Abstract
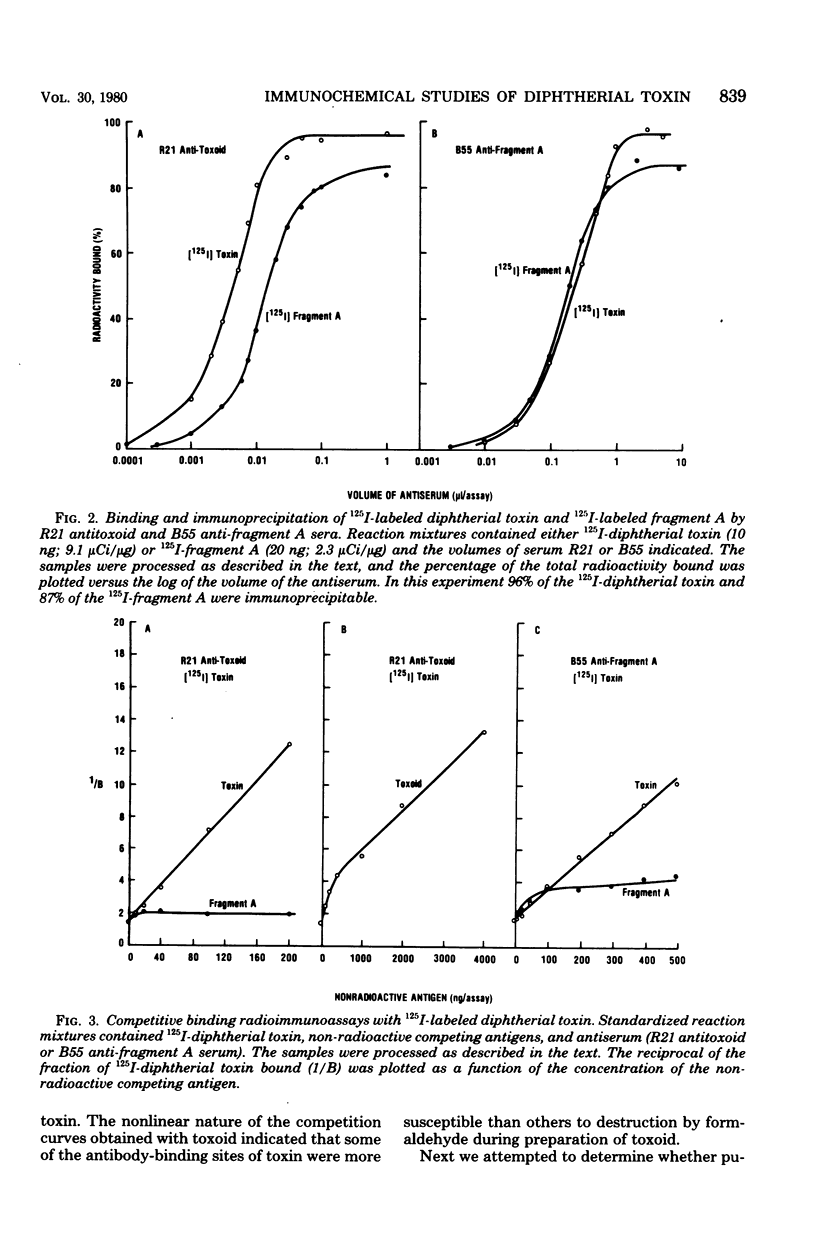
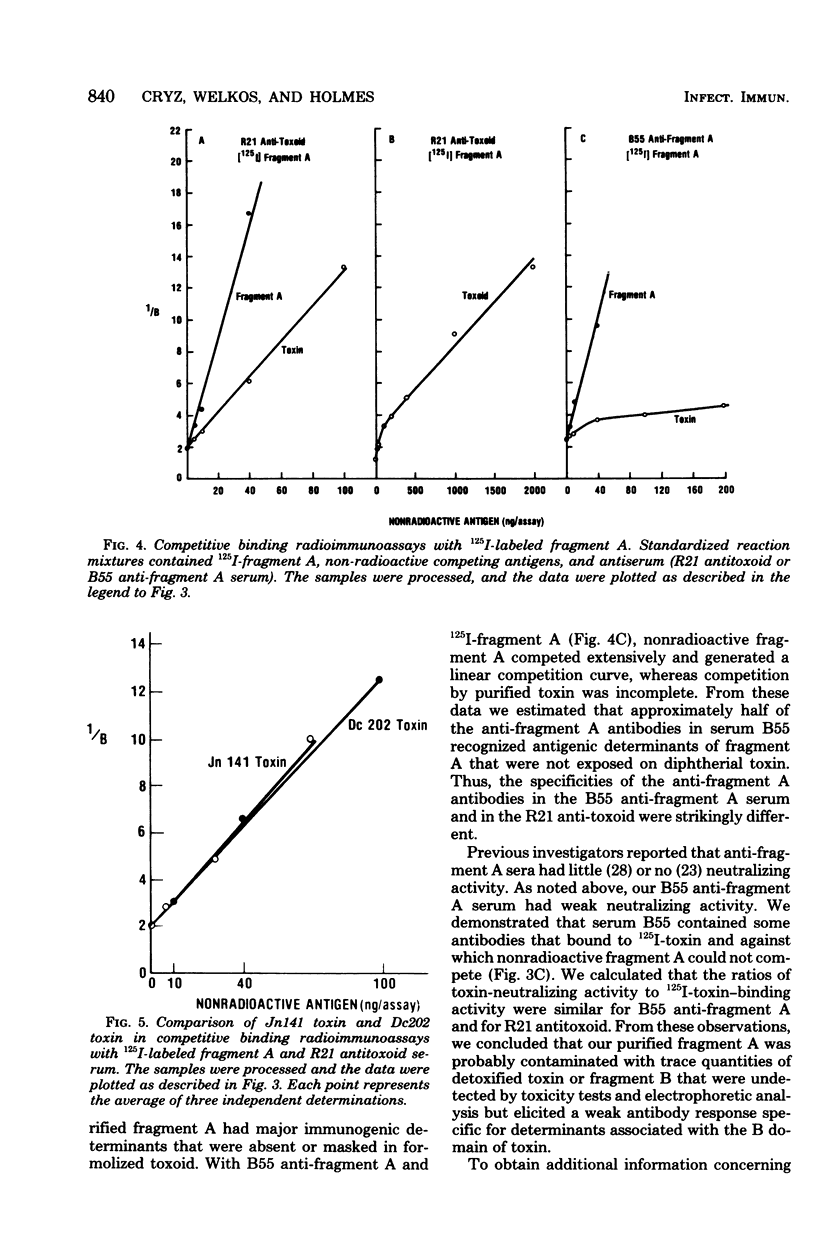
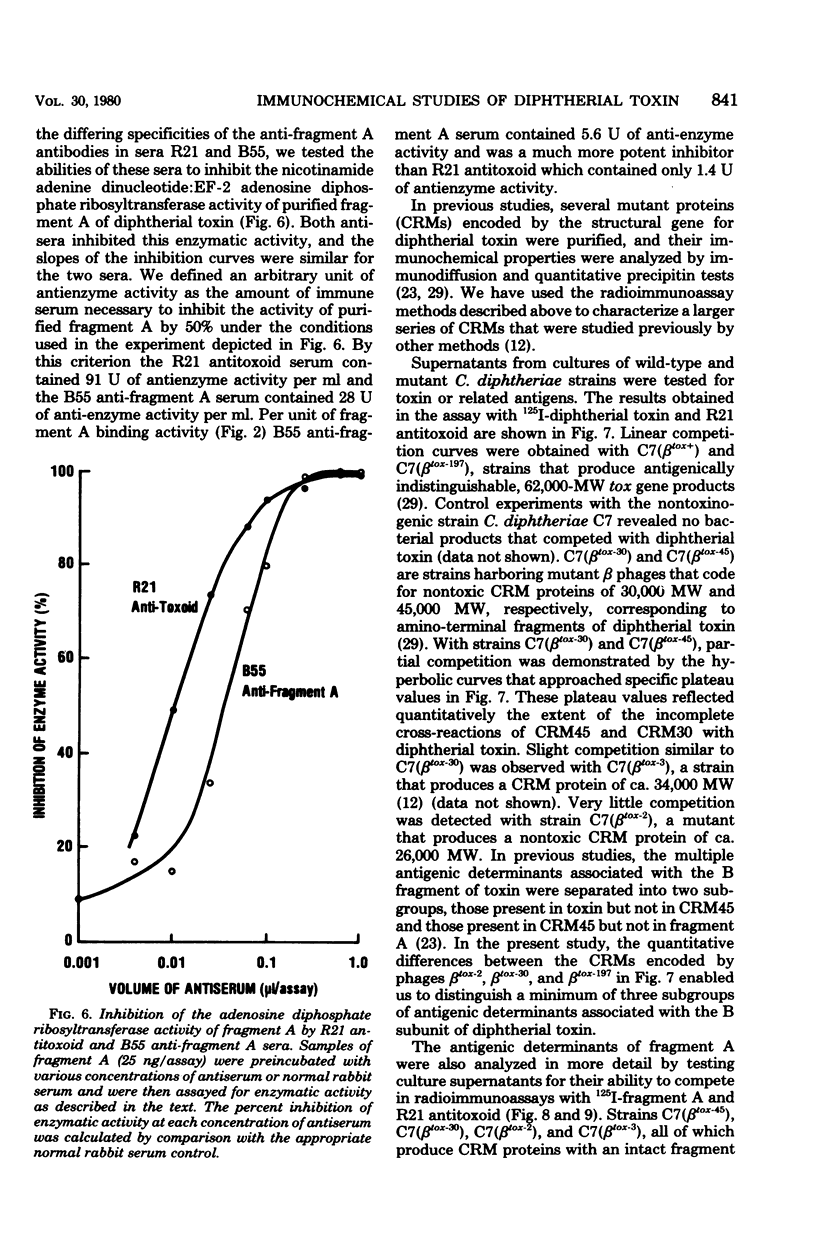
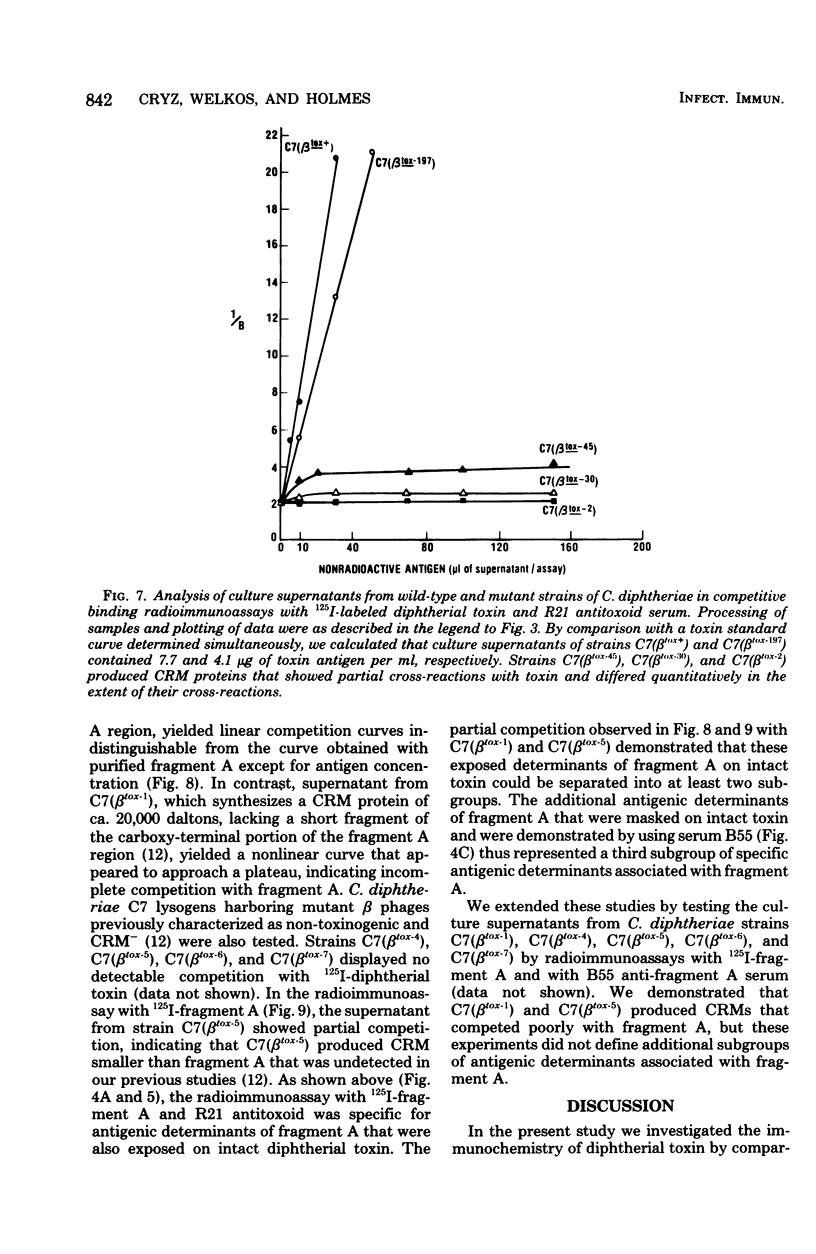
Competitive binding radioimmunoassays were used to analyze the immunochemistry of diphtherial toxin. Rabbit antisera obtained by immunization with formolized toxoid or fragment A were used to characterize purified toxin, toxoid, fragment A, and related nontoxic mutant proteins. Antitoxoid serum had a high titer of neutralizing activity. Most of the antibodies in antitoxoid bound to toxin but not to fragment A. The anti-fragment A antibodies that were present in antitoxoid recognized determinants of fragment A that were exposed on unnicked toxin. Formaldehyde treatment partially destroyed antibody-binding sites associated with the A and B domains of toxin. Anti-fragment A serum had a low titer of neutralizing activity. The specificities of the anti-fragment A antibodies in antitoxoid and anti-fragment A sera were different. Approximately half of the anti-fragment A antibodies in anti-fragment A serum recognized determinants of fragment A that were masked in toxin. Per unit of fragment A-binding activity, anti-fragment A serum was significantly more potent than antitoxoid serum as an inhibitor of the enzymatic activity of fragment A. By analyzing the antigenic structure of several nontoxic mutant proteins (cross-reacting materials) that cross-react with toxin, we distinguished three different subgroups of antigenic determinants associated with the B domain of toxin. Furthermore, the exposed antigenic determinants of the A domain of toxin were separated into two subgroups, both of which were distinct from the masked determinants of the A domain. The radioimmunoassays described here provide rapid, sensitive, quantitative, and versatile methods for immunochemical characterization of toxin or related cross-reacting proteins encoded by corynebacteriophages.