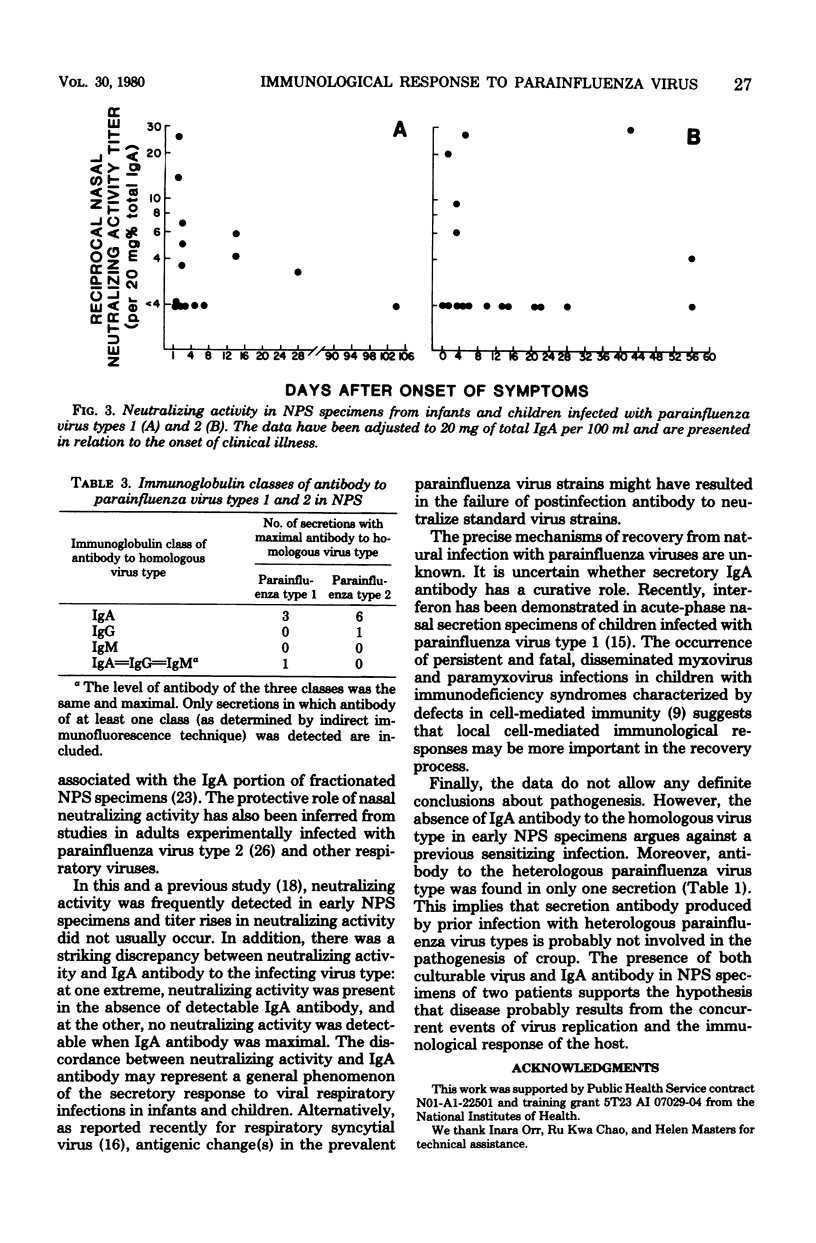
The secretory immunological responses to natural infection with parainfluenza viruses ae not well defined. Nasopharyngeal secretion specimens from 20 infants and children naturally infected with parainfluenza virus type 1 or type 2 were examined for class-specific antibody and virus-neutralizing activity. There was a marked discordance in individual secretions between immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibody (as measured by indirect immunofluorescence) and neutralizing activity (as determined by either hemadsorption plaque or 50% tissue culture infective dose reduction) to the infecting parainfluenza virus type. Many secretions contained neutralizing activity in the absence of detectable IgA antibody; conversely, secretions with measureable IgA antibody frequently lacked neutralizing activity. Moreover, there was no relationship between neutralizing activity and the course of illness. All 11 patients with serial secretion specimens showed a fourfold or greater titer rise in IgA antibody to the homologous parainfluenza virus type. Antibody usually appeared 7 to 10 days after the onset of symptoms and peaked at about 2 weeks. This response did not appear to be related to age or to severity of illness. in general, the secretory responses resembled those seen in infants infected with respiratory syncytial virus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHANOCK R. M., PARROTT R. H. ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISEASE IN INFANCY AND CHILDHOOD: PRESENT UNDERSTANDING AND PROSPECTS FOR PREVENTION. Pediatrics. 1965 Jul;36:21–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cate T. R., Rossen R. D., Douglas R. G., Jr, Butler W. T., Couch R. B. The role of nasal secretion and serum antibody in the rhinovirus common cold. Am J Epidemiol. 1966 Sep;84(2):352–363. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J., Magoffin R. L., Shearer L. A., Schieble J. H., Lennette E. H. Field evaluation of a respiratory syncytial virus vaccine and a trivalent parainfluenza virus vaccine in a pediatric population. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Apr;89(4):449–463. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooney M. K., Fox J. P., Hall C. E. The Seattle Virus Watch. VI. Observations of infections with and illness due to parainfluenza, mumps and respiratory syncytial viruses and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Am J Epidemiol. 1975 Jun;101(6):532–551. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICK E. C., MOGABGAB W. J., HOLMES B. Characteristics of para-influenza 1 (HA-2) virus. I. Incidence of infection and clinical features in adults. Am J Hyg. 1961 May;73:263–272. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas R. G., Jr, Rossen R. D., Butler W. T., Couch R. B. Rhinovirus neutralizing antibody in tears, parotid saliva, nasal secretions and serum. J Immunol. 1967 Aug;99(2):297–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döhner L., Herrmann R. Uber eine Methode zur schnellen Bestimmung plaquebildender Einheiten von Parainfluenzaviren der Typen 2 und 3. Pathol Microbiol (Basel) 1972;38(6):431–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishaut M., Tubergen D., McIntosh K. Cellular response to respiratory viruses with particular reference to children with disorders of cell-mediated immunity. J Pediatr. 1980 Feb;96(2):179–186. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80799-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulginiti V. A., Eller J. J., Sieber O. F., Joyner J. W., Minamitani M., Meiklejohn G. Respiratory virus immunization. I. A field trial of two inactivated respiratory virus vaccines; an aqueous trivalent parainfluenza virus vaccine and an alum-precipitated respiratory syncytial virus vaccine. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Apr;89(4):435–448. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner P. S., McQuillin J., McGuckin R., Ditchburn R. K. Observations on clinical and immunofluorescent diagnosis of parainfluenza virus infections. Br Med J. 1971 Apr 3;2(5752):7–12. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5752.