Abstract
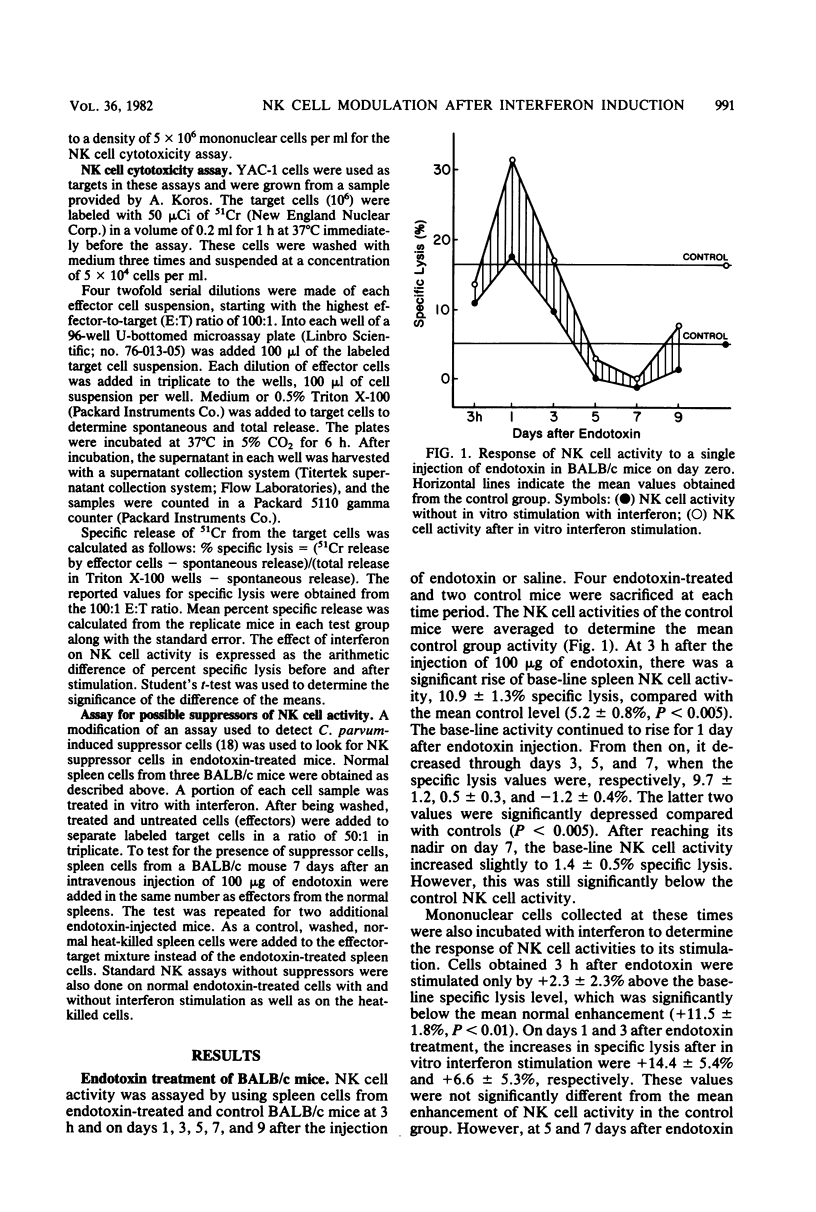
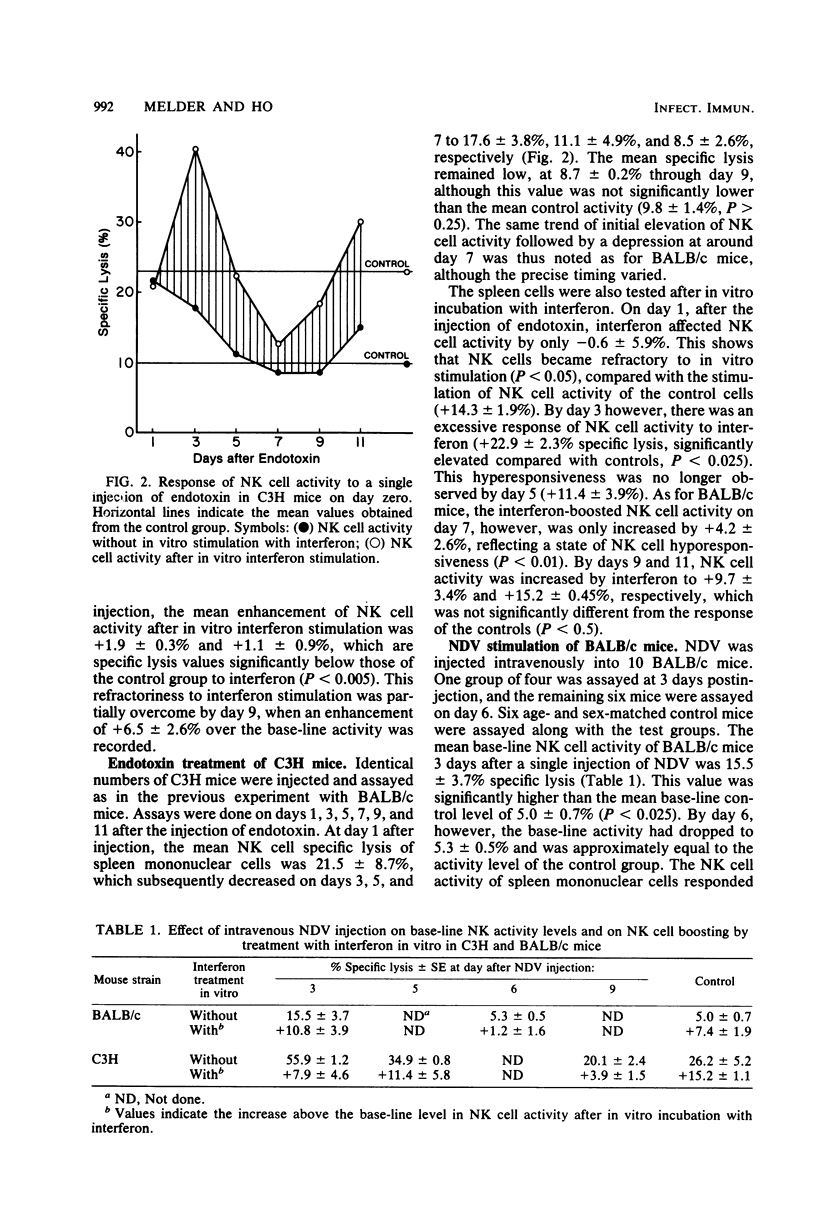
Splenic natural killer (NK) cell activity of BALB/c and C3H mice was assayed after administration of the interferon inducers Escherichia coli endotoxin or Newcastle disease virus (NDV). As expected, the NK cell activity rose early in response to the interferon inducers. At 1 to 3 days after an injection of endotoxin, NK activity was hyperesponsive to interferon stimulation. At 5 to 9 days after injection of either endotoxin or NDV, splenic NK activity was depressed, and the spleen cells showed a relative refractoriness to in vitro interferon stimulation. It is postulated that this phenomenon may be related to hyporeactivity, the inability to reinduce interferon after an initial period of interferon production.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A. Semi-micro, dye-binding assay for rabbit interferon. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):723–725. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.723-725.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARON S., BUCKLER C. E. CIRCULATING INTERFERON IN MICE AFTER INTRAVENOUS INJECTION OF VIRUS. Science. 1963 Sep 13;141(3585):1061–1063. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3585.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bancroft G. J., Shellam G. R., Chalmer J. E. Genetic influences on the augmentation of natural killer (NK) cells during murine cytomegalovirus infection: correlation with patterns of resistance. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):988–994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunda M. J., Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Inhibition of murine natural killer cell activity by prostaglandins. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2682–2687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudkowicz G., Hochman P. S. Do natural killer cells engage in regulated reactions against self to ensure homeostasis? Immunol Rev. 1979;44:13–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Heinbaugh J. A., Holden H. T., Herberman R. B. Augmentation of mouse natural killer cell activity by interferon and interferon inducers. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):175–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einhorn S., Blomgren H., Strander H. Interferon and spontaneous cytotoxicity in man. V. Enhancement of spontaneous cytotoxicity in patients receiving human leukocyte interferon. Int J Cancer. 1980 Oct 15;26(4):419–428. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910260406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidlund M., Orn A., Wigzell H., Senik A., Gresser I. Enhanced NK cell activity in mice injected with interferon and interferon inducers. Nature. 1978 Jun 29;273(5665):759–761. doi: 10.1038/273759a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Kuribayashi K., Kern D. E., Gillis S. Interleukin-2 augments natural killer cell activity. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):335–338. doi: 10.1038/291335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Djeu J., Kay H. D., Ortaldo J. R., Riccardi C., Bonnard G. D., Holden H. T., Fagnani R., Santoni A., Puccetti P. Natural killer cells: characteristics and regulation of activity. Immunol Rev. 1979;44:43–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M., Kono Y., Breinig M. K. Tolerance to the induction of interferons by endotoxin and virus: role of a humoral factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Aug-Sep;119(4):1227–1232. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Kunii A., Mori N., Nagata I. Effects of splenectomy on production of endotoxin-type interferon in mice. Virology. 1971 Jun;44(3):638–641. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90379-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuribayashi K., Gillis S., Kern D. E., Henney C. S. Murine NK cell cultures: effects of interleukin-2 and interferon on cell growth and cytotoxic reactivity. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2321–2327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M. J., Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Leary P. L., Zaia J. A., Hirsch M. S. Immune response to herpesvirus antigens in adults with acute cytomegaloviral mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):851–857. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macfarlan R. I., Ceredig R., White D. O. Comparison of natural killer cells induced by Kunjin virus and Corynebacterium parvum with those occurring naturally in nude mice. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):832–836. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.832-836.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoni A., Riccardi C., Sorci V., Herberman R. B. Effects of adriamycin on the activity of mouse natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2329–2335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savary C. A., Lotzová E. Suppression of natural killer cell cytotoxicity by splenocytes from Corynebacterium parvum-injected, bone marrow-tolerant, and infant mice. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):239–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senik A., Kolb J. P., Orn A., Gidlund M. Study of the mechanism for in vitro activation of mouse NK cells by interferon. Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(1):51–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringfellow D. A. Hyporeactivity to interferon induction: characterization of a hyporeactive factor in the serum of encephalomyocarditis virus-infected mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):294–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.294-302.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targan S. R. The dual interaction of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and interferon (IFN) on NK lytic activation: enhanced capacity of effector-target lytic interactions (recycling) and blockage of pre-NK cell recruitment. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1424–1428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey D. E., Adkinson N. F., Jr Prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors potentiate the BCG-induced augmentation of natural killer cell activity. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):136–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Jr Cytotoxic cells induced during lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection of mice. I. Characterization of natural killer cell induction. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):163–181. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe S. A., Tracey D. E., Henney C. S. Introduction of "natural" killer' cells by BCG. Nature. 1976 Aug 12;262(5569):584–586. doi: 10.1038/262584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling J. M., Schlais J., Eskra L., Greene J. J., Ts'o P. O., Carter W. A. Augmentation of human natural killer cell activity by polyinosinic acid-polycytidylic acid and its nontoxic mismatched analogues. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1852–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