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARDSDALE W. L., PAPPENHEIMER A. M., Jr Phage-host relationships in nontoxigenic and toxigenic diphtheria bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1954 Feb;67(2):220–232. doi: 10.1128/jb.67.2.220-232.1954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazaral M., Goscienski P. J., Hamburger R. N. Characteristics of human antibody to diphtheria toxin. Infect Immun. 1973 Feb;7(2):130–136. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.2.130-136.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin: mode of action and structure. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Mar;39(1):54–85. doi: 10.1128/br.39.1.54-85.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier R. J., Kandel J. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. I. Thiol-dependent dissociation of a fraction of toxin into enzymically active and inactive fragments. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1496–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange R. J., Drazin R. E., Collier R. J. Amino-acid sequence of fragment A, an enzymically active fragment from diphtheria toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):69–72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drazin R., Kandel J., Collier R. J. Structure and activity of diphtheria toxin. II. Attack by trypsin at a specific site within the intact toxin molecule. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1504–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekins R. P. Radioimmunoassay and saturation analysis. Basic principles and theory. Br Med Bull. 1974 Jan;30(1):3–11. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Dinius L. L. Observations on the structure of diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1485–1491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Structure-activity relationships in diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1492–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Uchida T., Singer R. A. Expression of diphtheria toxin genes carried by integrated and nonintegrated phage beta. Virology. 1972 Dec;50(3):664–668. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90420-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haustein D. Effective radioiodination by lactoperoxidase and solubilisation of cell-surface proteins of cultured murine T lymphoma cells. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Apr;7(1):25–38. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90127-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Barksdale L. Genetic analysis of tox+ and tox- bacteriophages of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):586–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.586-598.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K. Characterization and genetic mapping of nontoxinogenic (tox) mutants of corynebacteriophage beta. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):195–207. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.195-207.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Perlow R. B. Quantitative assay of diphtherial toxin and of immunologically cross-reacting proteins by reversed passive hemagglutination. Infect Immun. 1975 Dec;12(6):1392–1400. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.6.1392-1400.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo T., Nishizuka Y., Hayaishi O. Diphtheria toxin-dependent adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of aminoacyl transferase II and inhibition of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 25;243(12):3553–3555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ittelson T. R., Gill D. M. Diphtheria toxin: specific competition for cell receptors. Nature. 1973 Mar 30;242(5396):330–332. doi: 10.1038/242330b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel J., Collier R. J., Chung D. W. Interaction of fragment A from diphtheria toxin with nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2088–2097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE C. G., STEVENS M. F. The properties of crystalline diphtheria toxin-protein: its antigen composition as determined by gel-diffusion methods. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Apr;39(2):150–157. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE C. G., STEVENS M. F. The properties of crystalline diphtheria toxin-protein: observations on the pepsin and trypsin-stable antigens. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Oct;39(5):490–496. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE C. G., STEVENS M. F. The properties of crystalline diphtheria toxin-protein: observations on the phosphate-stable antigen. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Aug;39(4):386–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Uchida T., Harper A. A. An immunological study of the diphtheria toxin molecule. Immunochemistry. 1972 Sep;9(9):891–906. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg M. B., Pinney C. T., Jr, Iglewski B. H. Antigenic relationships on the diphtheria toxin molecule: antitoxin versus antitoxoid. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):122–128. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.122-128.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, Greany R. Diphtheria toxin and related proteins. I. Isolation and properties of mutant proteins serologically related to diphtheria toxin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3838–3844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



