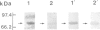Abstract
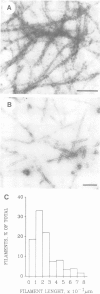
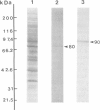
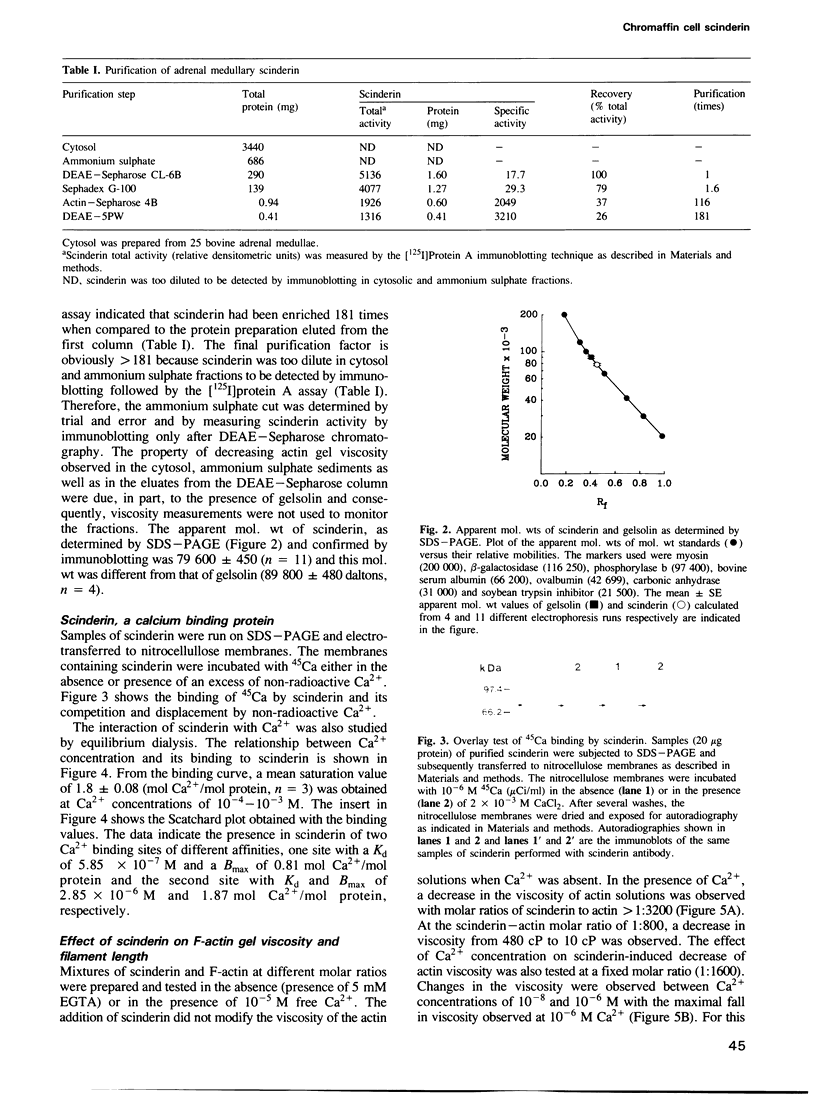
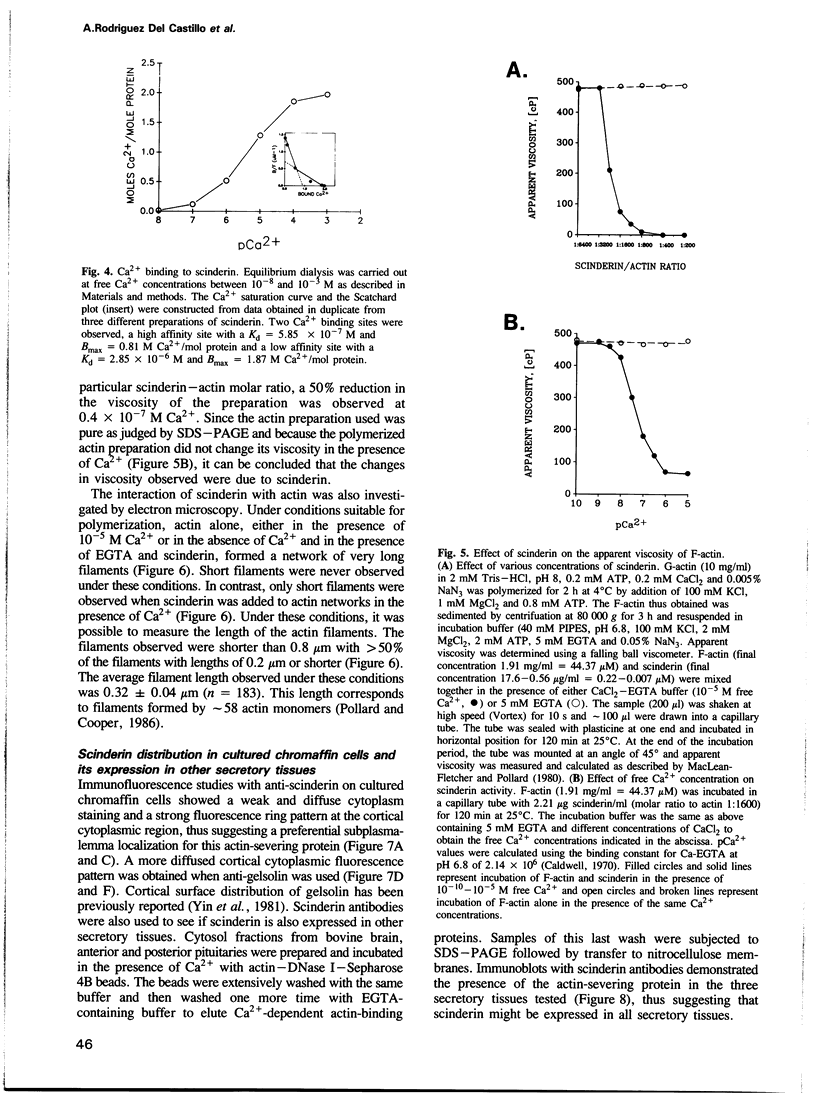
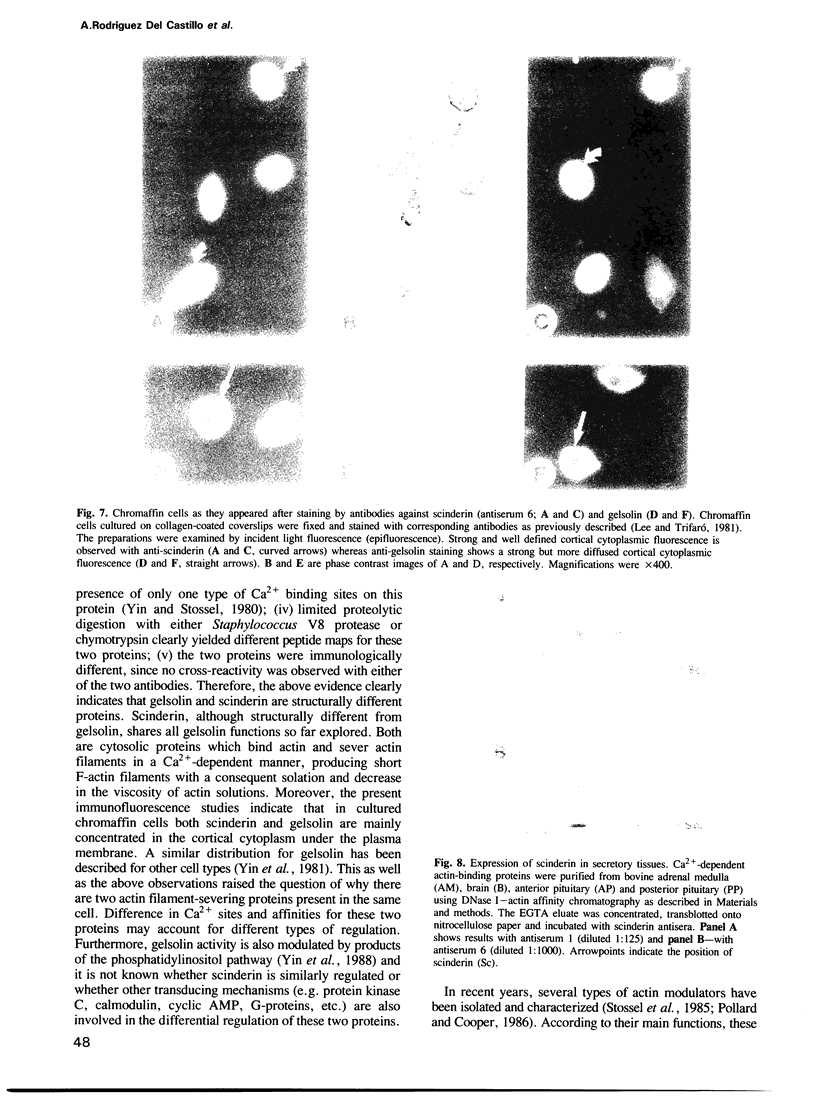
Scinderin, a novel Ca2+-activated actin filament-severing protein, has been purified to homogeneity from bovine adrenal medulla using a combination of several chromatographic procedures. The protein has an apparent mol. wt of 79,600 +/- 450 daltons, three isoforms (pIs 6.0, 6.1 and 6.2) and two Ca2+ binding sites (Kd 5.85 x 10(-7) M, Bmax 0.81 mol Ca2+/mol protein and Kd 2.85 x 10(-6) M, Bmax 1.87 mol Ca2+/mol protein). Scinderin interacts with F-actin in the presence of Ca2+ and produces a decrease in the viscosity of actin gels as a result of F-actin filament severing as demonstrated by electron microscopy. Scinderin is a structurally different protein from chromaffin cell gelsolin, another actin filament-severing protein described. Scinderin and gelsolin have different mol. wts, isoelectric points, amino acid composition and yield different peptide maps after limited proteolytic digestion by either Staphylococcus V8 protease or chymotrypsin. Moreover, scinderin antibodies do not cross-react with gelsolin and gelsolin antibodies fail to recognize scinderin. Immunofluorescence with anti-scinderin demonstrated that this protein is mainly localized in the subplasmalemma region of the chromaffin cell. Immunoblotting tests with the same antibodies indicated that scinderin is also expressed in brain and anterior as well as posterior pituitary. Presence of scinderin and gelsolin, two Ca2+-dependent actin filament-severing proteins in the same tissue, suggests the possibility of synergistic functions by the two proteins in the control of cellular actin filament networks. Alternatively, the actin filament-severing activity of the two proteins might be under the control of different transduction and modulating influences.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashino N., Sobue K., Seino Y., Yabuuchi H. Purification of an 80 kDa Ca2+-dependent actin-modulating protein, which severs actin filaments, from bovine adrenal medulla. J Biochem. 1987 Mar;101(3):609–617. doi: 10.1093/jb/101.3.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aunis D., Guerold B., Bader M. F., Cieselski-Treska J. Immunocytochemical and biochemical demonstration of contractile proteins in chromaffin cells in culture. Neuroscience. 1980;5(12):2261–2277. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aunis D., Perrin D. Chromaffin granule membrane-F-actin interactions and spectrin-like protein of subcellular organelles: a possible relationship. J Neurochem. 1984 Jun;42(6):1558–1569. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb12742.