Abstract
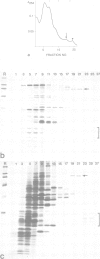
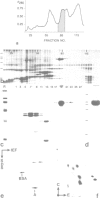
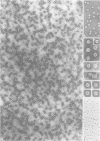
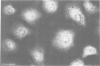
We have discovered a ring-shaped particle of 12.5 nm diameter, 14.5S and apparent molecular weight of approximately 570,000 that displays 6-fold radial symmetry and is composed of a single kind of an acidic (pI approximately 5.5) polypeptide of Mr 97,000 (p97). Using antibodies to this protein we have detected its occurrence in a wide range of cells and tissues of diverse species from frog to man, including highly specialized cells such as mammalian erythrocytes and spermatozoa. In Xenopus laevis oocytes, the particle is found in both isolated nuclei and in manually enucleated ooplasms, which corresponds to immunofluorescence staining dispersed over both nucleoplasm and cytoplasm. The particle has a N-ethylmaleimide (NEM)-inhibitable Mg2(+)-ATPase activity, and its amino acid sequence, as deduced from cDNA clones, displays considerable homology to the mammalian NEM-sensitive fusion protein (NSF) and yeast Sec18p believed to be essential for vesicle fusion in secretory processes, indicating that these three proteins belong to the same multigene family.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebersold R. H., Leavitt J., Saavedra R. A., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated by one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis after in situ protease digestion on nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6970–6974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Awqati Q. Proton-translocating ATPases. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:179–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo A. P., Darlix J. L., Khandjian E. W., Simon M., Spahr P. F. Characterization of the prosome from Drosophila and its similarity to the cytoplasmic structures formed by the low molecular weight heat-shock proteins. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):399–406. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03642.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo A. P., Simon M., Darlix J. L., Spahr P. F. A 20S particle ubiquitous from yeast to human. J Mol Evol. 1987;25(2):141–150. doi: 10.1007/BF02101756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo A. P., Tanaka K., Goldberg A. L., Welch W. J. Identity of the 19S 'prosome' particle with the large multifunctional protease complex of mammalian cells (the proteasome). Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):192–194. doi: 10.1038/331192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear D. G., Hicks P. S., Escudero K. W., Andrews C. L., McSwiggen J. A., von Hippel P. H. Interactions of Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho with RNA. II. Electron microscopy and nuclease protection experiments. J Mol Biol. 1988 Feb 20;199(4):623–635. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. R., Glick B. S., Wilcox C. A., Wieland F. T., Rothman J. E. Purification of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive protein catalyzing vesicular transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7852–7856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman B. J., Bowman E. J. H+-ATPases from mitochondria, plasma membranes, and vacuoles of fungal cells. J Membr Biol. 1986;94(2):83–97. doi: 10.1007/BF01871190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño J. G., Ornberg R., Koster J. G., Tobian J. A., Zasloff M. Eukaryotic pre-tRNA 5' processing nuclease: copurification with a complex cylindrical particle. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):377–385. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90658-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase in the regulation of glycogen metabolism in mammalian skeletal muscle. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1978;14:117–196. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152814-0.50008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The subunit structure of rabbit-skeletal-muscle phosphorylase kinase, and the molecular basis of its activation reactions. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domae N., Harmon F. R., Busch R. K., Spohn W., Subrahmanyam C. S., Busch H. Donut-shaped "miniparticles" in nuclei of human and rat cells. Life Sci. 1982 Feb 1;30(5):469–477. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90464-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eakle K. A., Bernstein M., Emr S. D. Characterization of a component of the yeast secretion machinery: identification of the SEC18 gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4098–4109. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Pickett R. A., 2nd, Hampton J., Lerner R. A. Radioiodination of proteins in single polyacrylamide gel slices. Tryptic peptide analysis of all the major members of complex multicomponent systems using microgram quantities of total protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6510–6515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkenburg P. E., Haass C., Kloetzel P. M., Niedel B., Kopp F., Kuehn L., Dahlmann B. Drosophila small cytoplasmic 19S ribonucleoprotein is homologous to the rat multicatalytic proteinase. Nature. 1988 Jan 14;331(6152):190–192. doi: 10.1038/331190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Winter S., Osborn M., Weber K. Widespread occurrence of intermediate-sized filaments of the vimentin-type in cultured cells from diverse vertebrates. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Oct 1;123(1):25–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. C., Kuby S. A., Mildvan A. S. ATP-binding site of adenylate kinase: mechanistic implications of its homology with ras-encoded p21, F1-ATPase, and other nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):907–911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUENTHER I. [Electron-microscopic studies of the germinating spores of Funaria hygrometrica]. J Ultrastruct Res. 1960 Dec;4:304–331. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(60)80025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J. S., Ghatei M. A., Domin J., Bloom S. R. The generation of valosin-like peptides from a precursor protein in vitro as an extraction artifact. Life Sci. 1989;44(7):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90464-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon F. R., Spohn W. H., Domae N., Ha C. S., Busch H. Purification and partial characterization of ring-shaped miniparticles. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1983 May;7(5):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(83)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. R. Biochemical and ultrastructural characterization of a high molecular weight soluble Mg2+ -ATPase from human erythrocytes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):705–721. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90091-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmingsen S. M., Woolford C., van der Vies S. M., Tilly K., Dennis D. T., Georgopoulos C. P., Hendrix R. W., Ellis R. J. Homologous plant and bacterial proteins chaperone oligomeric protein assembly. Nature. 1988 May 26;333(6171):330–334. doi: 10.1038/333330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix R. W. Purification and properties of groE, a host protein involved in bacteriophage assembly. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 15;129(3):375–392. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90502-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn T., Hohn B., Engel A., Wurtz M., Smith P. R. Isolation and characterization of the host protein groE involved in bacteriophage lambda assembly. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 15;129(3):359–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90501-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. C. Protein-RNA interactions during TMV assembly. J Supramol Struct. 1979;12(3):305–320. doi: 10.1002/jss.400120304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hügle B., Kleinschmidt J. A., Franke W. W. The 22 S cylinder particles of Xenopus laevis. II. Immunological characterization and localization of their proteins in tissues and cultured cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;32(1):157–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hügle B., Scheer U., Franke W. W. Ribocharin: a nuclear Mr 40,000 protein specific to precursor particles of the large ribosomal subunit. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):615–627. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapprell H. P., Owaribe K., Franke W. W. Identification of a basic protein of Mr 75,000 as an accessory desmosomal plaque protein in stratified and complex epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1679–1691. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann E., Geisler N., Weber K. SDS-PAGE strongly overestimates the molecular masses of the neurofilament proteins. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 7;170(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81373-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Dingwall C., Maier G., Franke W. W. Molecular characterization of a karyophilic, histone-binding protein: cDNA cloning, amino acid sequence and expression of nuclear protein N1/N2 of Xenopus laevis. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3547–3552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Escher C., Wolf D. H. Proteinase yscE of yeast shows homology with the 20 S cylinder particles of Xenopus laevis. FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 24;239(1):35–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80540-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Hügle B., Grund C., Franke W. W. The 22 S cylinder particles of Xenopus laevis. I. Biochemical and electron microscopic characterization. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;32(1):143–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp A. C., Franke W. W. Spontaneous losses of control of cytokeratin gene expression in transformed, non-epithelial human cells occurring at different levels of regulation. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):67–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90870-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller K. J., Brownstein M. J. Use of a cDNA clone to identify a supposed precursor protein containing valosin. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):542–545. doi: 10.1038/325542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konturek S. J., Schmidt W. E., Mutt V., Konturek J. W., Creutzfeldt W. Valosin stimulates gastric and exocrine pancreatic secretion and inhibits fasting small intestinal myoelectric activity in the dog. Gastroenterology. 1987 May;92(5 Pt 1):1181–1186. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(87)91075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopun M., Spring H., Granzow C. Nuclear glycogen synthase--fact or artifact? FEBS Lett. 1982 Oct 18;147(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kremp A., Schliephacke M., Kull U., Schmid H. P. Prosomes exist in plant cells too. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Oct;166(2):553–557. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90500-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Franke W. W. A major soluble acidic protein located in nuclei of diverse vertebrate species. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Sep;129(1):167–189. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90341-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Franke W. W. Proteins of pore complex--lamina structures from nuclei and nuclear membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:597–608. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Waizenegger I., Höger T. H. The conserved carboxy-terminal cysteine of nuclear lamins is essential for lamin association with the nuclear envelope. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2003–2011. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuenzel E. A., Mulligan J. A., Sommercorn J., Krebs E. G. Substrate specificity determinants for casein kinase II as deduced from studies with synthetic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9136–9140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyhse-Andersen J. Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 Dec;10(3-4):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Cowan N. J. Anomalous placement of introns in a member of the intermediate filament multigene family: an evolutionary conundrum. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1529–1534. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo F. J., Krohne G., Franke W. W. Basic proteins of the perinuclear theca of mammalian spermatozoa and spermatids: a novel class of cytoskeletal elements. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1105–1120. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra V., Orci L., Glick B. S., Block M. R., Rothman J. E. Role of an N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive transport component in promoting fusion of transport vesicles with cisternae of the Golgi stack. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):221–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90554-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martins de Sa C., Grossi de Sa M. F., Akhayat O., Broders F., Scherrer K., Horsch A., Schmid H. P. Prosomes. Ubiquity and inter-species structural variation. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 20;187(4):479–493. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90328-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullin T. W., Hallberg R. L. A highly evolutionarily conserved mitochondrial protein is structurally related to the protein encoded by the Escherichia coli groEL gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):371–380. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller W., Amons R. Phosphate-binding sequences in nucleotide-binding proteins. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 1;186(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Field C., Schekman R. Identification of 23 complementation groups required for post-translational events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda T., Takanami M. Observations on the structure of the termination factor rho and its attachment to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):799–802. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. B., Woodgett J. R., Cohen P., Kemp B. E. Substrate specificity of a multifunctional calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14471–14476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebhun L. I., Smith C., Larner J. Electron microscope studies of glycogen synthase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1973 May 11;1(1):55–61. doi: 10.1007/BF01659938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riezman H. Endocytosis in yeast: several of the yeast secretory mutants are defective in endocytosis. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):1001–1009. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. W. Termination factor for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1969 Dec 20;224(5225):1168–1174. doi: 10.1038/2241168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid H. P., Akhayat O., Martins De Sa C., Puvion F., Koehler K., Scherrer K. The prosome: an ubiquitous morphologically distinct RNP particle associated with repressed mRNPs and containing specific ScRNA and a characteristic set of proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):29–34. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01757.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W. E., Mutt V., Carlquist M., Kratzin H., Conlon J. M., Creutzfeldt W. Valosin: isolation and characterization of a novel peptide from porcine intestine. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):264–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldt C., Kloetzel P. M. Analysis of cytoplasmic 19 S ring-type particles in Drosophila which contain hsp 23 at normal growth temperature. Dev Biol. 1985 Jul;110(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shur S. A., Skolysheva L. K., Vul'fson P. L. Prisutstvie glikogensintazy v preparatakh kinazy fosforilazy, vydelennykh iz skeletnykh myshts krolika. Biokhimiia. 1986 Sep;51(9):1446–1453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt B. L., Webb M. R. Absence of a phosphorylated intermediate during ATP hydrolysis by Escherichia coli transcription termination protein rho. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):15906–15909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Yoshimura T., Ichihara A., Ikai A., Nishigai M., Morimoto Y., Sato M., Tanaka N., Katsube Y., Kameyama K. Molecular organization of a high molecular weight multi-protease complex from rat liver. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):985–996. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90123-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. An octamer of histones in chromatin and free in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukahara T., Tanaka K., Ogawa T., Ishiura S., Funabiki R., Sugita H. RNA degrading activity is tightly associated with the multicatalytic proteinase, ingensin. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 11;255(1):179–183. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh M. J., McDougall J., Wittmann-Liebold B. Extended N-terminal sequencing of proteins of archaebacterial ribosomes blotted from two-dimensional gels onto glass fiber and poly(vinylidene difluoride) membrane. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6867–6876. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel D., Flügge U. I. A method for the quantitative recovery of protein in dilute solution in the presence of detergents and lipids. Anal Biochem. 1984 Apr;138(1):141–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90782-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. D., Ralston G. B. A water-soluble Mg2+-ATPase from erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jul 1;436(3):567–576. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90441-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. D., Ralston G. B. Purification of a water-soluble Mg2+-ATPase from human erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul;599(2):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. W., Wilcox C. A., Flynn G. C., Chen E., Kuang W. J., Henzel W. J., Block M. R., Ullrich A., Rothman J. E. A fusion protein required for vesicle-mediated transport in both mammalian cells and yeast. Nature. 1989 Jun 1;339(6223):355–359. doi: 10.1038/339355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R., Gould K. L., Hunter T. Substrate specificity of protein kinase C. Use of synthetic peptides corresponding to physiological sites as probes for substrate recognition requirements. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):177–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]