Abstract
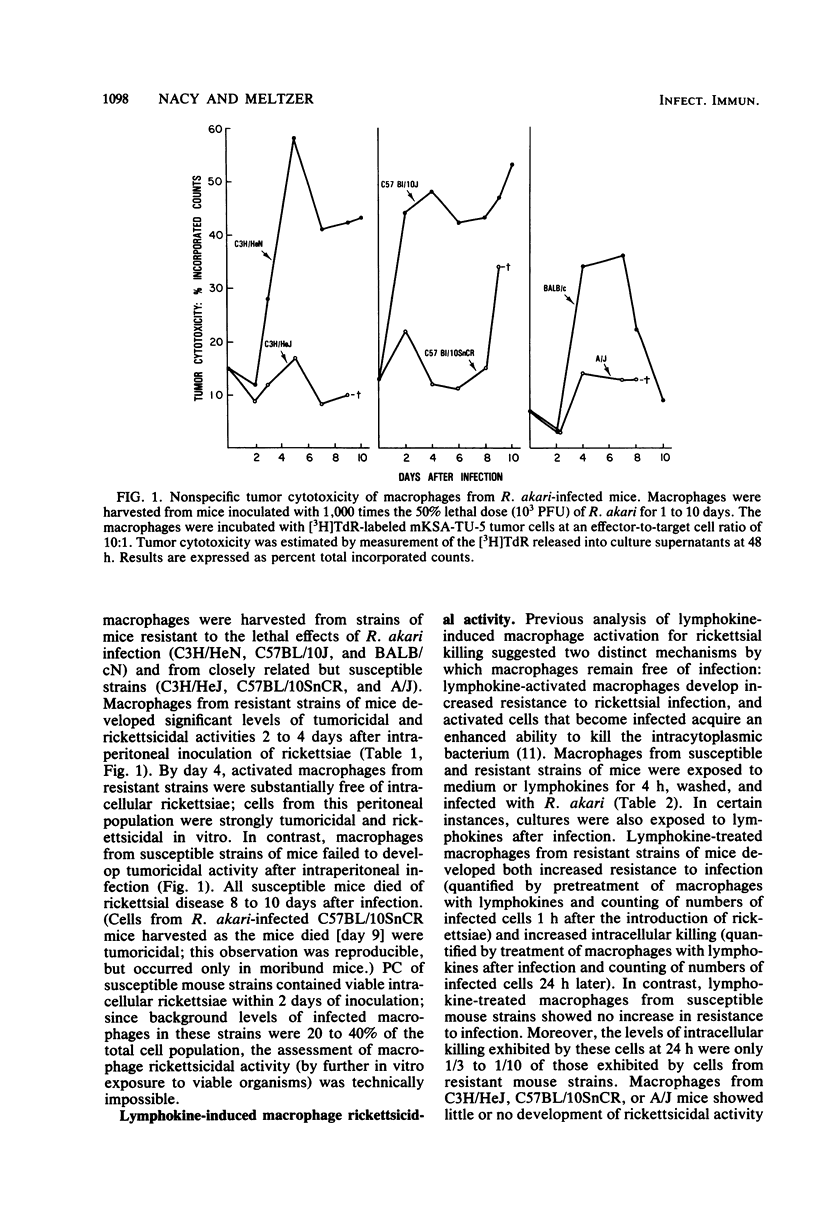
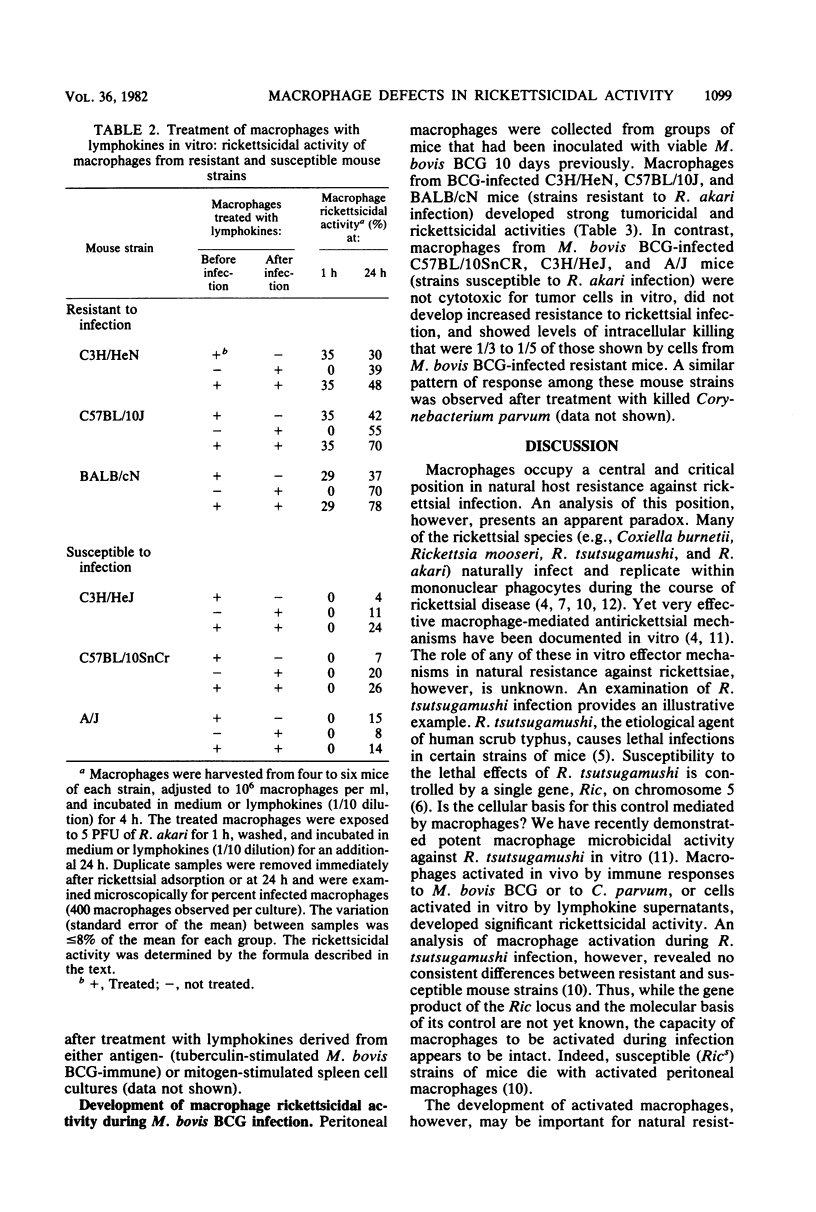
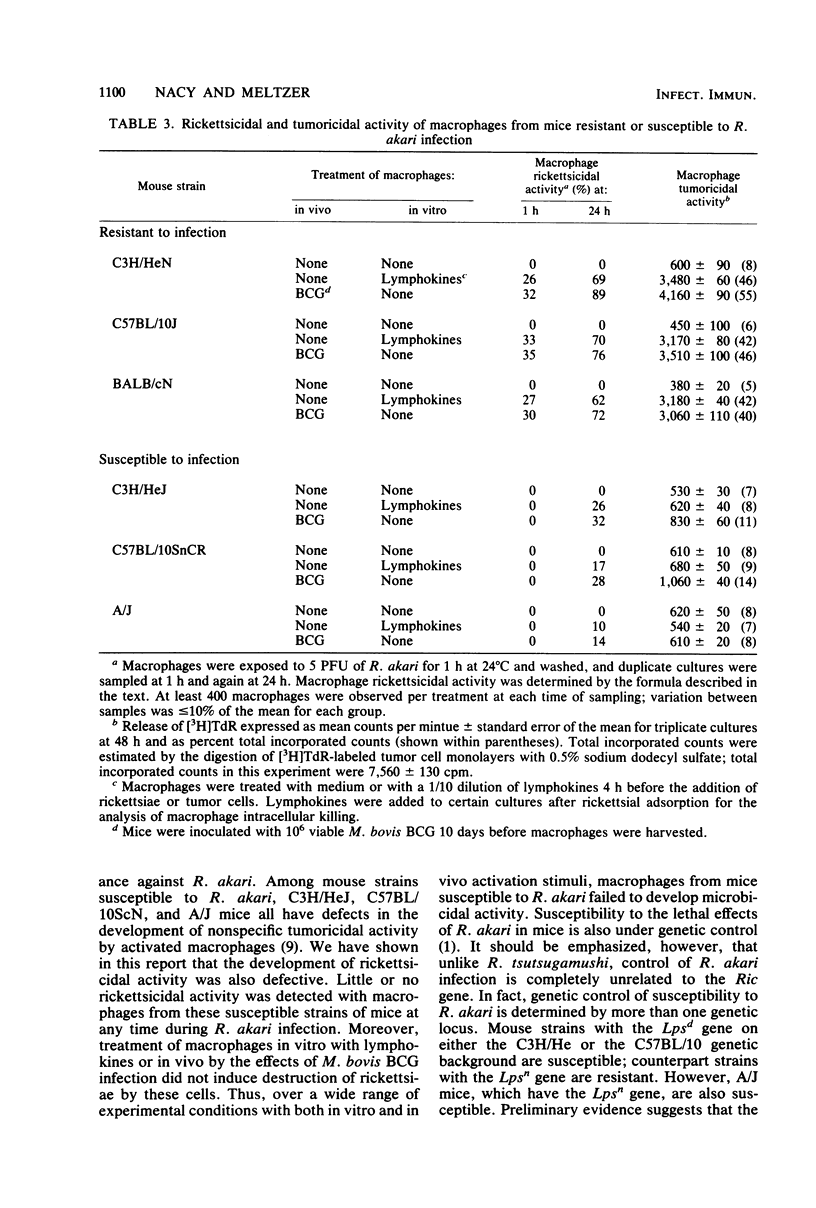
Activation of macrophages was assessed in strains of mice inoculated intraperitoneally with 1,000 times the 50% lethal dose of Rickettsia akari. Macrophages from mice resistant to R. akari infection (C3H/HeN, C57BL/10J, and BALB/cN) were nonspecifically tumoricidal 2 to 4 days after rickettsial inoculation. Moreover, these macrophages were microbial for R. akari in vitro; cells were resistant to infection with the bacterium and were capable of killing intracellular rickettsiae. In contrast, macrophages from strains of mice susceptible to R. akari (C3H/HeJ, C57BL/10SnCR, and A/J) failed to develop nonspecific tumoricidal activity over the course of lethal disease and became infected with R. akari in vivo within 2 days of rickettsial inoculation. Macrophages from uninfected mice of strains susceptible to R. akari also could not be activated for rickettsicidal or tumoricidal activities by treatment with macrophage-activating agents (Mycobacterium bovis BCG) in vivo or by treatment with lymphokines in vitro.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson G. W., Jr, Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental rickettsialpox: genetics of natural resistance to infection. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):132–136. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.132-136.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boraschi D., Meltzer M. S. Defective tumoricidal capacity of macrophages from A/J mice. II. Comparison of the macrophage cytotoxic defect of A/J mice with that of lipid A-unresponsive C3H/HeJ mice. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1592–1597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boraschi D., Meltzer M. S. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: genetic variation in macrophage tumoricidal capacity among mouse strains. Cell Immunol. 1979 Jun;45(1):188–194. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90375-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catanzaro P. J., Shirai A., Hilderbrandt P. K., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: histopathological correlates. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):861–875. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.861-875.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves M. G., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: genetics of natural resistance to infection. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):583–588. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.583-588.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves M. G., Rosenstreich D. L., Taylor B. A., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: mapping the gene that controls natural resistance in mice. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1395–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinrichs D. J., Jerrells T. R. In vitro evaluation of immunity to Coxiella burnetii. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):996–1003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S., Nacy C. A. Macrophages in resistance to rickettsial infection: susceptibility to lethal effects of Rickettsia akari infection in mouse strains with defective macrophage function. Cell Immunol. 1980 Sep 1;54(2):487–490. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90229-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Groves M. G. Macrophages in resistance to rickettsial infections: early host defense mechanisms in experimental scrub typhus. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1239–1250. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1239-1250.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Meltzer M. S. Macrophages in resistance to rickettsial infection: macrophage activation in vitro for killing of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2544–2549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: role of normal and activated macrophages. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):744–750. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.744-750.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks S. C., Jr, Osterman J. V., Hetrick F. M. Plaque assay and cloning of scrub typhus rickettsiae in irradiated L-929 cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jul;6(1):76–80. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.1.76-80.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. J., Lefford M. J. Induction of cell-mediated immunity to Mycobacterium leprae in mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):87–93. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.87-93.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Krahenbuhl J. L., Mendenhall J. W. A role for activated macrophages in resistance to infection with Toxoplasma. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):829–834. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.829-834.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruco L. P., Meltzer M. S. Defective tumoricidal capacity of macrophages from C3H/HeJ mice. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):329–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruco L. P., Meltzer M. S., Rosenstreich D. L. Macrophage activation for tumor cytotoxicity: control of macrophage tumoricidal capacity by the LPS gene. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartzberg J. E., Krahenbuhl J. L., Remington J. S. Dichotomy between macrophage activation and degree of protection against Listeria monocytogenes and Toxoplasma gondii in mice stimulated with Corynebacterium parvum. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):1037–1043. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.1037-1043.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Sawyer S., Remington J. S. Role of activated macrophages in resistance of mice to infection with Trypanosoma cruzi. J Infect Dis. 1976 Dec;134(6):610–623. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.6.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


