Abstract
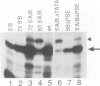
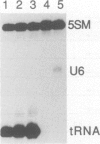
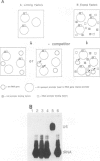
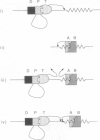
Consensus tRNA gene promoter elements, A and B boxes, were introduced into the coding sequence of a Xenopus U6 gene. Combinations in which A and B boxes were coupled to wild-type or mutant U6 promoters were made. In this way information about both the functions of individual promoter elements and functional relationships between different classes of RNA polymerase III promoter element were obtained. Mutants in which the U6 PSE was non-functional were rescued by the presence of a B box, indicating a degree of functional relationship between these two elements. Moreover, the B box acted to increase the transcriptional activity and competitive strength of the wild-type U6 promoter. In contrast, no evidence was obtained to suggest that a tRNA A box can interact productively with U6 promoter elements in the absence of a B box. Data obtained suggest that the U6 PSE functions as an 'adaptor', being necessary to enable the basal U6 promoter to respond to upstream enhancement. Certain combinations of U6 and tRNA promoter elements are shown to be mutually antagonistic by a mechanism which is likely to involve blockage of transcription initiation. In summary, the U6 and tRNA promoters are shown to consist of functionally related, but distinct, promoter elements whose interactions shed new light on their normal roles in transcription.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison D. S., Goh S. H., Hall B. D. The promoter sequence of a yeast tRNAtyr gene. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bark C., Weller P., Zabielski J., Janson L., Pettersson U. A distant enhancer element is required for polymerase III transcription of a U6 RNA gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):356–359. doi: 10.1038/328356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon P., Murgo S., Ebel J. P., Krol A., Tebb G., Mattaj L. W. A common octamer motif binding protein is involved in the transcription of U6 snRNA by RNA polymerase III and U2 snRNA by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Castagnoli L., Cortese R. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1983;18:59–88. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60579-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Castagnoli L., Melton D. A., Cortese R. Promoter of a eukaryotic tRNAPro gene is composed of three noncontiguous regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1195–1199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Palla F., Tebb G., Mattaj I. W., Philipson L. Properties of a U1 RNA enhancer-like sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2403–2416. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg J. E., Schenborn E. T. The human U1 snRNA promoter and enhancer do not direct synthesis of messenger RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):5827–5840. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.5827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G., Henning D., Wright D., Reddy R. Upstream regulatory elements are necessary and sufficient for transcription of a U6 RNA gene by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):503–512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairall L., Rhodes D., Klug A. Mapping of the sites of protection on a 5 S RNA gene by the Xenopus transcription factor IIIA. A model for the interaction. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 5;192(3):577–591. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90278-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilfoyle R., Weinmann R. Control region for adenovirus VA RNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3378–3382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. D., Clarkson S. G., Tocchini-Valentini G. Transcription initiation of eucaryotic transfer RNA genes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. G., Shu M. D. Epstein-Barr virus small RNA (EBER) genes: unique transcription units that combine RNA polymerase II and III promoter elements. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):825–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90797-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krol A., Carbon P., Ebel J. P., Appel B. Xenopus tropicalis U6 snRNA genes transcribed by Pol III contain the upstream promoter elements used by Pol II dependent U snRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2463–2478. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Transcription of a human U6 small nuclear RNA gene in vivo withstands deletion of intragenic sequences but not of an upstream TATATA box. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7371–7379. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Upstream elements required for efficient transcription of a human U6 RNA gene resemble those of U1 and U2 genes even though a different polymerase is used. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):196–204. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson D., Bradford-Wilcox J., Young L. S., Sprague K. U. A short 5' flanking region containing conserved sequences is required for silkworm alanine tRNA gene activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3416–3420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Hernandez N. A 7 bp mutation converts a human RNA polymerase II snRNA promoter into an RNA polymerase III promoter. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90402-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Dathan N. A., Parry H. D., Carbon P., Krol A. Changing the RNA polymerase specificity of U snRNA gene promoters. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):435–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., De Robertis E. M. Nuclear segregation of U2 snRNA requires binding of specific snRNP proteins. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90314-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. H., Baralle F. E. Construction and functional analysis of a series of synthetic RNA polymerase III promoters. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10208–10211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Di Liegro C., Melli M. The in vitro transcription of the 7SK RNA gene by RNA polymerase III is dependent only on the presence of an upstream promoter. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):81–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S., Moorefield B., Pieler T. Common mechanisms of promoter recognition by RNA polymerases II and III. Trends Genet. 1989 Apr;5(4):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry H. D., Tebb G., Mattaj I. W. The Xenopus U2 gene PSE is a single, compact, element required for transcription initiation and 3' end formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3633–3644. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Stable C., Ayres T. M., Shen C. K. Distinctive sequence organization and functional programming of an Alu repeat promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5291–5295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Hamm J., Roeder R. G. The 5S gene internal control region is composed of three distinct sequence elements, organized as two functional domains with variable spacing. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90359-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selker E. U., Morzycka-Wroblewska E., Stevens J. N., Metzenberg R. L. An upstream signal is required for in vitro transcription of Neurospora 5S RNA genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):189–192. doi: 10.1007/BF02428052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha N. D., Biernat J., McManus J., Köster H. Polymer support oligonucleotide synthesis XVIII: use of beta-cyanoethyl-N,N-dialkylamino-/N-morpholino phosphoramidite of deoxynucleosides for the synthesis of DNA fragments simplifying deprotection and isolation of the final product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4539–4557. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B. Surprises in polymerase III transcription. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):153–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90500-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Grossniklaus U., Herr W., Hernandez N. Activation of the U2 snRNA promoter by the octamer motif defines a new class of RNA polymerase II enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1764–1778. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trendelenburg M. F., Mathis D., Oudet P. Transcription units of chicken ovalbumin gene observed after injection of cloned complete genes into Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5984–5988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Weiner A. M. Upstream sequences modulate the internal promoter of the human 7SL RNA gene. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):371–374. doi: 10.1038/318371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson E. T., Larson D., Young L. S., Sprague K. U. A large region controls tRNA gene transcription. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90209-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]