Abstract
Inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase, an enzyme of the phosphatidylinositol signaling pathway, catalyzes the hydrolysis of the 1-position phosphate from inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate and inositol 1,4-bisphosphate. The protein was isolated from calf brain and digested with trypsin or CNBr, and the amino acid sequence of several peptides was determined. Degenerate oligonucleotide primers were designed from amino acid sequence and used to synthesize an 80-base-pair (bp) fragment by the polymerase chain reaction. This product was used to isolate a 1.6-kbp cDNA with an open reading frame of 400 amino acids, 185 bp of 5' untranslated region, and 171 bp of 3' untranslated region followed by a putative poly(A) tail. The coding region of the cDNA was inserted into an expression vector that was used to obtain the recombinant protein from Escherichia coli cells. The recombinant enzyme (44 kDa) had a specific activity and other properties similar to those of native bovine brain inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase. It hydrolyzed both inositol phosphate substrates and was inhibited by lithium ions. The enzyme shows minimal sequence similarity to inositol monophosphate phosphatase, the other enzyme inhibited by lithium ions in the signaling pathway.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balla T., Guillemette G., Baukal A. J., Catt K. J. Metabolism of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate to a new tetrakisphosphate isomer in angiotensin-stimulated adrenal glomerulosa cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):9952–9955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bansal V. S., Caldwell K. K., Majerus P. W. The isolation and characterization of inositol polyphosphate 4-phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1806–1811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bansal V. S., Inhorn R. C., Majerus P. W. The metabolism of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate to inositol 1,3-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9444–9447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi K. Y., Kim H. K., Lee S. Y., Moon K. H., Sim S. S., Kim J. W., Chung H. K., Rhee S. G. Molecular cloning and expression of a complementary DNA for inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinase. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):64–66. doi: 10.1126/science.2157285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Establishing homologies in protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:524–545. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl R. E., Whiting P., Potter J., Gee N., Ragan C. I., Linemeyer D., Schoepfer R., Bennett C., Dixon R. A. Cloning and expression of bovine brain inositol monophosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):5946–5949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee N. S., Reid G. G., Jackson R. G., Barnaby R. J., Ragan C. I. Purification and properties of inositol-1,4-bisphosphatase from bovine brain. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):777–782. doi: 10.1042/bj2530777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Schooler J., Tosteson D. C. Coupling of lithium to sodium transport in human red cells. Nature. 1975 Dec 4;258(5534):425–427. doi: 10.1038/258425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallcher L. M., Sherman W. R. The effects of lithium ion and other agents on the activity of myo-inositol-1-phosphatase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10896–10901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J. H., Stratowa C., Rutter W. J. Isolation of full-length putative rat lysophospholipase cDNA using improved methods for mRNA isolation and cDNA cloning. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1617–1625. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C. A., vom Dahl S., Huddell B., Williamson J. R. Characterization of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate phosphorylation in rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 15;236(1):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80284-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inhorn R. C., Bansal V. S., Majerus P. W. Pathway for inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate and 1,4-bisphosphate metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2170–2174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
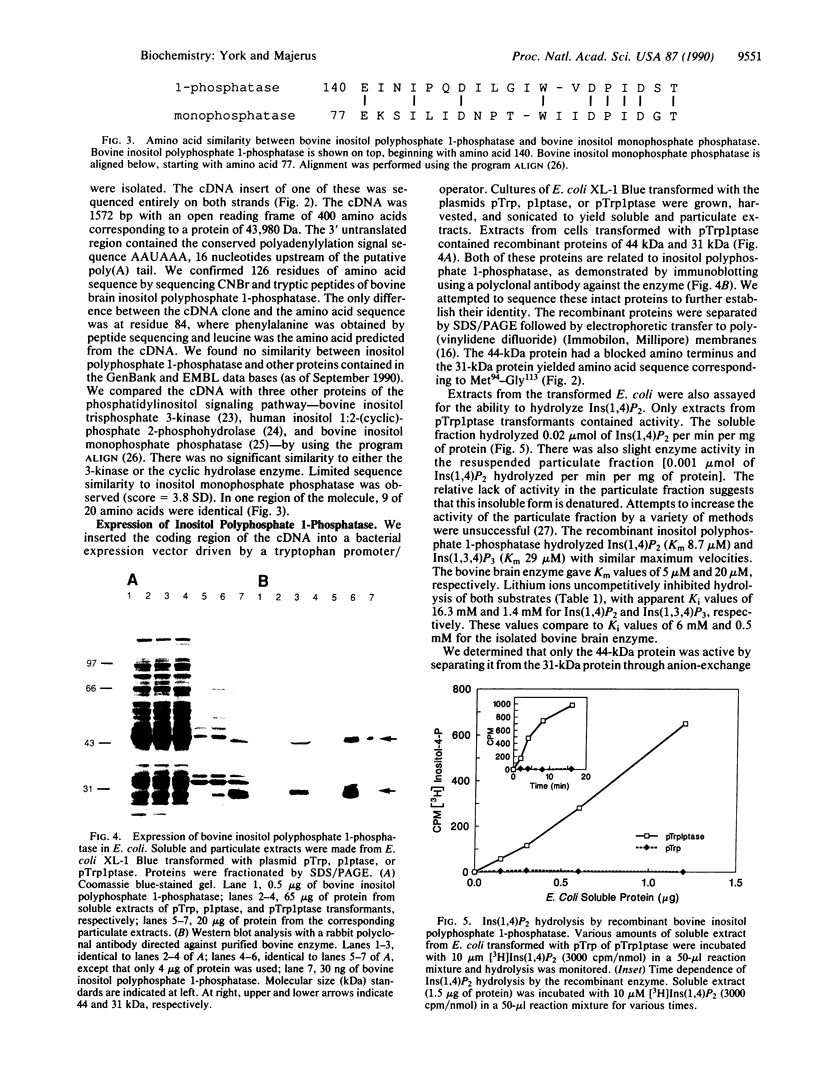
- Inhorn R. C., Majerus P. W. Inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase from calf brain. Purification and inhibition by Li+, Ca2+, and Mn2+. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15946–15952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inhorn R. C., Majerus P. W. Properties of inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14559–14565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross T. S., Tait J. F., Majerus P. W. Identity of inositol 1,2-cyclic phosphate 2-phosphohydrolase with lipocortin III. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):605–607. doi: 10.1126/science.2159184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shears S. B. The pathway of myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate phosphorylation in liver. Identification of myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 6-kinase, myo-inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate 5-kinase, and myo-inositol 1,3,4,6-tetrakisphosphate 5-kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19879–19886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Hawkins P. T., Barker C. J., Downes C. P. Synthesis of myo-inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate from inositol phosphates generated by receptor activation. Biochem J. 1988 Aug 1;253(3):721–733. doi: 10.1042/bj2530721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvia V., Curtin G., Norman J., Stec J., Busbee D. Activation of a low specific activity form of DNA polymerase alpha by inositol-1,4-bisphosphate. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):651–658. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. Selective inactivation of the exonuclease activity of bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase by in vitro mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6447–6458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]