Abstract
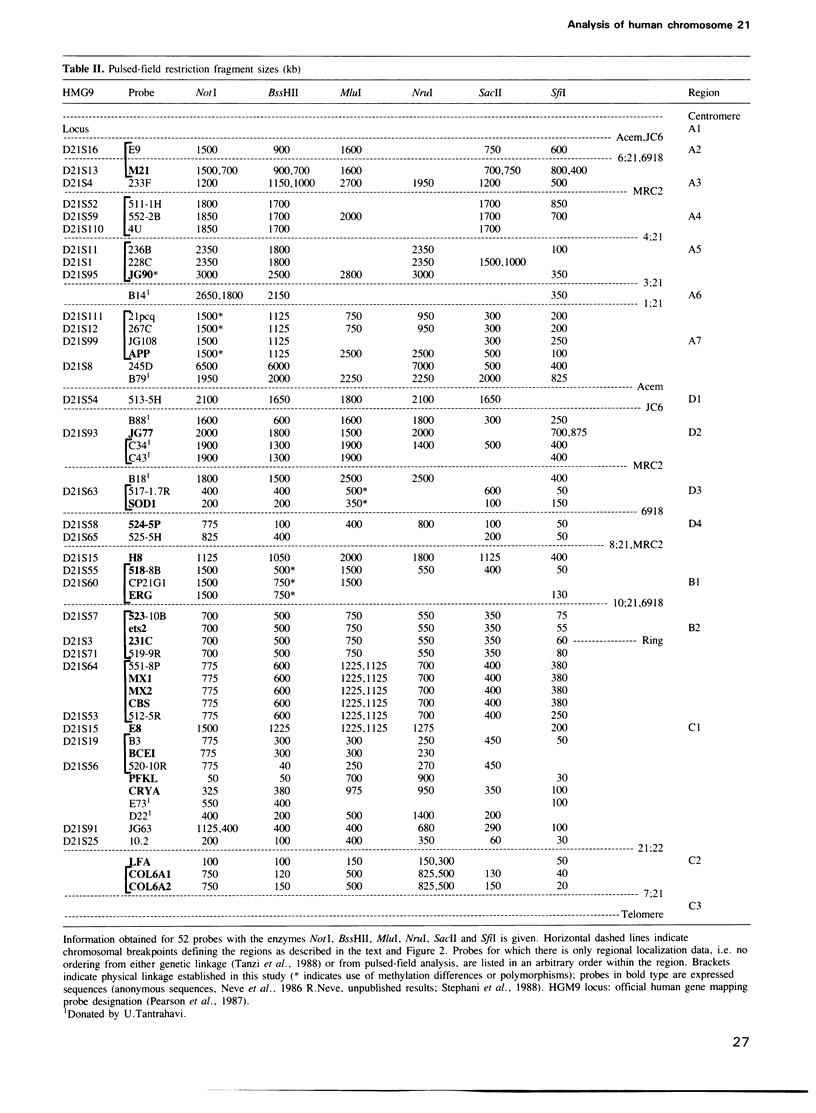
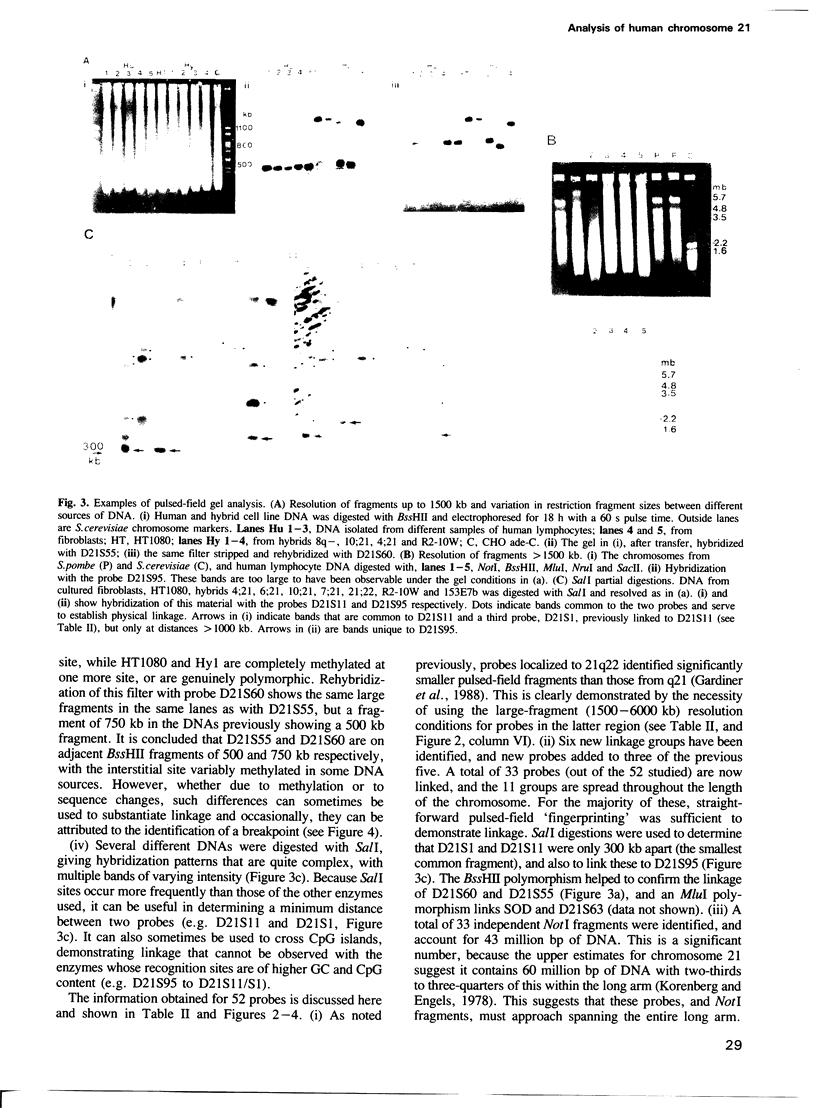
Human chromosome 21 has been analyzed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis using somatic cell hybrids containing limited regions of the chromosome and greater than 60 unique sequence probes. Thirty-three independent NotI fragments have been identified, totalling 43 million bp. This must account for essentially the entire long arm, and therefore gaps remaining in the map must be small. The extent of the pulsed-field map has allowed the direct correlation of the physical map with the cytogenetic map: translocation breakpoints can be unambiguously positioned along the long arm and the distances between them measured in base pairs. Three breakpoints have been identified, providing physical confirmation of cytogenetic landmarks. Information on sequence organization has been obtained: (i) 60% of the unique sequence probes are located within 11 physical linkage groups which can be contained in only 20% of the long arm; (ii) 9/21 genes are clustered within 4%; (iii) translocation breakpoints appear to occur within CpG island regions, making their identification difficult by pulsed-field techniques. This analysis contributes to the human genome mapping effort, and provides information to guide the rapid investigation of the biology of chromosome 21.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Wei J. F., Wei F. S., Hsu Y. C., Uehara H., Artzt K., Bennett D. Searching for coding sequences in the mammalian genome: the H-2K region of the mouse MHC is replete with genes expressed in embryos. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3441–3449. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03218.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allore R., O'Hanlon D., Price R., Neilson K., Willard H. F., Cox D. R., Marks A., Dunn R. J. Gene encoding the beta subunit of S100 protein is on chromosome 21: implications for Down syndrome. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1311–1313. doi: 10.1126/science.2964086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi G., Olofsson B., Filipski J., Zerial M., Salinas J., Cuny G., Meunier-Rotival M., Rodier F. The mosaic genome of warm-blooded vertebrates. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):953–958. doi: 10.1126/science.4001930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A., Taggart M., Frommer M., Miller O. J., Macleod D. A fraction of the mouse genome that is derived from islands of nonmethylated, CpG-rich DNA. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carritt B., Litt M. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of chromosomes 20 and 21. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;49(1-3):102–103. doi: 10.1159/000132660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadefaux B., Allard D., Rethoré M. O., Raoul O., Poissonnier M., Gilgenkrantz S., Cheruy C., Jérôme H. Assignment of human phosphoribosylglycinamide synthetase locus to region 21q221. Hum Genet. 1984;66(2-3):190–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00286599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E. Mechanisms of chromosome banding and implications for chromosome structure. Annu Rev Genet. 1978;12:25–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.12.120178.000325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. N., Taggart M. H., Bird A. P. Unmethylated domains in vertebrate DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):647–658. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drahovsky D., Boehm T. L., Kaul S., Wacker A. The persistence of chromosomes in somatic cell hybrids correlates with the enzymatic hypermethylation of their DNA. Int J Biochem. 1981;13(5):565–570. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(81)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend K. K., Chen S., Ruddle F. H. Differential staining of interspecific chromosomes in somatic cell hybrids by alkaline Giemsa stain. Somatic Cell Genet. 1976 Mar;2(2):183–188. doi: 10.1007/BF01542631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner-Garden M., Frommer M. CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):261–282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90689-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Laas W., Patterson D. Fractionation of large mammalian DNA restriction fragments using vertical pulsed-field gradient gel electrophoresis. