Abstract
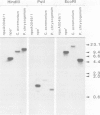
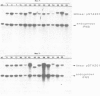
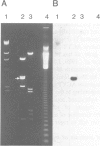
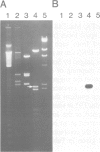
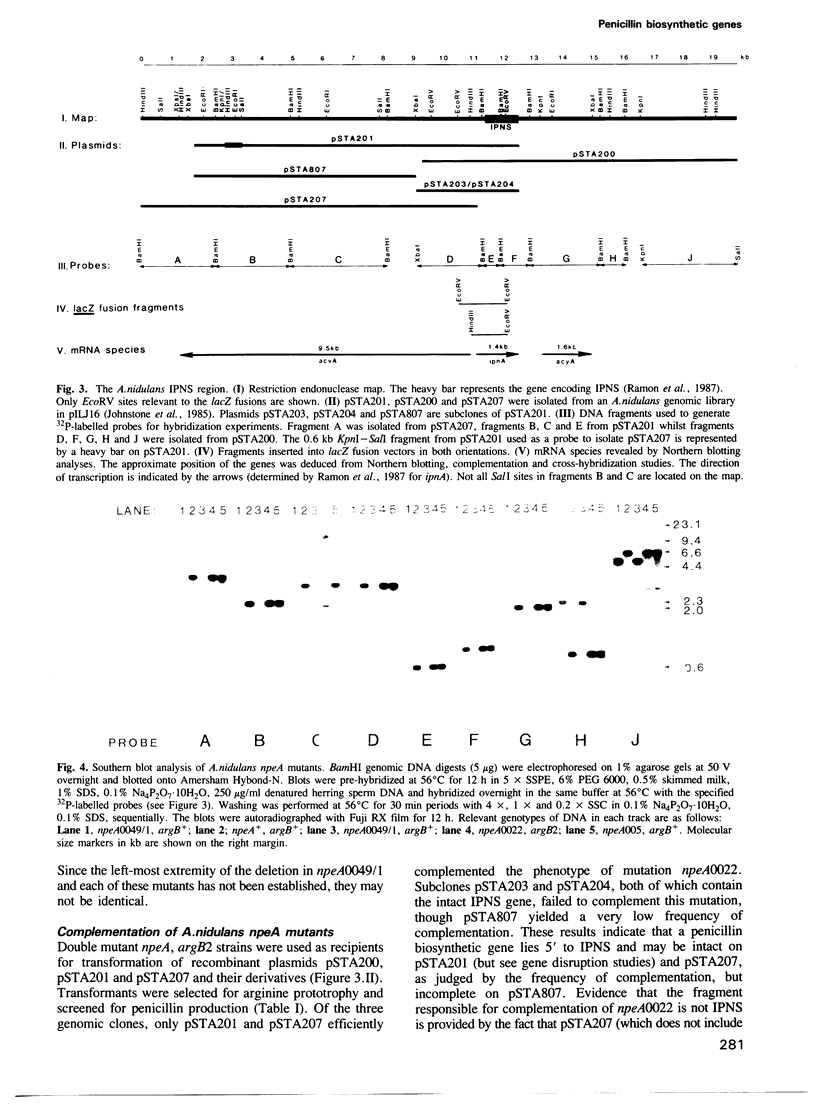
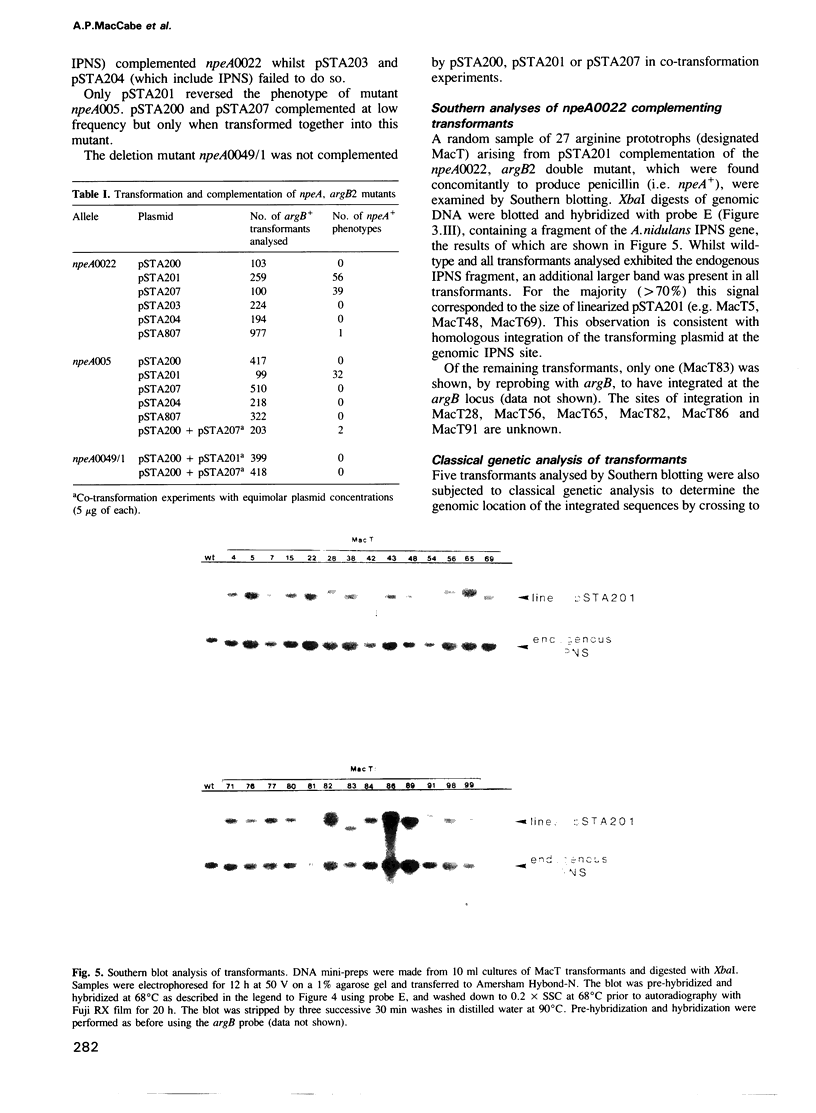
Clones of Aspergillus nidulans genomic DNA spanning 20 kb have been isolated and shown by a combination of classical and molecular genetic means to represent the npeA locus, previously found to be one of four loci (npeA, npeB, npeC and npeD) involved in the synthesis of penicillin. As well as containing the gene encoding the second enzyme for penicillin biosynthesis, namely isopenicillin N synthetase (IPNS) (designated ipnA), our results show that these clones (pSTA200, pSTA201 and pSTA207) contain two more genes to form a cluster of three contiguous penicillin biosynthetic genes. Our evidence suggests that these genes encode delta (L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine synthetase (ACVS) and acyl transferase (ACYT) (designated acvA and acyA respectively), the first and third enzymes required for penicillin biosynthesis, with the gene order being acvA-ipnA-acyA. Transcripts have been identified for the three genes and their approximate sizes determined--acvA 9.5 kb, ipnA 1.4 kb and acyA 1.6 kb. All three mRNA species are observed in cells grown in fermentation medium but not in cells grown in minimal medium, suggesting that the control of penicillin biosynthesis is, in part, at the level of mRNA accumulation. Finally our results show that acvA and ipnA genes are divergently transcribed, whilst acyA is transcribed in the same orientation as ipnA.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amons R. Vapor-phase modification of sulfhydryl groups in proteins. FEBS Lett. 1987 Feb 9;212(1):68–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81558-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arst H. N., Jr Regulation of gene expression in Aspergillus nidulans. Microbiol Sci. 1984 Sep;1(6):137–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballance D. J. Sequences important for gene expression in filamentous fungi. Yeast. 1986 Dec;2(4):229–236. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr L. G., Skatrud P. L., Scheetz M. E., 2nd, Queener S. W., Ingolia T. D. Cloning and expression of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene from Penicillium chrysogenum. Gene. 1986;48(2-3):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90084-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole D. S., Holt G., Macdonald K. D. Relationship of the genetic determination of impaired penicillin production in naturally occurring strains to that in induced mutants of Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Oct;96(2):423–426. doi: 10.1099/00221287-96-2-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cove D. J. The induction and repression of nitrate reductase in the fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 11;113(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards G. F., Holt G., Macdonald K. D. Mutants of Aspergillus nidulans impaired in penicillin biosynthesis. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Oct;84(2):420–423. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-2-420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidel S., Doonan J. H., Morris N. R. Aspergillus nidulans contains a single actin gene which has unique intron locations and encodes a gamma-actin. Gene. 1988 Oct 30;70(2):283–293. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Queener S. W. Beta-lactam biosynthetic genes. Med Res Rev. 1989 Apr-Jun;9(2):245–264. doi: 10.1002/med.2610090206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone I. L., Hughes S. G., Clutterbuck A. J. Cloning an Aspergillus nidulans developmental gene by transformation. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1307–1311. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03777.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leskiw B. K., Aharonowitz Y., Mevarech M., Wolfe S., Vining L. C., Westlake D. W., Jensen S. E. Cloning and nucleotide sequence determination of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene from Streptomyces clavuligerus. Gene. 1988;62(2):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90557-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makins J. F., Allsop A., Holt G. Intergeneric cosynthesis of penicillin by strains of Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum/notatum and Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Feb;122(2):339–343. doi: 10.1099/00221287-122-2-339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makins J. F., Holt G., Macdonald K. D. The genetic location of three mutations impairing penicillin production in Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Oct;129(10):3027–3033. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-10-3027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. F., Demain A. L. Control of antibiotic biosynthesis. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):230–251. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.230-251.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. R., Ingolia T. D. Cloning and characterization of beta-lactam biosynthetic genes. Mol Microbiol. 1989 May;3(5):689–695. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambosek J., Leach J. Recombinant DNA in filamentous fungi: progress and prospects. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 1987;6(4):357–393. doi: 10.3109/07388558709089387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramón D., Carramolino L., Patiño C., Sánchez F., Peñalva M. A. Cloning and characterization of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene mediating the formation of the beta-lactam ring in Aspergillus nidulans. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90120-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson S. M., Belagaje R., Blankenship D. T., Chapman J. L., Perry D., Skatrud P. L., VanFrank R. M., Abraham E. P., Baldwin J. E., Queener S. W. Isolation, sequence determination and expression in Escherichia coli of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene from Cephalosporium acremonium. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):191–194. doi: 10.1038/318191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilburn J., Scazzocchio C., Taylor G. G., Zabicky-Zissman J. H., Lockington R. A., Davies R. W. Transformation by integration in Aspergillus nidulans. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):205–221. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel B. J., Burgett S. G., Chen V. J., Skatrud P. L., Frolik C. A., Queener S. W., Ingolia T. D. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of isopenicillin N synthetase genes from Streptomyces lipmanii and Aspergillus nidulans. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3817–3826. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3817-3826.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gorcom R. F., Punt P. J., Pouwels P. H., van den Hondel C. A. A system for the analysis of expression signals in Aspergillus. Gene. 1986;48(2-3):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Liempt H., von Döhren H., Kleinkauf H. delta-(L-alpha-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine synthetase from Aspergillus nidulans. The first enzyme in penicillin biosynthesis is a multifunctional peptide synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3680–3684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]