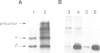Abstract
Cloning of the insulin receptor cDNA has earlier revealed the existence of two alternative forms of the receptor differing by the presence or absence of 12 amino acids near the C-terminus of the receptor alpha-subunit. This insert has been shown by others to be encoded by a discrete exon, and alternative splicing of this exon leads to tissue-specific expression of two receptor isoforms. We have studied the functional significance of the receptor isoforms and have confirmed that they are generated by alternative splicing. When cDNAs encoding the two forms of the insulin receptors are expressed in Rat 1 cells, the receptor lacking the insert (HIR-A) has a significantly higher affinity for insulin than the receptor with the insert (HIR-B). This difference in affinity is maintained when insulin binding activity is assayed in solution using detergent solubilized, partially purified receptors. These data, combined with the tissue specificity of HIR-A and HIR-B expression, suggest that alternative splicing may result in the modulation of insulin metabolism or responsiveness by different tissues.
Full text
PDF

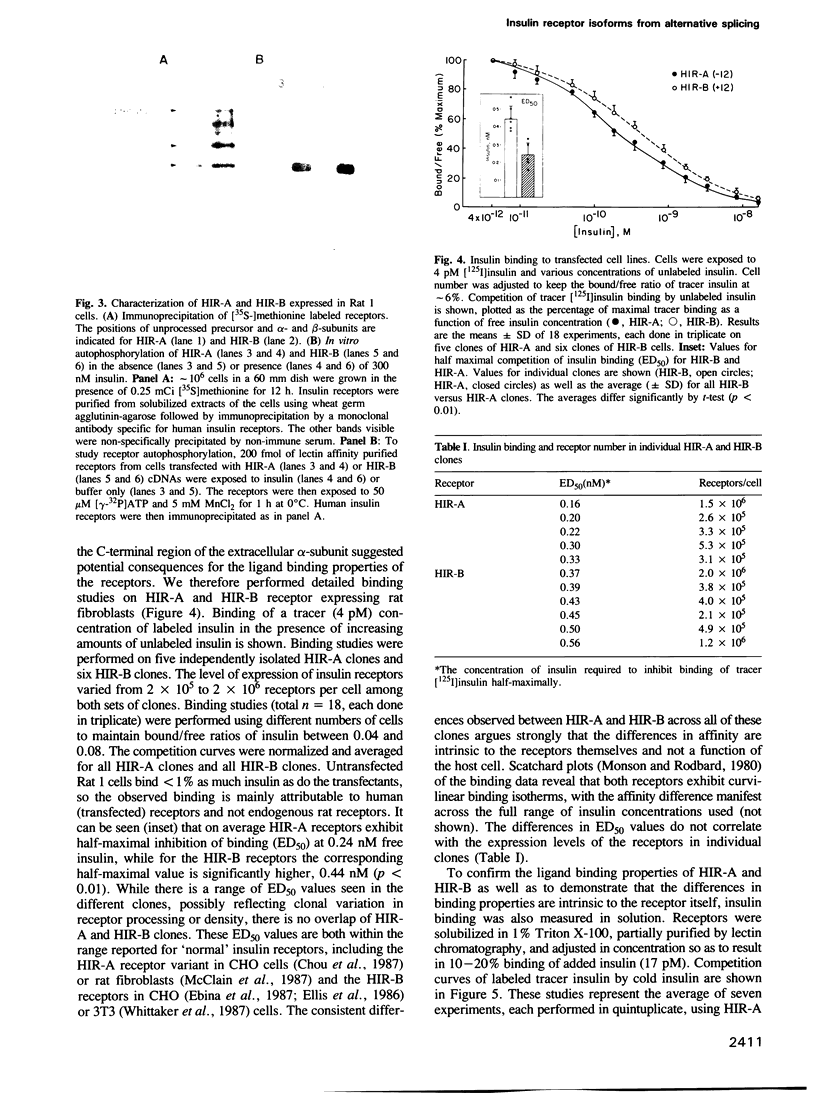
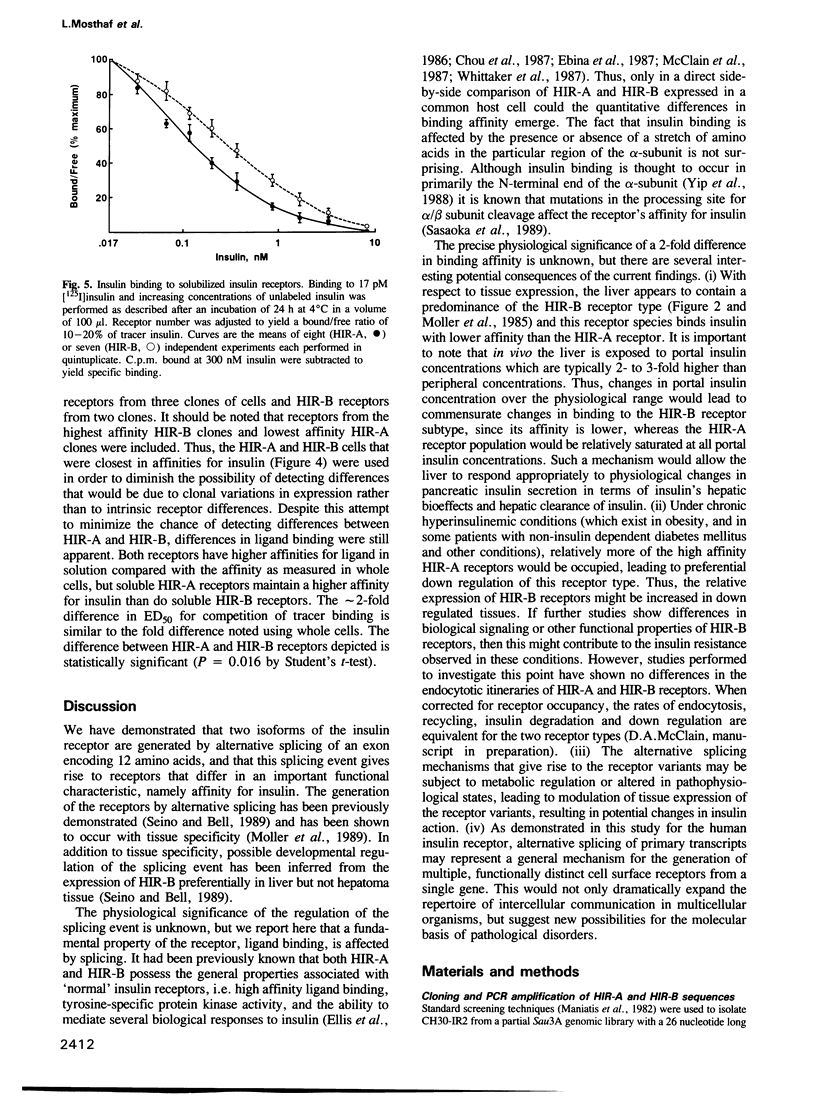

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chou C. K., Dull T. J., Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Lebwohl D., Ullrich A., Rosen O. M. Human insulin receptors mutated at the ATP-binding site lack protein tyrosine kinase activity and fail to mediate postreceptor effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Araki E., Taira M., Shimada F., Mori M., Craik C. S., Siddle K., Pierce S. B., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of lysine residue 1030 in the putative ATP-binding region of the insulin receptor abolishes insulin- and antibody-stimulated glucose uptake and receptor kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):704–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A., Maegawa H., Lee J., Dull T. J., Ulrich A., Olefsky J. M. A mutant insulin receptor with defective tyrosine kinase displays no biologic activity and does not undergo endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14663–14671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller D. E., Yokota A., Caro J. F., Flier J. S. Tissue-specific expression of two alternatively spliced insulin receptor mRNAs in man. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1263–1269. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-8-1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaoka T., Shigeta Y., Takata Y., Sugibayashi M., Hisatomi A., Kobayashi M. Binding specificity and intramolecular signal transmission of uncleaved insulin proreceptor in transformed lymphocytes from a patient with extreme insulin resistance. Diabetologia. 1989 Jun;32(6):371–377. doi: 10.1007/BF00277261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino S., Bell G. I. Alternative splicing of human insulin receptor messenger RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 28;159(1):312–316. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92439-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker J., Okamoto A. K., Thys R., Bell G. I., Steiner D. F., Hofmann C. A. High-level expression of human insulin receptor cDNA in mouse NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5237–5241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip C. C., Hsu H., Patel R. G., Hawley D. M., Maddux B. A., Goldfine I. D. Localization of the insulin-binding site to the cysteine-rich region of the insulin receptor alpha-subunit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):321–329. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]