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader M. F., Trifaró J. M., Langley O. K., Thiersé D., Aunis D. Secretory cell actin-binding proteins: identification of a gelsolin-like protein in chromaffin cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):636–646. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. The membrane skeleton of human erythrocytes and its implications for more complex cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:273–304. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidlingmeyer B. A., Cohen S. A., Tarvin T. L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 7;336(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Villin is a major protein of the microvillus cytoskeleton which binds both G and F actin in a calcium-dependent manner. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., Burgoyne R. D. Cyclic AMP inhibits both nicotine-induced actin disassembly and catecholamine secretion from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11663–11666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., Burgoyne R. D. Nicotine-evoked disassembly of cortical actin filaments in adrenal chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 20;207(1):110–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doucet J. P., Trifaró J. M. A discontinuous and highly porous sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide slab gel system of high resolution. Anal Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;168(2):265–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90317-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Burridge K. A rapid purification of alpha-actinin, filamin, and a 130,000-dalton protein from smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1194–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier S., Novas M. L., Trifaró J. M. Subcellular distribution of 65,000 calmodulin-binding protein (p65) and synaptophysin (p38) in adrenal medulla. J Neurochem. 1989 Oct;53(4):1043–1049. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier S., Trifaró J. M. A similar calmodulin-binding protein expressed in chromaffin, synaptic, and neurohypophyseal secretory vesicles. J Neurochem. 1988 Jan;50(1):27–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb13225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler V. M., Pollard H. B. Chromaffin granule membrane-F-actin interactions are calcium sensitive. Nature. 1982 Jan 28;295(5847):336–339. doi: 10.1038/295336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumet M., Lin S. Purification and characterization of an inhibitor protein with cytochalasin-like activity from bovine adrenal medulla. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 18;678(3):381–387. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Stossel T. P. Isolation and properties of actin, myosin, and a new actinbinding protein in rabbit alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5696–5705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa T., Takahashi S., Hayashi H., Hatano S. Fragmin: a calcium ion sensitive regulatory factor on the formation of actin filaments. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2677–2683. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hincke M. T. Conditions for improved adsorption of calmodulin to nitrocellulose: detection by 45Ca binding. Electrophoresis. 1988 Jul;9(7):303–306. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150090704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenigsberg R. L., Trifaró J. M. Microinjection of calmodulin antibodies into cultured chromaffin cells blocks catecholamine release in response to stimulation. Neuroscience. 1985 Jan;14(1):335–347. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Janmey P. A., Mole J. E., Yin H. L. Isolation and properties of two actin-binding domains in gelsolin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15232–15238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. W., Mushynski W. E., Trifaró J. M. Two forms of cytoplasmic actin in adrenal chromaffin cells. Neuroscience. 1979;4(6):843–852. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean-Fletcher S. D., Pollard T. D. Viscometric analysis of the gelation of Acanthamoeba extracts and purification of two gelation factors. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):414–428. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannherz H. G., Leigh J. B., Leberman R., Pfrang H. A specific 1:1 G-actin:DNAase i complex formed by the action of DNAase I on F-actin. FEBS Lett. 1975 Dec 1;60(1):34–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80412-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter K., Dreyer F., Aktories K. Actin involvement in exocytosis from PC12 cells: studies on the influence of botulinum C2 toxin on stimulated noradrenaline release. J Neurochem. 1989 Feb;52(2):370–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09131.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. A practical computer-based approach to the analysis of radioligand binding experiments. Comput Programs Biomed. 1983 Aug-Oct;17(1-2):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(83)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyström L. E., Lindberg U., Kendrick-Jones J., Jakes R. The amino acid sequence of profilin from calf spleen. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 1;101(1):161–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81317-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overall C. M. A microtechnique for dialysis of small volume solutions with quantitative recoveries. Anal Biochem. 1987 Aug 15;165(1):208–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90221-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee J. D., Spudich J. A. Purification of muscle actin. Methods Cell Biol. 1982;24:271–289. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60661-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrucci T. C., Thomas C., Bray D. Isolation of a Ca2+-dependent actin-fragmenting protein from brain, spinal cord, and cultured neurones. J Neurochem. 1983 Jun;40(6):1507–1516. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb08119.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Actin and actin-binding proteins. A critical evaluation of mechanisms and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:987–1035. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. D., Strang-Brown P., Walker P. L., Iida S. Ca2+ binding to calmodulin. Methods Enzymol. 1983;102:135–143. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)02014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Chaponnier C., Ezzell R. M., Hartwig J. H., Janmey P. A., Kwiatkowski D. J., Lind S. E., Smith D. B., Southwick F. S., Yin H. L. Nonmuscle actin-binding proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:353–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifaró J. M., Bader M. F., Doucet J. P. Chromaffin cell cytoskeleton: its possible role in secretion. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;63(6):661–679. doi: 10.1139/o85-084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifaró J. M., Kenigsberg R. L., Côté A., Lee R. W., Hikita T. Adrenal paraneurone contractile proteins and stimulus-secretion coupling. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1984 Apr;62(4):493–501. doi: 10.1139/y84-079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Ash J. F., Singer S. J. Filamin, a new high-molecular-weight protein found in smooth muscle and non-muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4483–4486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Albrecht J. H., Fattoum A. Identification of gelsolin, a Ca2+-dependent regulatory protein of actin gel-sol transformation, and its intracellular distribution in a variety of cells and tissues. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):901–906. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Iida K., Janmey P. A. Identification of a polyphosphoinositide-modulated domain in gelsolin which binds to the sides of actin filaments. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):805–812. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. Control of cytoplasmic actin gel-sol transformation by gelsolin, a calcium-dependent regulatory protein. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):583–586. doi: 10.1038/281583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. Purification and structural properties of gelsolin, a Ca2+-activated regulatory protein of macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9490–9493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]