Abstract
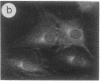
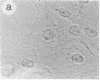
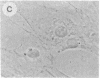
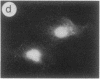
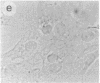
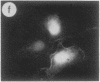
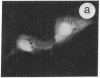
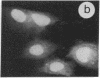
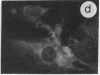
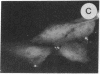
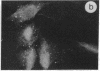
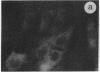
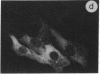
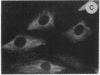
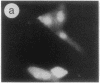
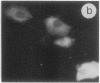
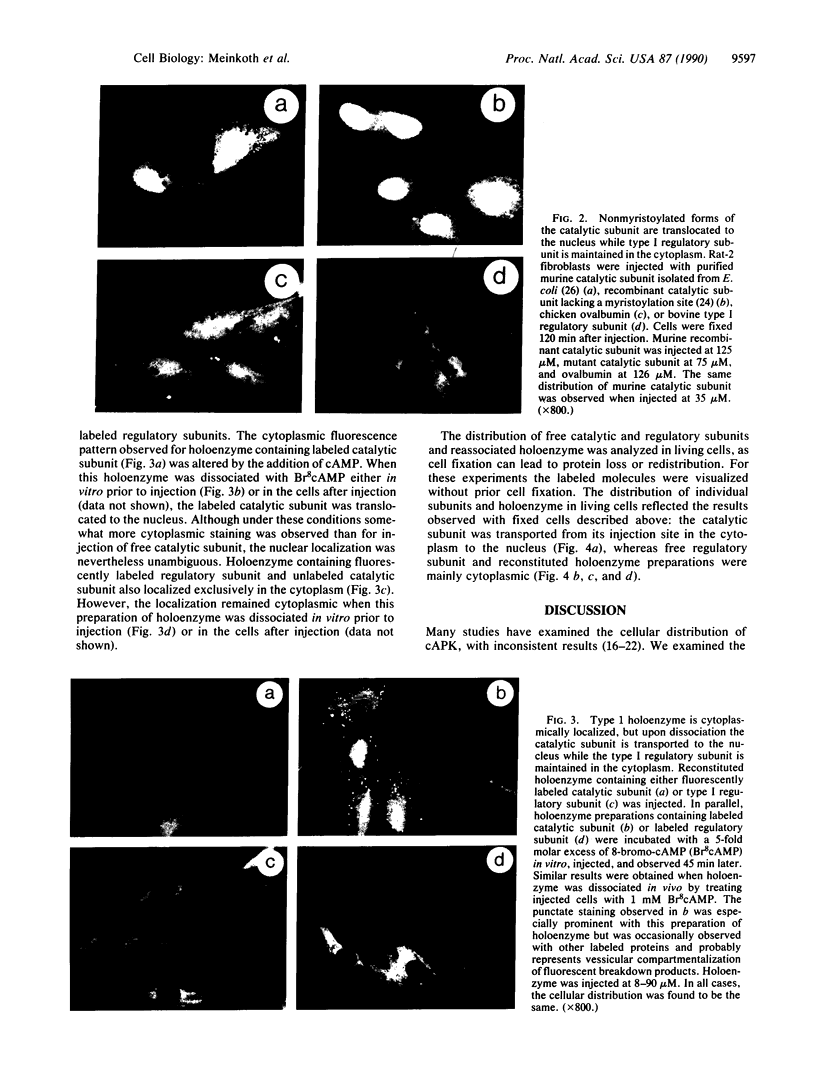
The intracellular distribution of regulatory molecules may provide a mechanism for controlling gene expression. The subcellular location of cAMP-dependent protein kinase was analyzed in living cells by microinjection of regulatory and catalytic subunits labeled with fluorescein. Following microinjection, type I holoenzyme was found in the cytoplasm and remained there for up to 4 hr. Upon dissociation of holoenzyme with 8-bromo-cAMP, free catalytic subunit appeared in the nucleus while regulatory subunit remained in the cytoplasm. Similarly, purified catalytic subunit was transported to the nucleus in the absence of elevated intracellular cAMP following its introduction into the cytoplasm. Translocation to the nucleus was apparent within 10 min and persisted for at least 2 hr. In contrast, purified regulatory subunit, like holoenzyme, was maintained in the cytoplasm. These results suggest that one function of the type I regulatory subunit is to serve as a cytoplasmic anchor, sequestering the catalytic subunit in the cytoplasm until holoenzyme dissociates in response to increased cAMP.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Activation of protein kinase by physiological concentrations of cyclic AMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3580–3583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byus C. V., Fletcher W. H. Direct cytochemical localization of catalytic subunits dissociated from cAMP-dependent protein kinase in Reuber H-35 hepatoma cells. II. Temporal and spatial kinetics. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):727–734. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchler W., Walter U., Jastorff B., Lohmann S. M. Catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase is essential for cAMP-mediated mammalian gene expression. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 8;228(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80577-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr S. A., Biemann K., Shoji S., Parmelee D. C., Titani K. n-Tetradecanoyl is the NH2-terminal blocking group of the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho-Chung Y. S. Hypothesis. Cyclic AMP and its receptor protein in tumor growth regulation in vivo. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;6(3):163–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantinou A. I., Squinto S. P., Jungmann R. A. The phosphoform of the regulatory subunit RII of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase possesses intrinsic topoisomerase activity. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):429–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. F., Neville M. E., Jr, Vrana K. E., Hartl F. T., Roskoski R., Jr Adenosine cyclic 3',5'-monophosphate dependent protein kinase: kinetic mechanism for the bovine skeletal muscle catalytic subunit. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 9;21(23):5794–5799. doi: 10.1021/bi00266a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Keely S. L., Park C. R. The distribution and dissociation of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases in adipose, cardiac, and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):218–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbin J. D., Sugden P. H., Lincoln T. M., Keely S. L. Compartmentalization of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase in heart tissue. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3854–3861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Protein import into the cell nucleus. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:367–390. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durgerian S., Taylor S. S. The consequences of introducing an autophosphorylation site into the type I regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9807–9813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duronio R. J., Jackson-Machelski E., Heuckeroth R. O., Olins P. O., Devine C. S., Yonemoto W., Slice L. W., Taylor S. S., Gordon J. I. Protein N-myristoylation in Escherichia coli: reconstitution of a eukaryotic protein modification in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1506–1510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher W. H., Ishida T. A., Van Patten S. M., Walsh D. A. Direct cytochemical localization of regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase using fluoresceinated catalytic subunit. Methods Enzymol. 1988;159:255–267. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)59026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J. R., Price D. J., Goodman H. M., Avruch J. Recombinant fragment of protein kinase inhibitor blocks cyclic AMP-dependent gene transcription. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):530–533. doi: 10.1126/science.2821622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway D. R., Adelstein R. S., Klee C. B. Interaction of calmodulin with myosin light chain kinase and cAMP-dependent protein kinase in bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8183–8189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Comparison of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinases from rabbit skeletal and bovine heart muscle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7795–7801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. Cytoplasmic anchoring proteins and the control of nuclear localization. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):949–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90747-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuettel M. R., Squinto S. P., Kwast-Welfeld J., Schwoch G., Schweppe J. S., Jungmann R. A. Localization of nuclear subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase by the immunocolloidal gold method. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):965–975. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb N. J., Fernandez A., Conti M. A., Adelstein R., Glass D. B., Welch W. J., Feramisco J. R. Regulation of actin microfilament integrity in living nonmuscle cells by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase and the myosin light chain kinase. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1955–1971. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann S. M., Walter U. Regulation of the cellular and subcellular concentrations and distribution of cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;18:63–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Alberts A. S., Feramisco J. R. Construction of mammalian cell lines with indicator genes driven by regulated promoters. Ciba Found Symp. 1990;150:47–56. doi: 10.1002/9780470513927.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P., Walter U., Theurkauf W. E., Vallee R. B., De Camilli P. Frozen tissue sections as an experimental system to reveal specific binding sites for the regulatory subunit of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase in neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5562–5566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N. C., Taylor S. S. Differential labeling and identification of the cysteine-containing tryptic peptides of catalytic subunit from porcine heart cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3743–3750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Hilz H., Eppenberger H. M., Dutly F. Rapid and reversible translocation of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase type II from the Golgi complex to the nucleus. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2801–2806. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Schäfer G., Hilz H., Eppenberger H. M. Cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase type II is associated with the Golgi complex and with centrosomes. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1039–1051. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K. T., Fink J. S., Gilman M. Z., Walsh D. A., Goodman R. H., Feramisco J. R. The catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase induces expression of genes containing cAMP-responsive enhancer elements. Nature. 1988 Nov 3;336(6194):83–86. doi: 10.1038/336083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K. T., Gilman M. Z., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase induces expression of the c-fos gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):85–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Erlichman J. Reversible autophosphorylation of a cyclic 3':5'-AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7788–7794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S. Characterization and comparison of membrane-associated and cytosolic cAMP-dependent protein kinases. Studies on human erythrocyte protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12439–12449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slice L. W., Taylor S. S. Expression of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20940–20946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squinto S. P., Kelley-Geraghty D. C., Kuettel M. R., Jungmann R. A. Ultrastructural localization of cAMP-dependent protein kinase subunits in regenerating rat hepatocytes using immunogold electron microscopy. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1985;10(1):65–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S., Buechler J. A., Yonemoto W. cAMP-dependent protein kinase: framework for a diverse family of regulatory enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:971–1005. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B., DiBartolomeis M. J., Theurkauf W. E. A protein kinase bound to the projection portion of MAP 2 (microtubule-associated protein 2). J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):568–576. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Kerlavage A. R., Taylor S. S. Structural comparisons of cAMP-dependent protein kinases I and II from porcine skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2408–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]