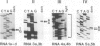Abstract
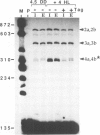
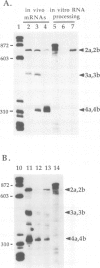
The synthesis of reaction center protein D2 and mRNAs which encode this protein are differentially maintained at high levels in mature barley chloroplasts. To understand the differential maintenance of psbD mRNA abundance, we have studied the transcription and the RNAs produced from the psbD-psbC operon in plastids of light and dark-grown barley seedlings. Ten psbD-psbC RNAs synthesized in dark-grown barley share four different 5'-ends, two of which arise by transcription initiation, and one of which is generated by 5'-processing of longer psbD-psbC transcripts. Illumination of dark-grown barley causes the decline of these ten transcripts, and the accumulation of two different psbD-psbC RNAs. Capping assays, in vitro transcription and RNA processing experiments and treatment of plants with tagetitoxin (a selective inhibitor of chloroplast transcription), indicate that the light-induced transcripts arise by transcription initiation. Run-on transcription and RNA quantitation experiments provide evidence that both light-induced transcription and RNA stability play roles in the accumulation of the light-induced RNAs. These data document a novel mechanism for regulating plastid gene expression involving a light-induced switch in psbD-psbC promoter utilization.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apel K. Phytochrome-induced appearance of mRNA activity for the apoprotein of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):183–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkan A. Tissue-dependent plastid RNA splicing in maize: transcripts from four plastid genes are predominantly unspliced in leaf meristems and roots. Plant Cell. 1989 Apr;1(4):437–445. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner B. J., Rapp J. C., Mullet J. E. Plastid transcription activity and DNA copy number increase early in barley chloroplast development. Plant Physiol. 1989 Mar;89(3):1011–1018. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.3.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
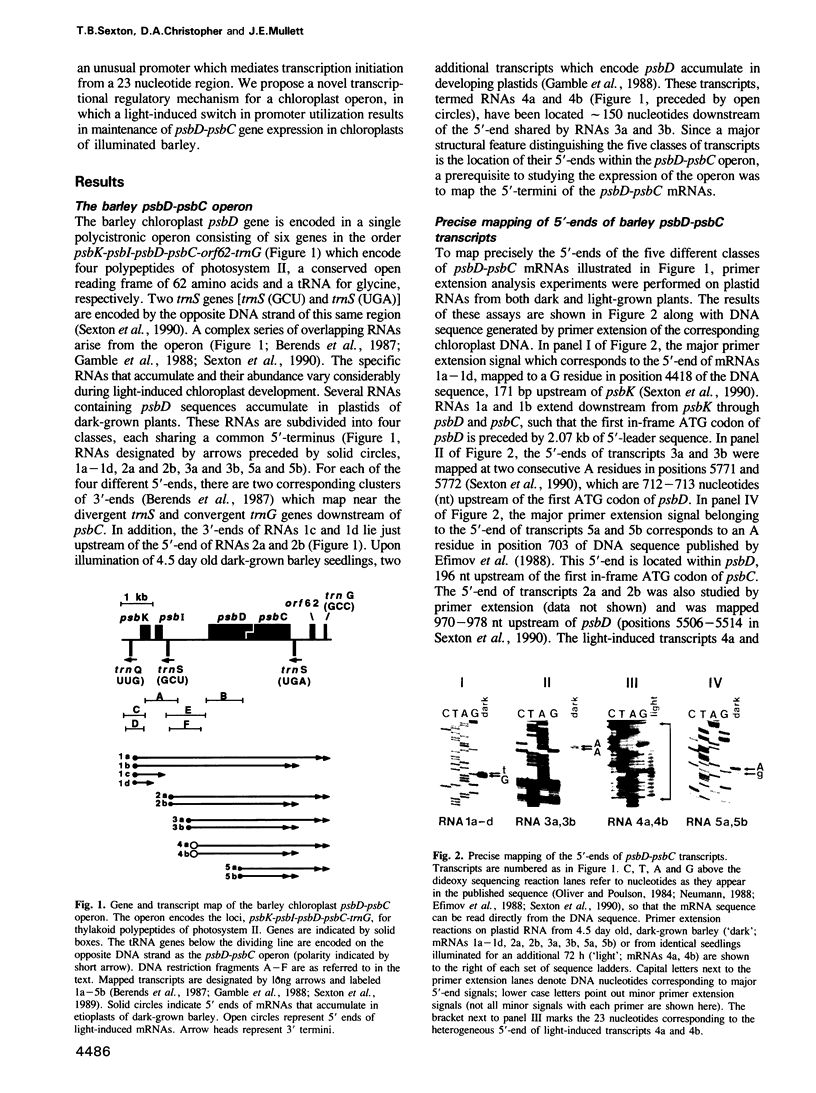
- Berends Sexton T., Jones J. T., Mullet J. E. Sequence and transcriptional analysis of the barley ctDNA region upstream of psbD-psbC encoding trnK(UUU), rps16, trnQ(UUG), psbK, psbI, and trnS(GCU). Curr Genet. 1990 May;17(5):445–454. doi: 10.1007/BF00334526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berends T., Gamble P. E., Mullet J. E. Characterization of the barley chloroplast transcription units containing psaA-psaB and psbD-psbC. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5217–5240. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer S. K., Mullet J. E. Sequence and transcript map of barley chloroplast psbA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):8184–8184. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.8184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. mRNA decay: finding the right targets. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90166-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter H. L., 3rd, Moran C. P., Jr New RNA polymerase sigma factor under spo0 control in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9438–9442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. J., Orozco E. M., Jr Recognition of prokaryotic transcription terminators by spinach chloroplast RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8411–8431. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. J., Rogers S. A., Bennett D. C., Hu M. C., Orozco E. M., Jr An in vitro transcription termination system to analyze chloroplast promoters: identification of multiple promoters for the spinach atpB gene. Curr Genet. 1990 Jan;17(1):55–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00313249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopher D. A., Hallick R. B. Complex RNA maturation pathway for a chloroplast ribosomal protein operon with an internal tRNA cistron. Plant Cell. 1990 Jul;2(7):659–671. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.7.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossland L. D., Rodermel S. R., Bogorad L. Single gene for the large subunit of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase in maize yields two differentially regulated mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4060–4064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Gruissem W. Constitutive transcription and regulation of gene expression in non-photosynthetic plastids of higher plants. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3301–3308. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Gruissem W. Control of plastid gene expression during development: the limited role of transcriptional regulation. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90290-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efimov V. A., Andreeva A. V., Reverdatto S. V., Chakhmakhcheva O. G. Nucleotide sequence of the barley chloroplast psbD gene for the D2 protein of photosystem II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5686–5686. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita N., Nomura T., Ishihama A. Promoter selectivity of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Purification and properties of holoenzyme containing the heat-shock sigma subunit. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1855–1859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble P. E., Mullet J. E. Blue light regulates the accumulation of two psbD-psbC transcripts in barley chloroplasts. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2785–2794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08424.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble P. E., Sexton T. B., Mullet J. E. Light-dependent changes in psbD and psbC transcripts of barley chloroplasts: accumulation of two transcripts maintains psbD and psbC translation capability in mature chloroplasts. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1289–1297. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02943.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg B. M., Gaba V., Canaani O., Malkin S., Mattoo A. K., Edelman M. Separate photosensitizers mediate degradation of the 32-kDa photosystem II reaction center protein in the visible and UV spectral regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6617–6620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W. Chloroplast gene expression: how plants turn their plastids on. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):161–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90889-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Zurawski G. Analysis of promoter regions for the spinach chloroplast rbcL, atpB and psbA genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3375–3383. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04093.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Zurawski G. Identification and mutational analysis of the promoter for a spinach chloroplast transfer RNA gene. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1637–1644. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03831.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley J., Bogorad L. Alternative promoters are used for genes within maize chloroplast polycistronic transcription units. Plant Cell. 1990 Apr;2(4):323–333. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.4.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson G. S., Mason J. G., Holton T. A., Koller B., Cox G. B., Whitfeld P. R., Bottomley W. A gene cluster in the spinach and pea chloroplast genomes encoding one CF1 and three CF0 subunits of the H+-ATP synthase complex and the ribosomal protein S2. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):283–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90690-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet M. A., Reiss C. Transcription in vivo directed by consensus sequences of E.coli promoters: their context heavily affects efficiencies and start sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1137–1143. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. R., Gamble P. E., Mullet J. E. Light-Dependent Accumulation of Radiolabeled Plastid-Encoded Chlorophyll a-Apoproteins Requires Chlorophyll a: I. Analysis of Chlorophyll-Deficient Mutants and Phytochrome Involvement. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):1246–1256. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.1246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. R., Mullet J. E. Control of gene expression during higher plant chloroplast biogenesis. Protein synthesis and transcript levels of psbA, psaA-psaB, and rbcL in dark-grown and illuminated barley seedlings. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4341–4348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. R., Mullet J. E. Light-induced transcription of chloroplast genes. psbA transcription is differentially enhanced in illuminated barley. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1895–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. R., Mullet J. E. Regulation of chloroplast-encoded chlorophyll-binding protein translation during higher plant chloroplast biogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11138–11145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung S. D., Lin C. M. Chloroplast promoters from higher plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7543–7549. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews D. E., Durbin R. D. Tagetitoxin inhibits RNA synthesis directed by RNA polymerases from chloroplasts and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):493–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoo A. K., Hoffman-Falk H., Marder J. B., Edelman M. Regulation of protein metabolism: Coupling of photosynthetic electron transport to in vivo degradation of the rapidly metabolized 32-kilodalton protein of the chloroplast membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1380–1384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoo A. K., Marder J. B., Edelman M. Dynamics of the photosystem II reaction center. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):241–246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90897-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Utilization of the guanylyltransferase and methyltransferases of vaccinia virus to modify and identify the 5'-terminals of heterologous RNA species. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):374–383. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullet J. E., Klein R. R. Transcription and RNA stability are important determinants of higher plant chloroplast RNA levels. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1571–1579. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann E. M. Primary structure of barley genes encoding quinone and chlorophyll a binding proteins of photosystem II. Carlsberg Res Commun. 1988;53(4):259–275. doi: 10.1007/BF02907182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohad I., Kyle D. J., Hirschberg J. Light-dependent degradation of the Q(B)-protein in isolated pea thylakoids. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1655–1659. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03833.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco E. M., Jr, Mullet J. E., Chua N. H. An in vitro system for accurate transcription initiation of chloroplast protein genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1283–1302. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D., Laetsch W. M. Structure and function of developing barley plastids. Plant Physiol. 1974 Aug;54(2):148–159. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock C. D., Barkan A., Taylor W. C. The maize plastid psbB-psbF-petB-petD gene cluster: spliced and unspliced petB and petD RNAs encode alternative products. Curr Genet. 1987;12(1):69–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00420729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster G., Timberg R., Ohad I. Turnover of thylakoid photosystem II proteins during photoinhibition of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 1;177(2):403–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14389.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Gruissem W. Chloroplast mRNA 3' end maturation is biochemically distinct from prokaryotic mRNA processing. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Dec;13(6):615–625. doi: 10.1007/BF00016017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. B., Jones H., Gruissem W. Function of plastid mRNA 3' inverted repeats. RNA stabilization and gene-specific protein binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18742–18750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhoff P., Herrmann R. G. Complex RNA maturation in chloroplasts. The psbB operon from spinach. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;171(3):551–564. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury N. W., Dobres M., Thompson W. F. The identification and localization of 33 pea chloroplast transcription initiation sites. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):433–445. doi: 10.1007/BF00340723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao W. B., Meng B. Y., Tanaka M., Sugiura M. An additional promoter within the protein-coding region of the psbD-psbC gene cluster in tobacco chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9583–9591. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Clegg M. T., Brown A. H. The Nature of Nucleotide Sequence Divergence between Barley and Maize Chloroplast DNA. Genetics. 1984 Apr;106(4):735–749. doi: 10.1093/genetics/106.4.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]