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Mar;12(2):185–195. doi: 10.1007/BF01560665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Patterson D. Transverse alternating field electrophoresis and applications to mammalian genome mapping. Electrophoresis. 1989 May-Jun;10(5-6):296–302. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150100505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Watkins P., Münke M., Drabkin H., Jones C., Patterson D. Partial physical map of human chromosome 21. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Nov;14(6):623–637. doi: 10.1007/BF01535316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goate A. M., Haynes A. R., Owen M. J., Farrall M., James L. A., Lai L. Y., Mullan M. J., Roques P., Rossor M. N., Williamson R. Predisposing locus for Alzheimer's disease on chromosome 21. Lancet. 1989 Feb 18;1(8634):352–355. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91725-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. A., Holmquist G. P., Gray M. C., Caston L. A., Nag A. Replication timing of genes and middle repetitive sequences. Science. 1984 May 18;224(4650):686–692. doi: 10.1126/science.6719109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habedank M., Rodewald A. Moderate Down's syndrome in three siblings having partial trisomy 21q22.2 to qter and therefore no SOD-1 excess. Hum Genet. 1982;60(1):74–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00281269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins J. W., Van Keuren M. L., Piatigorsky J., Law M. L., Patterson D., Kao F. T. Confirmation of assignment of the human alpha 1-crystallin gene (CRYA1) to chromosome 21 with regional localization to q22.3. Hum Genet. 1987 Aug;76(4):375–380. doi: 10.1007/BF00272448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg M., Jonasson J. Preferential location of x-ray induced chromosome breakage in the R-bands of human chromosomes. Hereditas. 1973;74(1):57–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1973.tb01104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M. A., Wathelet M., Szpirer J., Szpirer C., Islam Q., Levan G., Huez G., Content J. cDNA cloning and assignment to chromosome 21 of IFI-78K gene, the human equivalent of murine Mx gene. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Mar;14(2):123–131. doi: 10.1007/BF01534397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Aota S. Global variation in G+C content along vertebrate genome DNA. Possible correlation with chromosome band structures. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins E. C., Duncan C. J., Wright C. E., Giordano F. M., Wilbur L., Wisniewski K., Sklower S. L., French J. H., Jones C., Brown W. T. Atypical Down syndrome and partial trisomy 21. Clin Genet. 1983 Aug;24(2):97–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1983.tb02219.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. K., O'Connor K., Lee A., Roberts T. M., Springer T. A. Cloning of the beta subunit of the leukocyte adhesion proteins: homology to an extracellular matrix receptor defines a novel supergene family. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90246-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Croyle M. L., Cox D. R. Isolation and regional mapping of DNA sequences unique to human chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Dec;41(6):963–978. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Engels W. R. Base ratio, DNA content, and quinacrine-brightness of human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3382–3386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Rykowski M. C. Human genome organization: Alu, lines, and the molecular structure of metaphase chromosome bands. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90159-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn E. M., Therman E., Denniston C. Mitotic chiasmata, gene density, and oncogenes. Hum Genet. 1985;70(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/BF00389448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levanon D., Danciger E., Dafni N., Groner Y. Construction of a cDNA clone containing the entire coding region of the human liver-type phosphofructokinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 30;147(3):1182–1187. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter P., Cremer T., Tang C. J., Watkins P. C., Manuelidis L., Ward D. C. Rapid detection of human chromosome 21 aberrations by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9664–9668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick M. K., Schinzel A., Petersen M. B., Stetten G., Driscoll D. J., Cantu E. S., Tranebjaerg L., Mikkelsen M., Watkins P. C., Antonarakis S. E. Molecular genetic approach to the characterization of the "Down syndrome region" of chromosome 21. Genomics. 1989 Aug;5(2):325–331. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitelman F., Heim S. Consistent involvement of only 71 of the 329 chromosomal bands of the human genome in primary neoplasia-associated rearrangements. Cancer Res. 1988 Dec 15;48(24 Pt 1):7115–7119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore E. E., Jones C., Kao F. T., Oates D. C. Synteny between glycinamide ribonucleotide synthetase and superoxide dismutase (soluble). Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Jul;29(4):389–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. G., Hays T., Patterson D., Robinson A. Giemsa-11 technique. Applications in the chromosomal characterization of hematologic specimens. Hum Genet. 1982;61(2):141–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00274204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M., McClelland M. The effect of site-specific methylation on restriction-modification enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987;15 (Suppl):r219–r230. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.suppl.r219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neve R. L., Stewart G. D., Newcomb P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Drabkin H. A., Kurnit D. M. Human chromosome 21-encoded cDNA clones. Gene. 1986;49(3):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90372-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Castillo A., Del Mazo J., Abrisqueta J. A. Three interesting cases of Down's syndrome. Ann Genet. 1983;26(2):123–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani Z., Blouin J. L., Creau-Goldberg N., Watkins P. C., Mattei J. F., Poissonnier M., Prieur M., Chettouh Z., Nicole A., Aurias A. Critical role of the D21S55 region on chromosome 21 in the pathogenesis of Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5958–5962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. N., Papas T. S., Reddy E. S. erg, a human ets-related gene on chromosome 21: alternative splicing, polyadenylation, and translation. Science. 1987 Aug 7;237(4815):635–639. doi: 10.1126/science.3299708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Riggs A. D. DNA methylation and gene function. Science. 1980 Nov 7;210(4470):604–610. doi: 10.1126/science.6254144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. H., Robakis N. K., Oster-Granite M. L., Wisniewski H. M., Coyle J. T., Gearhart J. D. Genetic linkage in the mouse of genes involved in Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease in man. Brain Res. 1987 Sep;388(3):215–221. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(87)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. F., Wyandt H. E., Kelly T. E. De novo 21q interstitial deletion in a retarded boy with ulno-fibular dysostosis. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Jan;20(1):173–180. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacchi N., Watson D. K., Guerts van Kessel A. H., Hagemeijer A., Kersey J., Drabkin H. D., Patterson D., Papas T. S. Hu-ets-1 and Hu-ets-2 genes are transposed in acute leukemias with (4;11) and (8;21) translocations. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):379–382. doi: 10.1126/science.3941901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L., Dafni N., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Groner Y. Nucleotide sequence and expression of human chromosome 21-encoded superoxide dismutase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5465–5469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shmookler Reis R. J., Goldstein S. Variability of DNA methylation patterns during serial passage of human diploid fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3949–3953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinet P. M., Couturier J., Dutrillaux B., Poissonnier M., Raoul O., Rethore M. O., Allard D., Lejeune J., Jerome H. Trisomie 21 et superoxyde dismutase-1 (IPO-A). Tentative de localisation sur la sous bande 21Q22.1. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jan;97:47–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90653-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefani L., Galt J., Palmer A., Affara N., Ferguson-Smith M., Nevin N. C. Expression of chromosome 21 specific sequences in normal and Down's syndrome tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):2885–2896. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.2885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. D., Harris P., Galt J., Ferguson-Smith M. A. Cloned DNA probes regionally mapped to human chromosome 21 and their use in determining the origin of nondisjunction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):4125–4132. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.4125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. D., Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F. RFLPS at the D21S19 locus of human chromosome 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):7168–7168. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.7168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tantravahi U., Stewart G. D., Van Keuren M., McNeil G., Roy S., Patterson D., Drabkin H., Lalande M., Kurnit D. M., Latt S. A. Isolation of DNA sequences on human chromosome 21 by application of a recombination-based assay to DNA from flow-sorted chromosomes. Hum Genet. 1988 Jul;79(3):196–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00366237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Haines J. L., Watkins P. C., Stewart G. D., Wallace M. R., Hallewell R., Wong C., Wexler N. S., Conneally P. M., Gusella J. F. Genetic linkage map of human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1988 Aug;3(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Keuren M. L., Stewart G. D., Bradley C. M., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L., Watkins P. C., Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Patterson D. Characterization of an unusual and complex chromosome 21 rearrangement using somatic cell genetics and cloned DNA probes. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Jul;33(3):369–375. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320330316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Keuren M. L., Watkins P. C., Drabkin H. A., Jabs E. W., Gusella J. F., Patterson D. Regional localization of DNA sequences on chromosome 21 using somatic cell hybrids. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Jun;38(6):793–804. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren A. C., Slaugenhaupt S. A., Lewis J. G., Chakravarti A., Antonarakis S. E. A genetic linkage map of 17 markers on human chromosome 21. Genomics. 1989 May;4(4):579–591. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90282-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. C., Tanzi R. E., Gibbons K. T., Tricoli J. V., Landes G., Eddy R., Shows T. B., Gusella J. F. Isolation of polymorphic DNA segments from human chromosome 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6075–6088. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil D., Mattei M. G., Passage E., N'Guyen V. C., Pribula-Conway D., Mann K., Deutzmann R., Timpl R., Chu M. L. Cloning and chromosomal localization of human genes encoding the three chains of type VI collagen. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Mar;42(3):435–445. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Stetten G., Earnshaw W. C., Van Keuren M. L., Antonarakis S. E. Molecular mechanism in the formation of a human ring chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1914–1918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J. Mid-prophase human chromosomes. The attainment of 2000 bands. Hum Genet. 1981;56(3):293–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00274682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial M., Salinas J., Filipski J., Bernardi G. Gene distribution and nucleotide sequence organization in the human genome. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 3;160(3):479–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]