Abstract
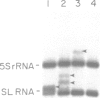
We have used block substitution mutagenesis and in vitro transcription to define sequence elements important for efficient initiation and 3' end-formation of the trans-spliced leader RNA (SL RNA) of the parasitic nematode Ascaris lumbricoides. These experiments indicate that the SL RNA has an unusual promoter structure containing elements which include the 22 nt trans-spliced leader exon itself. Efficient transcription is correlated with the binding of a factor to the 22 nt (SL) sequence; mutations within the SL which abolish transcription lead to a loss in binding of this factor. In addition to internal sequences, synthesis of SL RNA in vitro requires an element centered 50 bases upstream of the cap site. Mutations within this element dramatically affect the level of SL RNA synthesis but do not affect accuracy of initiation. Finally, all of the information required for accurate 3' end-formation of SL RNA lies within the transcribed region. Thus, the arrangement of sequences necessary for the synthesis of SL RNAs does not resemble that of sequences important for the synthesis of vertebrate U snRNAs despite the similarities between SL RNAs and U snRNAs.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumenthal T., Thomas J. Cis and trans mRNA splicing in C. elegans. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzik J. P., Van Doren K., Hirsh D., Steitz J. A. Trans splicing involves a novel form of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):559–562. doi: 10.1038/335559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon P., Murgo S., Ebel J. P., Krol A., Tebb G., Mattaj L. W. A common octamer motif binding protein is involved in the transcription of U6 snRNA by RNA polymerase III and U2 snRNA by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Dathan N., Frank R., Philipson L., Mattaj I. W. Formation of the 3' end on U snRNAs requires at least three sequence elements. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2931–2937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04589.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Equipotent mouse ribosomal protein promoters have a similar architecture that includes internal sequence elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1789–1800. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N. Formation of the 3' end of U1 snRNA is directed by a conserved sequence located downstream of the coding region. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1827–1837. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03857.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Weiner A. M. Formation of the 3' end of U1 snRNA requires compatible snRNA promoter elements. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Hirsh D. A trans-spliced leader sequence on actin mRNA in C. elegans. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90613-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroney P. A., Hannon G. J., Nilsen T. W. Transcription and cap trimethylation of a nematode spliced leader RNA in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):709–713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrokhi L. J., Georgieva S. G., Ilyin Y. V. jockey, a mobile Drosophila element similar to mammalian LINEs, is transcribed from the internal promoter by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):685–691. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moura-Neto R., Dudov K. P., Perry R. P. An element downstream of the cap site is required for transcription of the gene encoding mouse ribosomal protein L32. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):3997–4001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.3997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Shambaugh J., Denker J., Chubb G., Faser C., Putnam L., Bennett K. Characterization and expression of a spliced leader RNA in the parasitic nematode Ascaris lumbricoides var. suum. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3543–3547. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W. Trans-splicing in nematodes. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Nov;69(4):413–416. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90191-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takacs A. M., Denker J. A., Perrine K. G., Maroney P. A., Nilsen T. W. A 22-nucleotide spliced leader sequence in the human parasitic nematode Brugia malayi is identical to the trans-spliced leader exon in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7932–7936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tebb G., Mattaj I. W. Positionally exact initiation is required for the formation of a stable RNA polymerase II transcription complex in vivo. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3785–3792. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03263.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. D., Conrad R. C., Blumenthal T. The C. elegans trans-spliced leader RNA is bound to Sm and has a trimethylguanosine cap. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):533–539. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Doren K., Hirsh D. Trans-spliced leader RNA exists as small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):556–559. doi: 10.1038/335556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K., Elder R. T. A region internal to the coding sequences is essential for transcription of the yeast Ty-D15 element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3667–3678. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuo C. Y., Ares M., Jr, Weiner A. M. Sequences required for 3' end formation of human U2 small nuclear RNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):193–202. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vegvar H. E., Lund E., Dahlberg J. E. 3' end formation of U1 snRNA precursors is coupled to transcription from snRNA promoters. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90448-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]