Abstract
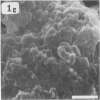
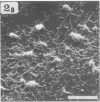
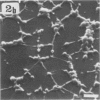
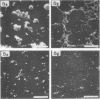
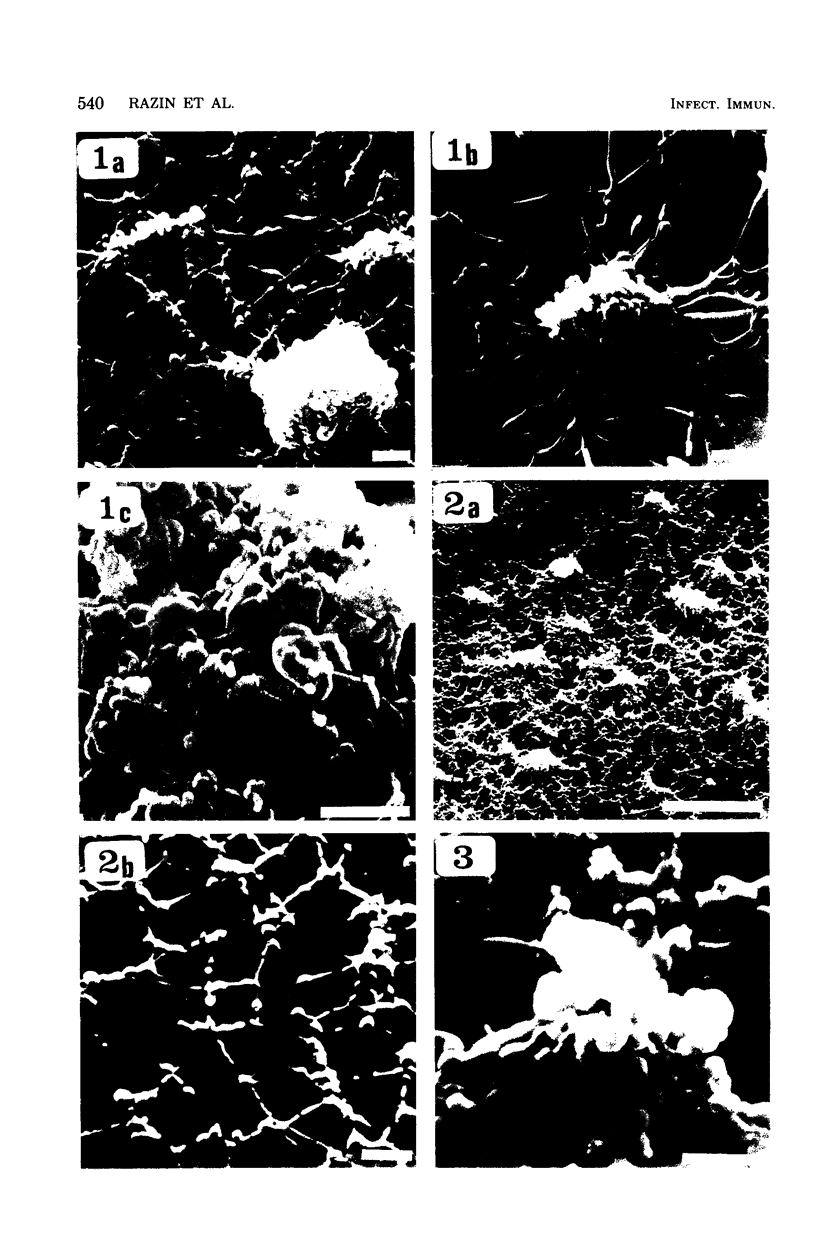
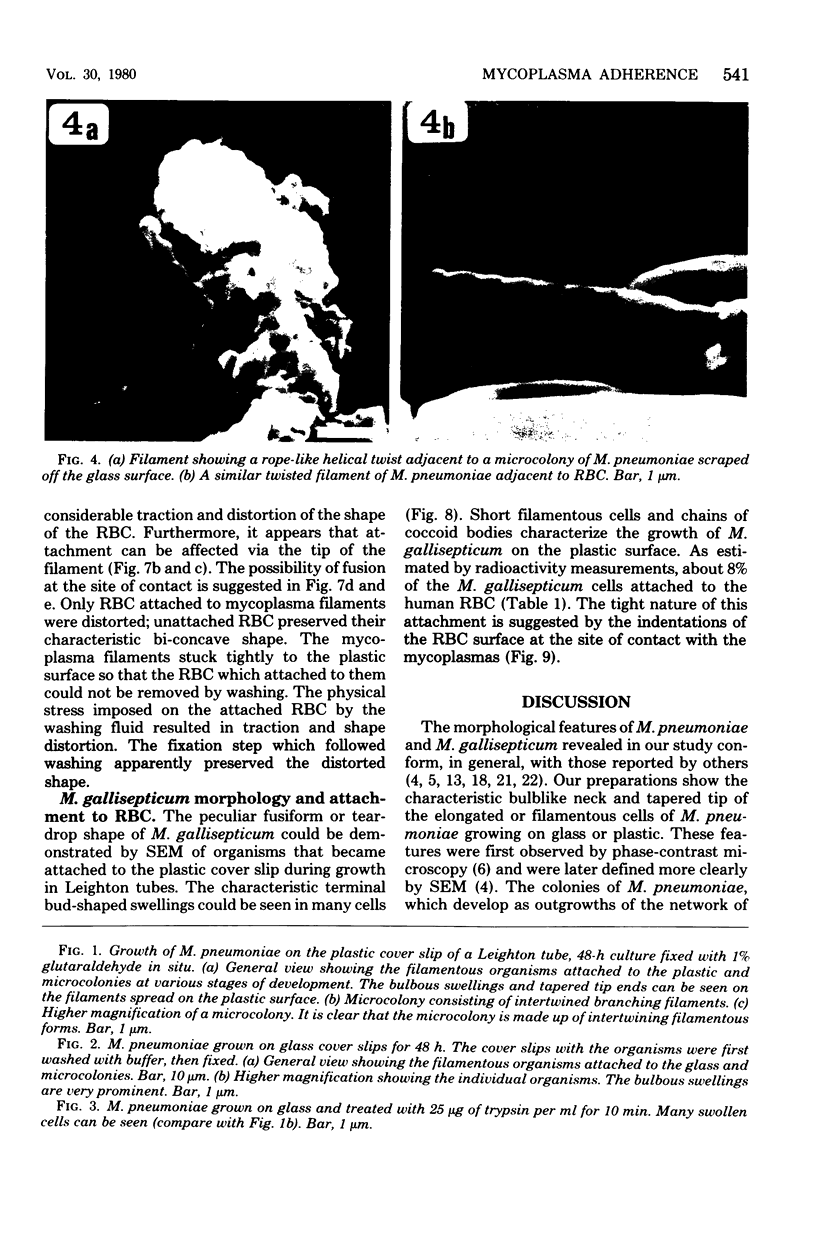
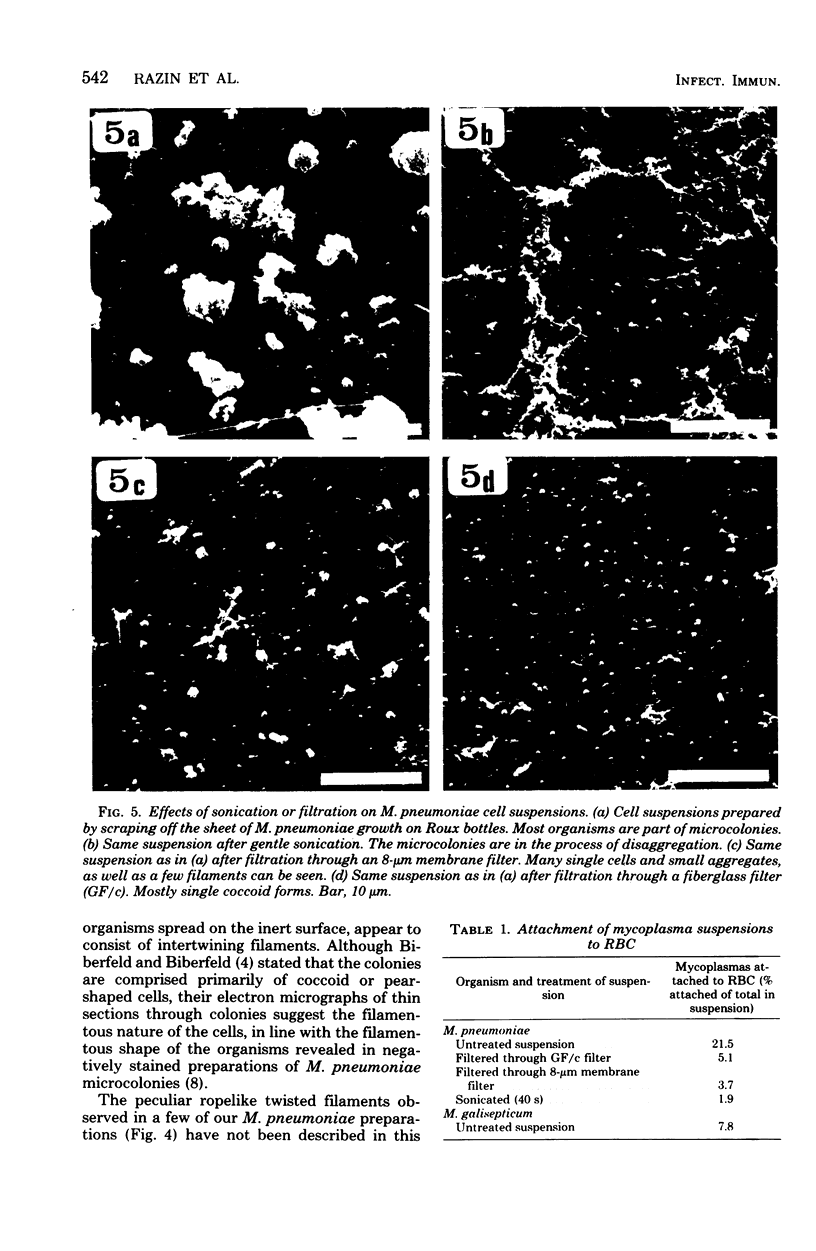
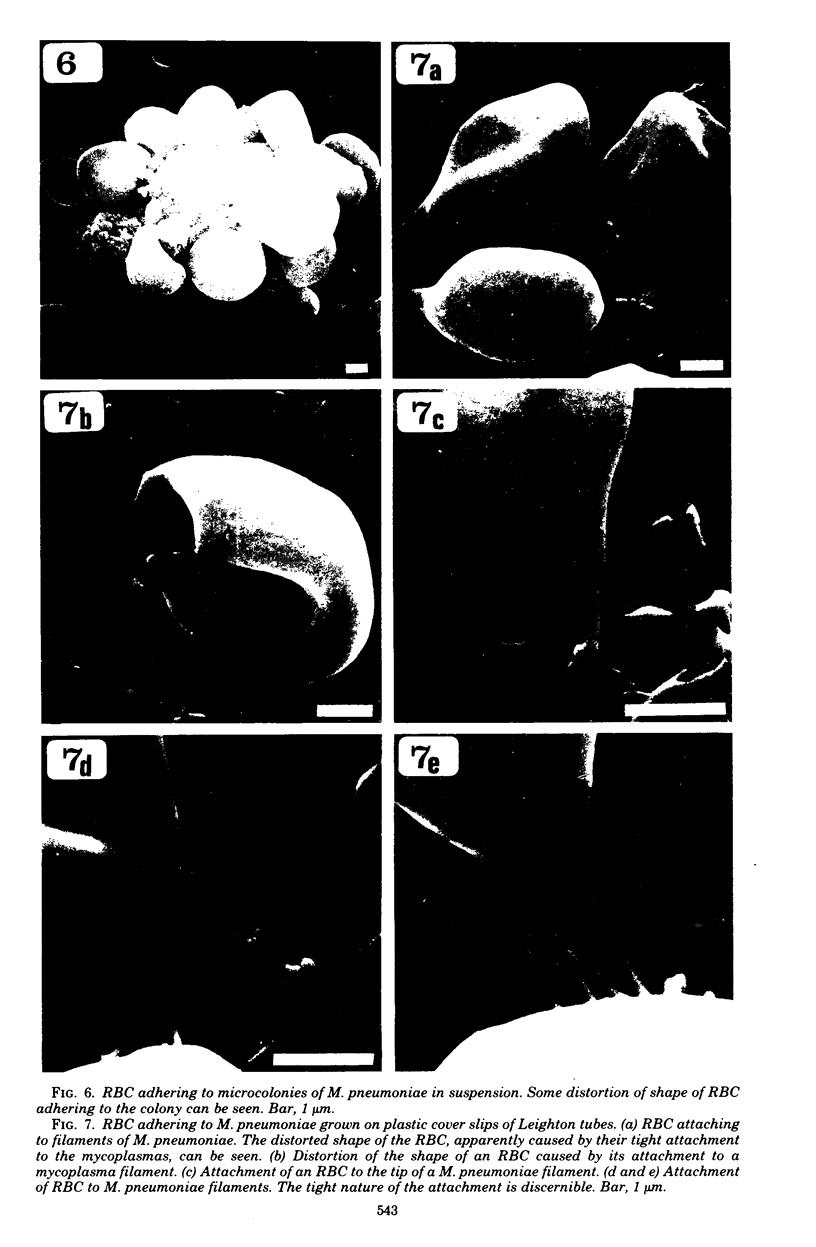
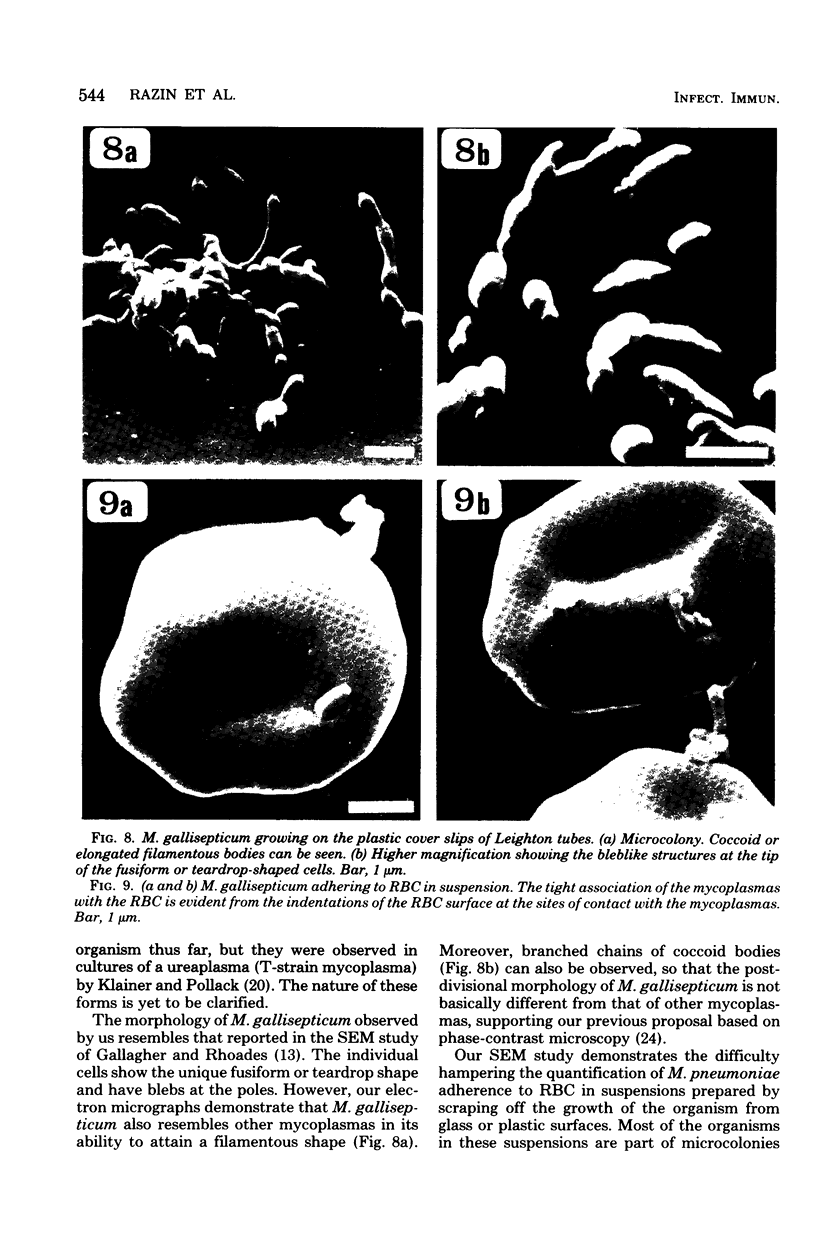
The interaction of Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Mycoplasma gallisepticum with human erythrocytes (RBC) was studied by scanning electron microscopy. The tight nature of the attachment of the microorganisms to the RBC was indicated by the indentation of the RBC surface at the site of attachment of M. gallisepticum cells and by traction and resulting distortion in the shape of the RBC at the point of its attachment to M. pneumoniae filaments growing on glass or plastic. In many cases attachment took place via the tip of the filaments, the membrane of the parasite appearing to be fused with that of the RBC. The morphology of the mycoplasmas growing on cover slips conformed in general with previous descriptions obtained by scanning electron microscopy. Growth of M. pneumoniae on glass or plastic consisted of branching filaments spread on the inert surface and microcolonies made up of intertwining filaments projecting into the medium. The filaments had a bulbous swelling adjacent to a tapered tip end. A few filaments were shown to have a ropelike helical twist. M. gallisepticum grown on the cover slips of Leighton tubes had a peculiar fusiform or teardrop shape with blebs at one or both poles of the cells. Elongated filamentous forms and chains of coccobacillary bodies were observed as well.