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glezen P., Denny F. W. Epidemiology of acute lower respiratory disease in children. N Engl J Med. 1973 Mar 8;288(10):498–505. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197303082881005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glezen W. P., Loda F. A., Clyde W. A., Jr, Senior R. J., Sheaffer C. I., Conley W. G., Denny F. W. Epidemiologic patterns of acute lower respiratory disease of children in a pediatric group practice. J Pediatr. 1971 Mar;78(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. B., Douglas R. G., Jr, Simons R. L., Geiman J. M. Interferon production in children with respiratory syncytial, influenza, and parainfluenza virus infections. J Pediatr. 1978 Jul;93(1):28–32. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C., Hirsch M. S. Croup and pneumonia in human infants associated with a new strain of respiratory syncytial virus. J Infect Dis. 1979 Nov;140(5):826–828. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.5.826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loda F. A., Glezen W. P., Clyde W. A., Jr Respiratory disease in group day care. Pediatrics. 1972 Mar;49(3):428–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh K., Masters H. B., Orr I., Chao R. K., Barkin R. M. The immunologic response to infection with respiratory syncytial virus in infants. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):24–32. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARROTT R. H., VARGOSKO A. J., KIMHW, BELL J. A., CHANOCK R. M. Acute respiratory diseases of viral etiology. III. parainfluenza. Myxoviruses. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1962 Jun;52:907–917. doi: 10.2105/ajph.52.6.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARROTT R. H., VARGOSKO A., LUCKEY A., KIM H. W., CUMMING C., CHANOCK R. Clinical features of infection with hemadsorption viruses. N Engl J Med. 1959 Apr 9;260(15):731–738. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195904092601501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Murphy B. R., Tierney E. L., Chanock R. M. Specificity of the local secretory antibody to influenza A virus infection. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1654–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H., Hanahoe M. F. A micro method for performing parainfluenza virus neutralization tests. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Aug-Sep;122(4):1062–1067. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Bellanti J. A., Chanock R. M. Immunoglobulins in serum and nasal secretions following infection with type 1 parainfluenza virus and injection of inactivated vaccines. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):133–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Canchola J., Chanock R. M. A micro-method for assay of neutralizing antibodies against parainfluenza virus types 1 and 3. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jan;124(1):4–7. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Purcell R. H., Bellanti J. A., Chanock R. M. Protective effect of antibody to parainfluenza type 1 virus. N Engl J Med. 1966 Nov 24;275(21):1145–1152. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196611242752101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremonti L. P., Lin J. S., Jackson G. G. Neutralizing activity in nasal secretions and serum in resistance of volunteers to parainfluenza virus type 2. J Immunol. 1968 Sep;101(3):572–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VARGOSKO A. J., CHANOCK R. M., HUEBNER R. J., LUCKEY A. H., KIM H. W., CUMMING C., PARROTT R. H. Association of type 2 hemadsorption (parainfluenza 1) virus and Asian influenza A virus with infections croup. N Engl J Med. 1959 Jul 2;261(1):1–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195907022610101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakstelskaya L. J., Arnaudova V. I., Yakhno M. A. Humoral immunity factors to parainfluenza viruses type 1, 2 and 3 in infants under the age of one year. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1969;13(3):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


