Abstract
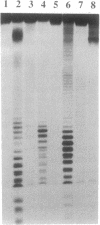
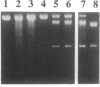
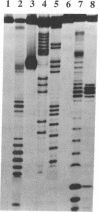
A Lys-84----Cys mutant staphylococcal nuclease was selectively linked to the 5' and/or 3' terminus of a thiol-containing polypyrimidine oligonucleotide via a disulfide bond. The oligonucleotide-staphylococcal nuclease adduct is capable of binding to a homopurine-homopyrimidine region of Watson-Crick duplex DNA by the formation of a triple-helical structure. Upon the addition of Ca2+, the nuclease cleaves DNA at sites adjacent to the homopurine tract. Specific double-strand cleavage occurred predominantly at A + T-rich sites to the 5' side of the homopurine tract for both the 5'-derivatized and the 5',3'-diderivatized nucleases; the 3'-derivatized nuclease gave no cleavage. The cleavage pattern is asymmetric and consists of multiple cleavage sites shifted to the 5' side on each strand, centered at the terminal base pair of the binding site. Microgram amounts of plasmid pDP20 DNA (4433 base pairs) containing a homopurine-homopyrimidine tract were selectively cleaved by a semisynthetic nuclease with greater than 75% efficiency at room temperature within 1 hr. Cleavage reaction conditions were optimized with respect to pH, temperature, reaction times, and reaction components. Semisynthetic nucleases of this type should provide a powerful tool in chromosomal DNA manipulations.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Bond P. J., Selsing E., Smith P. J. Models of triple-stranded polynucleotides with optimised stereochemistry. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2459–2470. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly B. A., Rider P. Chemical synthesis of oligonucleotides containing a free sulphydryl group and subsequent attachment of thiol specific probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4485–4502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey D. R., Pei D., Schultz P. G. Generation of a catalytic sequence-specific hybrid DNase. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8277–8286. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey D. R., Schultz P. G. Generation of a hybrid sequence-specific single-stranded deoxyribonuclease. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1401–1403. doi: 10.1126/science.3685986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton F. A., Hazen E. E., Jr, Legg M. J. Staphylococcal nuclease: proposed mechanism of action based on structure of enzyme-thymidine 3',5'-bisphosphate-calcium ion complex at 1.5-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2551–2555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Fuchs S., Anfinsen C. B. Catalytic properties and specificity of the extracellular nuclease of Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1541–1547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Lomonossoff G. P., Laskey R. A. High sequence specificity of micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2659–2673. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin L. C., Dervan P. B. Recognition of thymine adenine.base pairs by guanine in a pyrimidine triple helix motif. Science. 1989 Sep 1;245(4921):967–971. doi: 10.1126/science.2549639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Altenburger W. Sequence specific cleavage of DNA by micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2643–2658. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser H. E., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific cleavage of double helical DNA by triple helix formation. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):645–650. doi: 10.1126/science.3118463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrouault L., Asseline U., Rivalle C., Thuong N. T., Bisagni E., Giovannangeli C., Le Doan T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific artificial photo-induced endonucleases based on triple helix-forming oligonucleotides. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):358–360. doi: 10.1038/344358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praseuth D., Perrouault L., Le Doan T., Chassignol M., Thuong N., Hélène C. Sequence-specific binding and photocrosslinking of alpha and beta oligodeoxynucleotides to the major groove of DNA via triple-helix formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1349–1353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluka J. P., Horvath S. J., Bruist M. F., Simon M. I., Dervan P. B. Synthesis of a sequence-specific DNA-cleaving peptide. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1129–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.3120311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S. A., Dervan P. B. Site-specific cleavage of a yeast chromosome by oligonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):73–75. doi: 10.1126/science.2195655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker P. W., Hazen E. E., Jr, Cotton F. A. Staphylococcal nuclease reviewed: a prototypic study in contemporary enzymology. I. Isolation; physical and enzymatic properties. Mol Cell Biochem. 1978 Dec 22;22(2-3):67–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00496235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlassov V. V., Gaidamakov S. A., Zarytova V. F., Knorre D. G., Levina A. S., Nikonova A. A., Podust L. M., Fedorova O. S. Sequence-specific chemical modification of double-stranded DNA with alkylating oligodeoxyribonucleotide derivatives. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckermann R. N., Schultz P. G. Site-selective cleavage of structured RNA by a staphylococcal nuclease-DNA hybrid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1766–1770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckermann R., Corey D., Schultz P. Efficient methods for attachment of thiol specific probes to the 3'-ends of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5305–5321. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]