Abstract
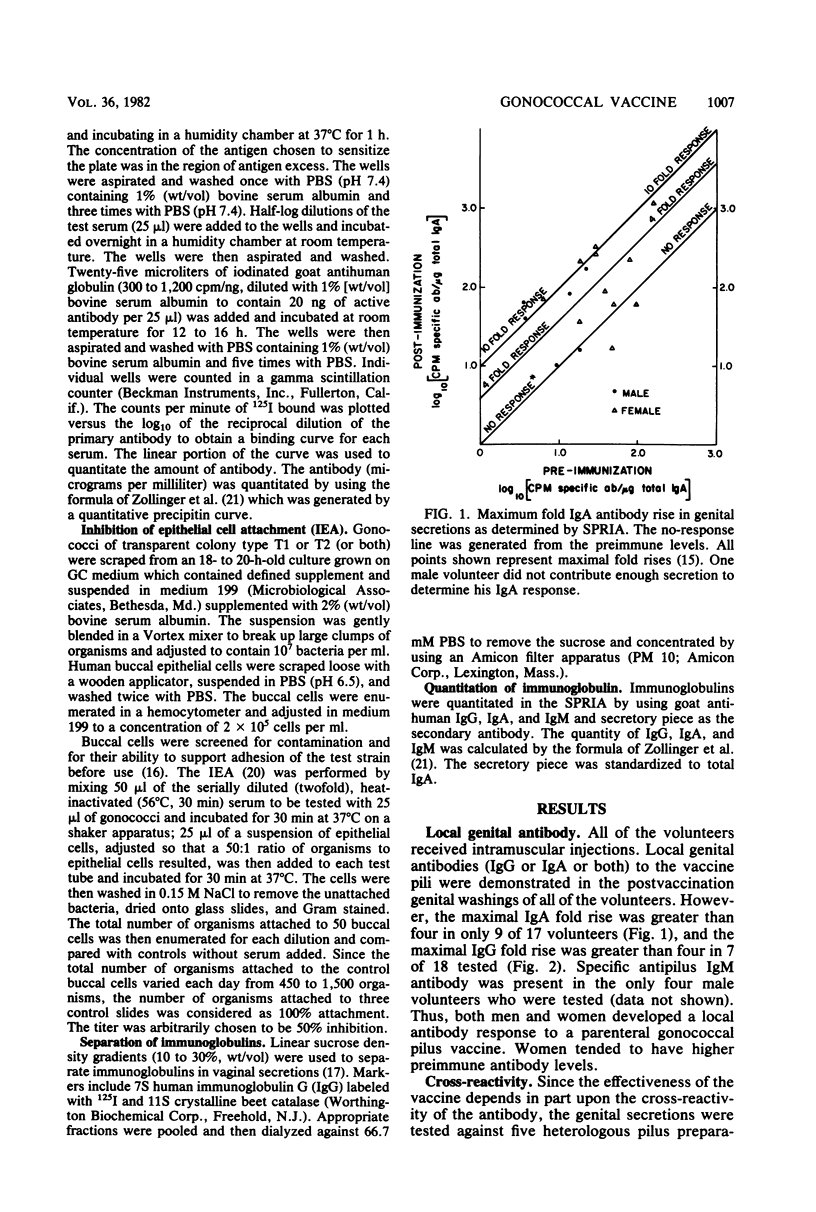
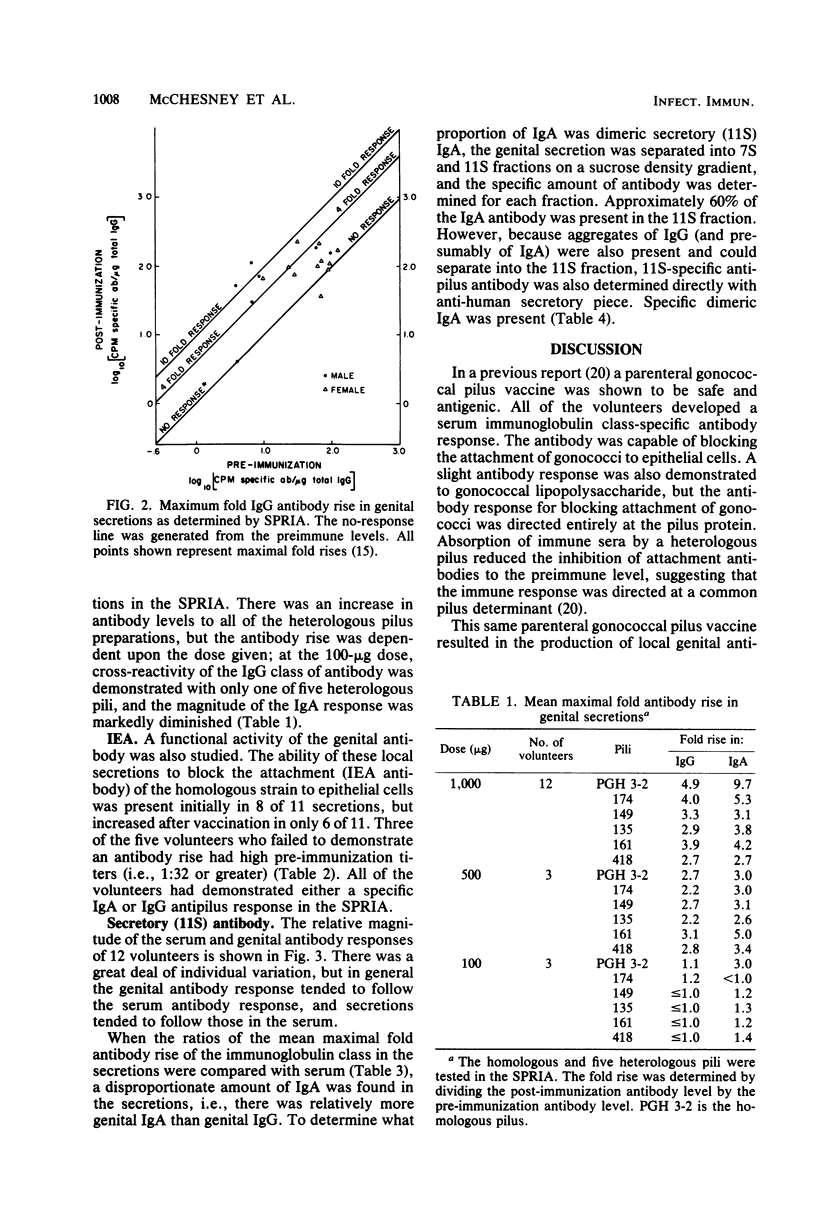
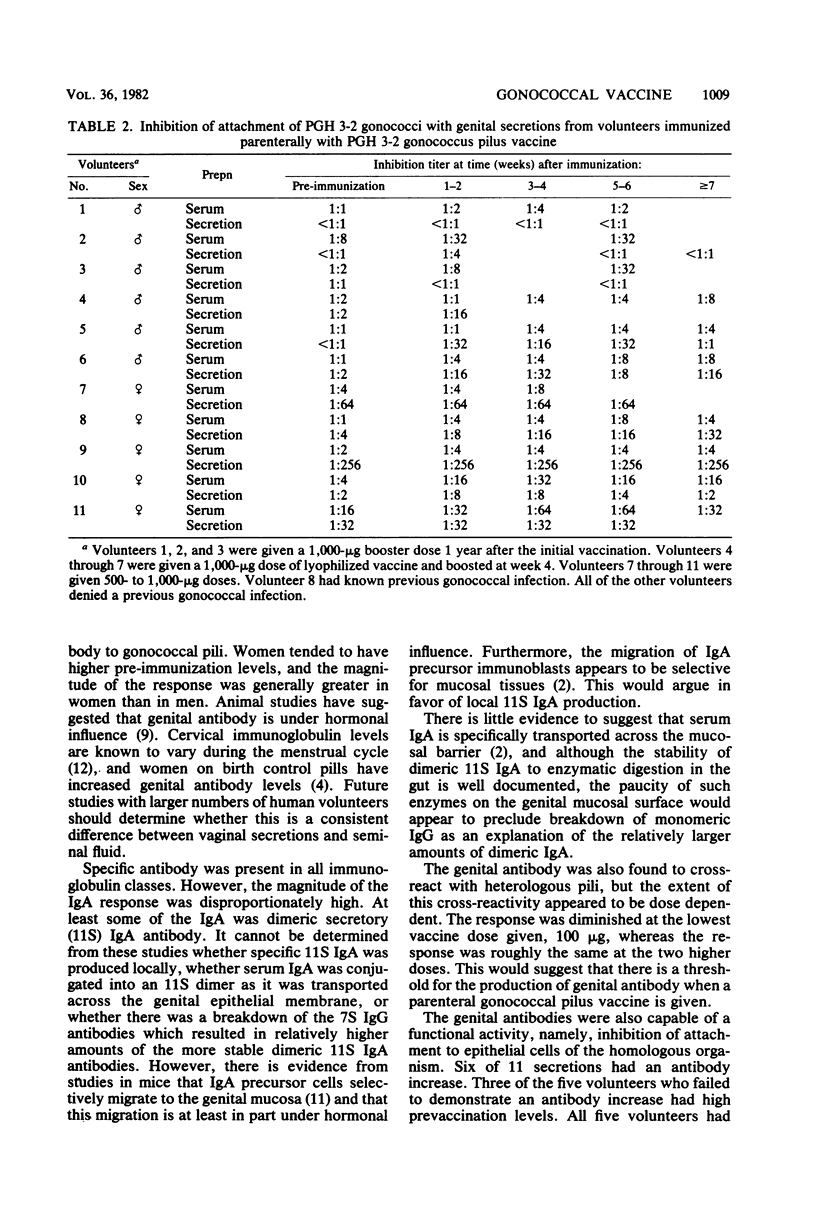
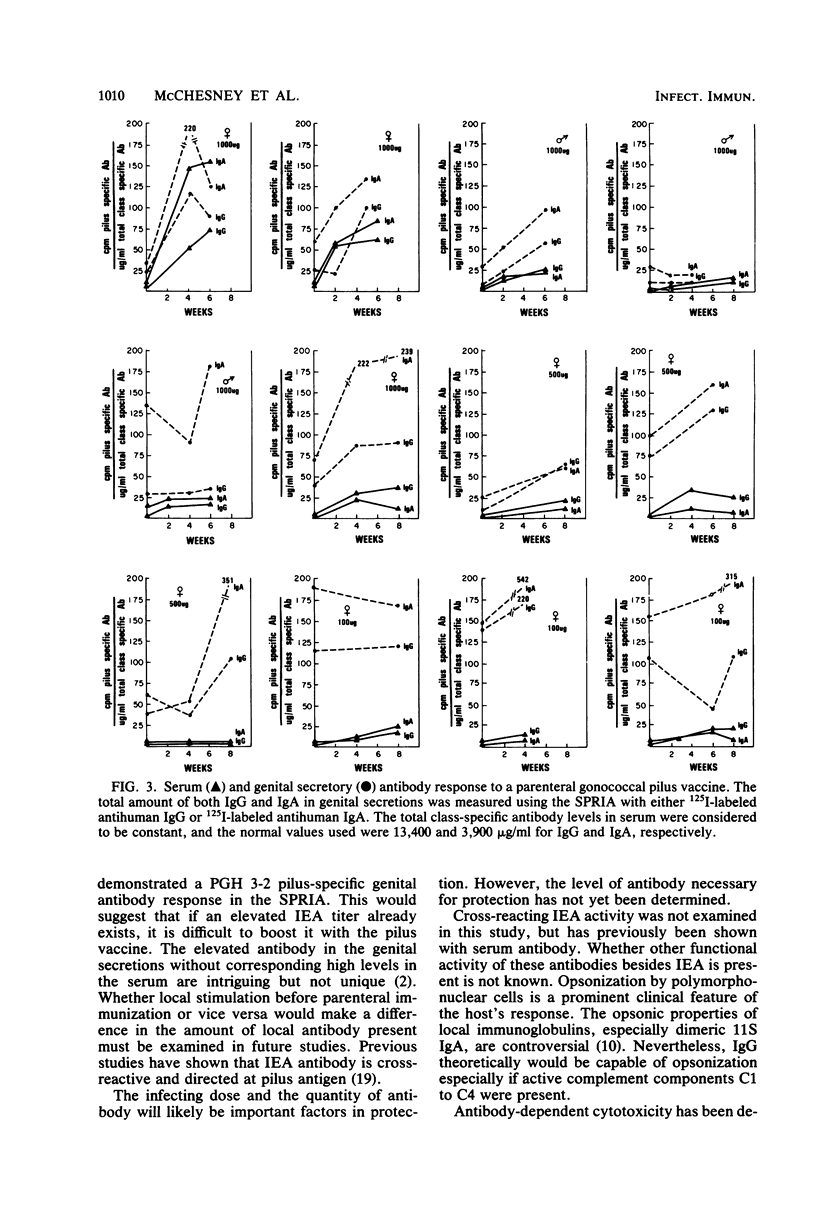
A parenteral gonococcal pilus vaccine which has previously been shown to be safe and antigenic also results in the production of specific local genital antibody. All three major antibody classes were present in the local secretions, but immunoglobulin A predominated, a portion of which is dimeric 11S immunoglobulin A. This mucosal antibody is also capable of blocking the attachment of gonococci to epithelial cells. The antibody cross-reacted with five heterologous pili in a solid-phase radioimmunoassay. These results are encouraging and suggest that a gonococcal pilus vaccine may be efficacious in preventing gonorrhea.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artenstein M. S., Gold R., Zimmerly J. G., Wyle F. A., Schneider H., Harkins C. Prevention of meningococcal disease by group C polysaccharide vaccine. N Engl J Med. 1970 Feb 19;282(8):417–420. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197002192820803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienenstock J., Befus A. D. Mucosal immunology. Immunology. 1980 Oct;41(2):249–270. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipperfield E. J., Evans B. A. Effect of local infection and oral contraception on immunoglobulin levels in cervical mucus. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):215–221. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.215-221.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner T., Challacombe S. J., Caldwell J. Oral immunization with Streptococcus mutants in rhesus monkeys and the development of immune response and dental caries. Immunology. 1980 Dec;41(4):857–864. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M. R., Bienenstock J. Evidence for a common mucosal immunologic system. I. Migration of B immunoblasts into intestinal, respiratory, and genital tissues. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1892–1898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M. R., Clark D. A., Bienenstock J. Evidence for a common mucosal immunologic system. II. Influence of the estrous cycle on B immunoblast migration into genital and intestinal tissues. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2536–2539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan A., McNeillage G., Young H. Antibodies to Neisseria gonorrhoeae: a study of the urethral exudates of 232 men. J Infect Dis. 1979 Jul;140(1):89–95. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. L., Isaacson R. E., Moon H. W., Brinton C. C., To C. C. Immunization of suckling pigs against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-induced diarrheal disease by vaccinating dams with purified 987 or K99 pili: protection correlates with pilus homology of vaccine and challenge. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):771–777. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.771-777.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B., Moon H. W., Isaacson R. E., To C. C., Brinton C. C. Immunization of suckling pigs against enteric enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection by vaccinating dams with purified pili. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):269–274. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.269-274.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce W. A., Buchanan T. M. Attachment role of gonococcal pili. Optimum conditions and quantitation of adherence of isolated pili to human cells in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):931–943. doi: 10.1172/JCI109018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siber G. R., Ransil B. J., Schiffman G. Graphical method for evaluating antibody response to vaccines. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):641–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.641-644.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Ciak J., Boslego J., McChesney D. G., Brinton C. C., Zollinger W. Antigenic specificity of antibodies in vaginal secretions during infection with Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jul;142(1):23–31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C. Inhibition of adherence of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by human genital secretions. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jan;59(1):117–124. doi: 10.1172/JCI108608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C., Sadoff J. C., Boslego J. W., Ciak J., McChesney D., Brinton C. C., Wood S., Takafuji E. Gonococcal pilus vaccine. Studies of antigenicity and inhibition of attachment. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):881–888. doi: 10.1172/JCI110343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramont E. C. Specificity of inhibition of epithelial cell adhesion of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1976 Aug;14(2):593–595. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.2.593-595.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Dalrymple J. M., Artenstein M. S. Analysis of parameters affecting the solid phase radioimmunoassay quantitation of antibody to meningococcal antigens. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1788–1798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