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abu-Zahr M. N., Butler M. Growth, cytopathogenicity and morphology of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and M. gallinarum in tracheal explants. J Comp Pathol. 1976 Jul;86(3):455–463. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(76)90014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banai M., Kahane I., Razin S., Bredt W. Adherence of Mycoplasma gallisepticum to human erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):365–372. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.365-372.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld G., Biberfeld P. Ultrastructural features of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):855–861. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.855-861.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boatman E. S., Kenny G. E. Morphology and ultrastructure of Mycoplasma pneumoniae spherules. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):1005–1015. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.1005-1015.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt W. Growth morphology of Mycoplasma pneumoniae strain FH on glass surface. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Jun;128(2):338–340. doi: 10.3181/00379727-128-33009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H., Krauss H., Schaar H., Schiefer H. G. Electron microscopic studies on the attachment of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to guinea pig erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):906–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.906-911.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H., Razin S., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M. Lysis and death of Mycoplasma pneumoniae by antibody and complement. J Immunol. 1971 Apr;106(4):907–916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier A. M., Clyde W. A. Relationships Between Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Human Respiratory Epithelium. Infect Immun. 1971 May;3(5):694–701. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.5.694-701.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldner J., Bredt W., Kahane I. Adherence of erythrocytes to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):60–67. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.60-67.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldner J., Bredt W., Razin S. Adherence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to glass surfaces. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):70–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.70-75.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. E., Rhoades K. R. Simplified preparation of mycoplasmas, an acholeplasma, and a spiroplasma for scanning electron microscopy. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):972–976. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.972-976.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Interaction of virulent Mycoplasma pneumoniae with hamster tracheal organ cultures. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):217–224. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.217-224.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Surface parasitism by Mycoplasma pneumoniae of respiratory epithelium. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1328–1343. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Pollack J. D., Klainer A. S. Scanning-beam electron microscopy of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):499–502. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.499-502.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazia D., Schatten G., Sale W. Adhesion of cells to surfaces coated with polylysine. Applications to electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1975 Jul;66(1):198–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.66.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muse K. E., Powell D. A., Collier A. M. Mycoplasma pneumoniae in hamster tracheal organ culture studied by scanning electron microscopy. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):229–237. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.229-237.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. A., Muse K. A. Scanning electron microscopy of guinea pig alveolar macrophages: in vitro phagocytosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Lab Invest. 1977 Dec;37(6):535–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Cosenza B. J. Growth phases of Mycoplasma in liquid media observed with phase-contrast microscope. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):858–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.858-869.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. The mycoplasmas. Microbiol Rev. 1978 Jun;42(2):414–470. doi: 10.1128/mr.42.2.414-470.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J., Weiss R. L. Mycoplasma capping on lymphocytes. Nature. 1978 Dec 7;276(5688):583–587. doi: 10.1038/276583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uppal P. K., Chu H. P. Attachment of Mycoplasma gallisepticum to the tracheal epithelium of fowls. Res Vet Sci. 1977 Mar;22(2):259–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise K. S., Cassell G. H., Action R. T. Selective association of murine T lymphoblastoid cell surface alloantigens with Mycoplasma hyorhinis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4479–4483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker-Franklin D., Davidson M., Thomas L. The interaction of mycoplasmas with mammalian cells. I. HeLa cells, neutrophils, and eosinophils. J Exp Med. 1966 Sep 1;124(3):521–532. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]