Abstract
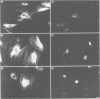
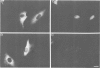
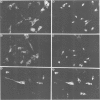
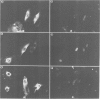
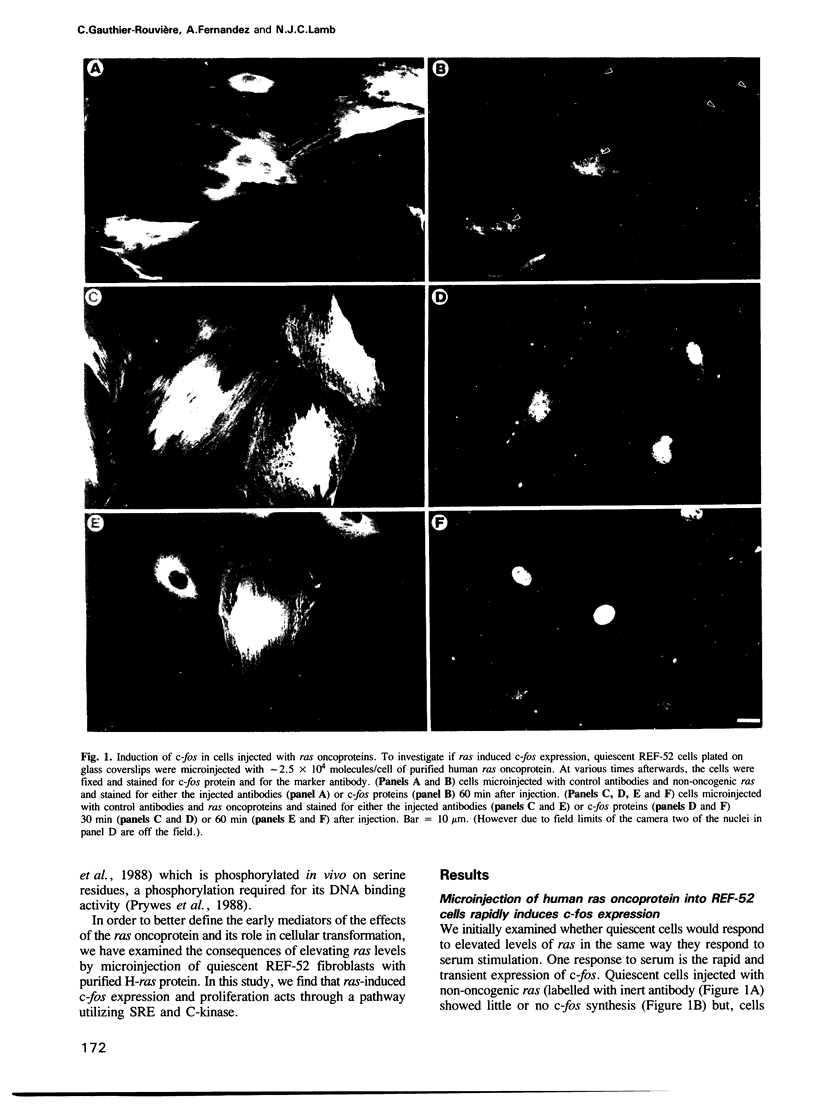
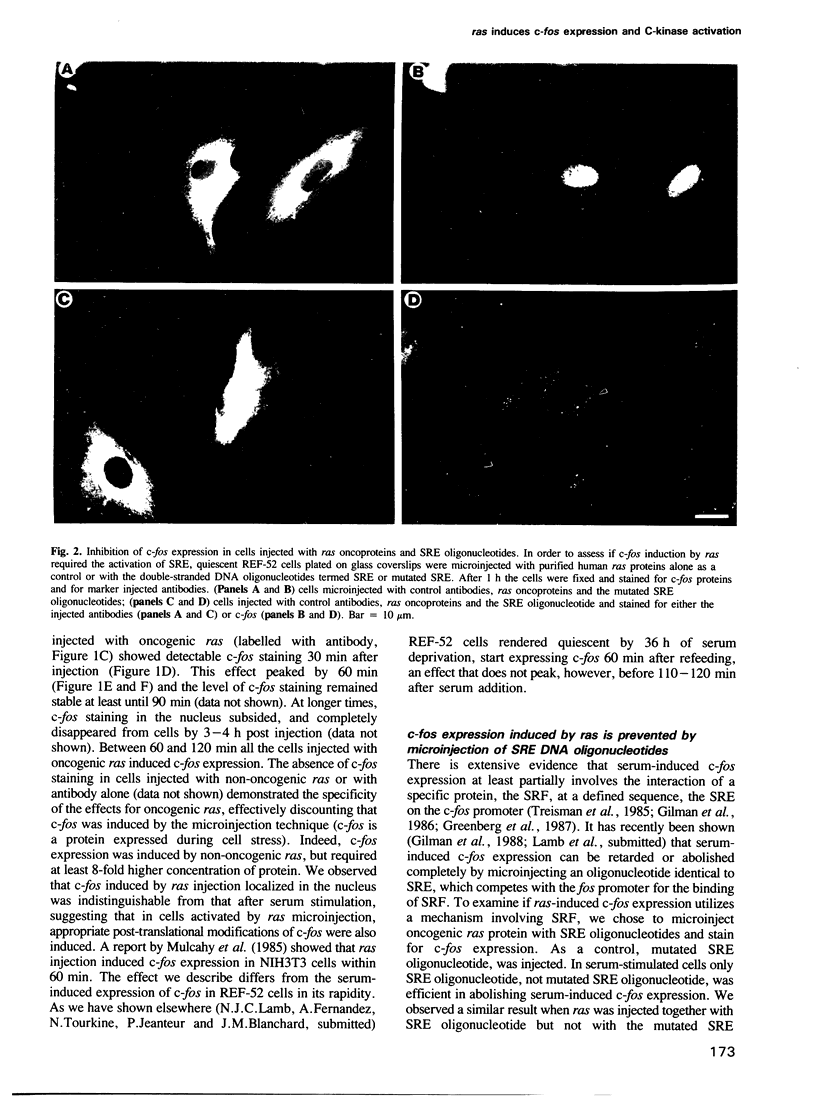
We have examined the early events involved in the proliferative activation of quiescent rat embryo fibroblasts by microinjection of oncogenic ras protein. Cells injected with ras show a transient expression of c-fos after 30-60 min visualized by immunofluorescence in the nucleus. This c-fos expression can be specifically suppressed by coinjection of a double-stranded oligonucleotide which corresponds to the serum response element (SRE) present in the c-fos promoter, implying that ras utilizes a pathway which activates the binding of serum response factor(s) (SRF) to SRE to induce c-fos transcription. Inhibition of this pathway also abolished ras-induced DNA synthesis indicating that the proliferative induction by ras requires expression of SRE-regulated genes. Both c-fos induction and DNA synthesis were prevented when ras oncoprotein was injected into quiescent cells together with either antibodies against calcium phospholipid-dependent protein kinase (C-kinase) or a synthetic peptide that specifically inhibits C-kinase. These data demonstrate the involvement of both functional C-kinase and the SRE pathway in the activation of quiescent cells by ras and suggest a potential relationship in their mechanism of action.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckner S. K., Hattori S., Shih T. Y. The ras oncogene product p21 is not a regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):71–72. doi: 10.1038/317071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berggren P. O., Hallberg A., Welsh N., Arkahammar P., Nilsson T., Welsh M. Transfection of insulin-producing cells with a transforming c-Ha-ras oncogene stimulates phospholipase C activity. Biochem J. 1989 May 1;259(3):701–707. doi: 10.1042/bj2590701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackshear P. J., Wen L., Glynn B. P., Witters L. A. Protein kinase C-stimulated phosphorylation in vitro of a Mr 80,000 protein phosphorylated in response to phorbol esters and growth factors in intact fibroblasts. Distinction from protein kinase C and prominence in brain. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1459–1469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büscher M., Rahmsdorf H. J., Litfin M., Karin M., Herrlich P. Activation of the c-fos gene by UV and phorbol ester: different signal transduction pathways converge to the same enhancer element. Oncogene. 1988 Sep;3(3):301–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Gross M., Kamata T., Rosenberg M., Sweet R. W. Microinjection of the oncogene form of the human H-ras (T-24) protein results in rapid proliferation of quiescent cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch T. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G. c-fos sequence necessary for basal expression and induction by epidermal growth factor, 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate and the calcium ionophore. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3490–3502. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischman L. F., Chahwala S. B., Cantley L. ras-transformed cells: altered levels of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate and catabolites. Science. 1986 Jan 24;231(4736):407–410. doi: 10.1126/science.3001936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Berkowitz L. A., Feramisco J. R., Franza B. R., Jr, Graham R. M., Riabowol K. T., Ryan W. A., Jr Intracellular mediators of c-fos induction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):761–767. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z. The c-fos serum response element responds to protein kinase C-dependent and -independent signals but not to cyclic AMP. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):394–402. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman M. Z., Wilson R. N., Weinberg R. A. Multiple protein-binding sites in the 5'-flanking region regulate c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4305–4316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Siegfried Z., Ziff E. B. Mutation of the c-fos gene dyad symmetry element inhibits serum inducibility of transcription in vivo and the nuclear regulatory factor binding in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1217–1225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- House C., Kemp B. E. Protein kinase C contains a pseudosubstrate prototope in its regulatory domain. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1726–1728. doi: 10.1126/science.3686012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao W. L., Housey G. M., Johnson M. D., Weinstein I. B. Cells that overproduce protein kinase C are more susceptible to transformation by an activated H-ras oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2641–2647. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. P., Nakabayashi H., Huang F. L. Isozymic forms of rat brain Ca2+-activated and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8535–8539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imler J. L., Schatz C., Wasylyk C., Chatton B., Wasylyk B. A Harvey-ras responsive transcription element is also responsive to a tumour-promoter and to serum. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):275–278. doi: 10.1038/332275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., Fleming T. P., Warren B. S., Blumberg P. M., Aaronson S. A. Involvement of functional protein kinase C in the mitogenic response to the H-ras oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4146–4149. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., Moscat J., Aaronson S. A. Novel source of 1,2-diacylglycerol elevated in cells transformed by Ha-ras oncogene. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):269–272. doi: 10.1038/330269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb N. J., Fernandez A., Conti M. A., Adelstein R., Glass D. B., Welch W. J., Feramisco J. R. Regulation of actin microfilament integrity in living nonmuscle cells by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase and the myosin light chain kinase. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1955–1971. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd A. C., Paterson H. F., Morris J. D., Hall A., Marshall C. J. p21H-ras-induced morphological transformation and increases in c-myc expression are independent of functional protein kinase C. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1099–1104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03479.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T., Garrett N., Treisman R. Xenopus cytoskeletal actin and human c-fos gene promoters share a conserved protein-binding site. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):667–673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. D., Price B., Lloyd A. C., Self A. J., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Scrape-loading of Swiss 3T3 cells with ras protein rapidly activates protein kinase C in the absence of phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Oncogene. 1989 Jan;4(1):27–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy L. S., Smith M. R., Stacey D. W. Requirement for ras proto-oncogene function during serum-stimulated growth of NIH 3T3 cells. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):241–243. doi: 10.1038/313241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman C., Runswick M., Pollock R., Treisman R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):989–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Dutta A., Cromlish J. A., Roeder R. G. Phosphorylation of serum response factor, a factor that binds to the serum response element of the c-FOS enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7206–7210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Roeder R. G. Inducible binding of a factor to the c-fos enhancer. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):777–784. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90520-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Roeder R. G. Purification of the c-fos enhancer-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3482–3489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K. T., Vosatka R. J., Ziff E. B., Lamb N. J., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection of fos-specific antibodies blocks DNA synthesis in fibroblast cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1670–1676. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Pena A., Rozengurt E. Phosphorylation of an acidic mol. wt. 80 000 cellular protein in a cell-free system and intact Swiss 3T3 cells: a specific marker of protein kinase C activity. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):77–83. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04180.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Early signals in the mitogenic response. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):161–166. doi: 10.1126/science.3018928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambucetti L. C., Curran T. The Fos protein complex is associated with DNA in isolated nuclei and binds to DNA cellulose. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1417–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.3491427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Der C. J., Verma I. M. ras-induced neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells: possible involvement of fos and jun. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3174–3183. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seuwen K., Lagarde A., Pouysségur J. Deregulation of hamster fibroblast proliferation by mutated ras oncogenes is not mediated by constitutive activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):161–168. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02796.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Dougan S. T., McFadden G., Greenberg M. E. Calcium and growth factor pathways of c-fos transcriptional activation require distinct upstream regulatory sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2787–2796. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Watson T., Kung H. F., Curran T. Microinjection of transforming ras protein induces c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):523–527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpo D. J., Stewart T. N., Gilman M. Z., Blackshear P. J. Identification of c-fos sequences involved in induction by insulin and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1611–1614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabin C. J., Bradley S. M., Bargmann C. I., Weinberg R. A., Papageorge A. G., Scolnick E. M., Dhar R., Lowy D. R., Chang E. H. Mechanism of activation of a human oncogene. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):143–149. doi: 10.1038/300143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification and purification of a polypeptide that binds to the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2711–2717. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E. The molecular genetics of cellular oncogenes. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:553–612. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.003005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrier B., Müller D., Bravo R., Müller R. Wounding a fibroblast monolayer results in the rapid induction of the c-fos proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):913–917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04303.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Davies S. A., Houslay M. D., McKay I., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Normal p21N-ras couples bombesin and other growth factor receptors to inositol phosphate production. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):173–176. doi: 10.1038/323173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfman A., Macara I. G. Elevated levels of diacylglycerol and decreased phorbol ester sensitivity in ras-transformed fibroblasts. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):359–361. doi: 10.1038/325359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]