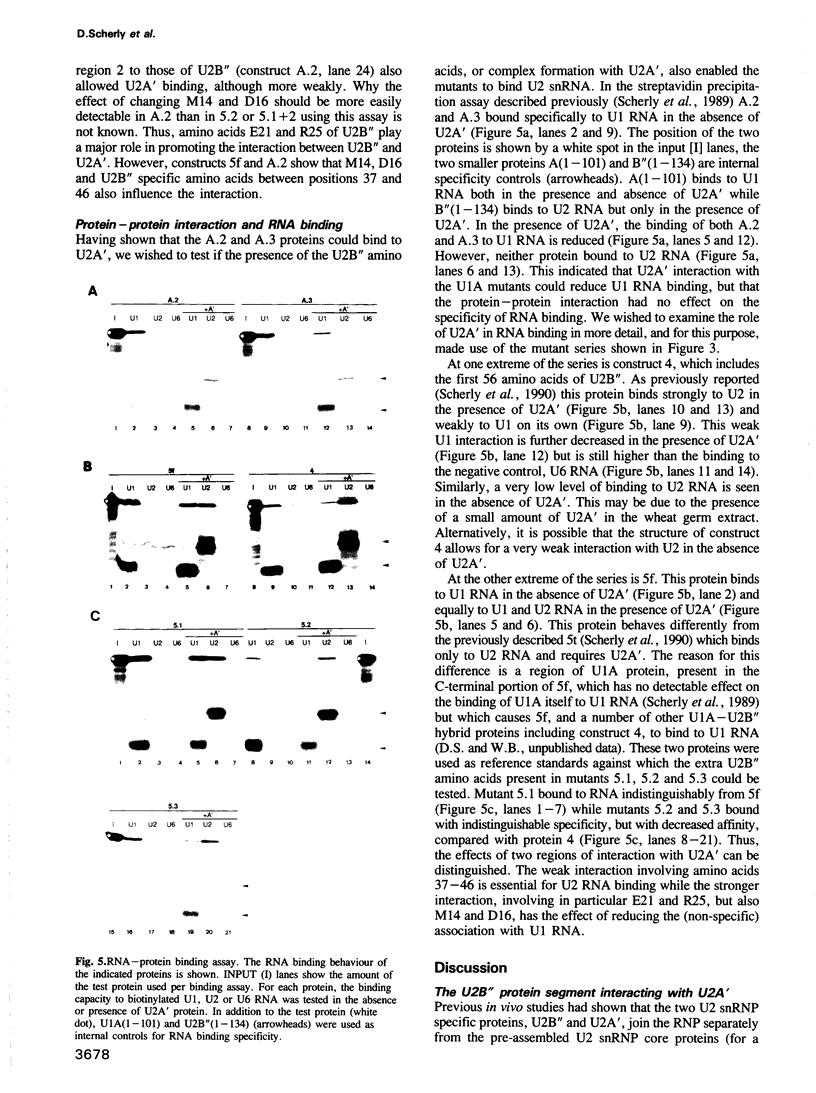
Abstract
The U2 snRNP contains two specific proteins, U2B'' and U2A'. Neither of these proteins, on its own, is capable of specific interactions with U2 RNA. Here, a complex between U2B'' and U2A' that forms in the absence of RNA is identified. Analysis of mutant forms of U2B'' shows that the smallest fragment able to bind specifically U2 RNA (amino acids 1-88) is also the minimal region required for complex formation with U2A', and implies that this region must be largely structurally intact for U2A' interaction. Although this truncated U2B'' fragment is capable of making specific protein--RNA and protein-protein interactions its structure, as measured by the ability to bind to U2A'', appears to depend on the rest of the protein. Hybrids between U2B'' and the closely related U1A protein are used to localize U2B'' specific amino acids involved in protein-protein interaction. These can be divided into two functional groups. U2A' interaction with U2B'' amino acids 37-46 permits binding to U2 RNA whereas interaction with U2B'' specific amino acids between positions 14 and 25 reduces non-specific binding to U1 RNA. These two proteins may serve as a general example of how RNA binding may be modulated by protein-protein interaction in the assembly of RNPs, particularly since the region of U2'' involved in interaction with U2A' consists mainly of a conserved RNP motif.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Nakagawa T., Swanson M. S., Woodruff T. K., Dreyfuss G. mRNA polyadenylate-binding protein: gene isolation and sequencing and identification of a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2932–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandziulis R. J., Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Swanson M. S., Piñol-Roma S. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles and the pathway of mRNA formation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Mar;13(3):86–91. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeney R. J., Zieve G. W. Nuclear exchange of the U1 and U2 snRNP-specific proteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):871–881. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghetti A., Bolognesi M., Cobianchi F., Morandi C. Modelling by homology of RNA binding domain. Mol Biol Rep. 1990;14(2-3):87–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00360427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghetti A., Padovani C., Di Cesare G., Morandi C. Secondary structure prediction for RNA binding domain in RNP proteins identifies beta alpha beta as the main structural motif. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 6;257(2):373–376. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81575-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habets W. J., Sillekens P. T., Hoet M. H., Schalken J. A., Roebroek A. J., Leunissen J. A., van de Ven W. J., van Venrooij W. J. Analysis of a cDNA clone expressing a human autoimmune antigen: full-length sequence of the U2 small nuclear RNA-associated B" antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2421–2425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. A binding consensus: RNA-protein interactions in splicing, snRNPs, and sex. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90164-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima S., Nomura M. Assembly mapping of 30S ribosomal proteins from E. coli. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1214–1214. doi: 10.1038/2261214a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Bentley R. C., Keene J. D. A common RNA recognition motif identified within a defined U1 RNA binding domain of the 70K U1 snRNP protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Argos P. Protein folding. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:497–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Boelens W., Dathan N. A., van Venrooij W. J., Mattaj I. W. Major determinants of the specificity of interaction between small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1A and U2B'' and their cognate RNAs. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):502–506. doi: 10.1038/345502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Boelens W., van Venrooij W. J., Dathan N. A., Hamm J., Mattaj I. W. Identification of the RNA binding segment of human U1 A protein and definition of its binding site on U1 snRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4163–4170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillekens P. T., Beijer R. P., Habets W. J., van Verooij W. J. Molecular cloning of the cDNA for the human U2 snRNA-specific A' protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1893–1906. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sillekens P. T., Habets W. J., Beijer R. P., van Venrooij W. J. cDNA cloning of the human U1 snRNA-associated A protein: extensive homology between U1 and U2 snRNP-specific proteins. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3841–3848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Powers T., Changchien L. M., Noller H. F. RNA-protein interactions in 30S ribosomal subunits: folding and function of 16S rRNA. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):783–790. doi: 10.1126/science.2658053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Walter P. Assembly of the Alu domain of the signal recognition particle (SRP): dimerization of the two protein components is required for efficient binding to SRP RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):777–784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]