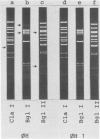
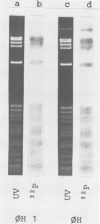
Abstract
Phage øH, a novel virus of the archaebacterium Halobacterium halobium, resembles in size and morphology two other Halobacterium phages. One-step growth curves show a 5.5 h eclipse, a latent period of 7 h, and an apparent burst size of 170. Phage øH contains linear, double-stranded DNA which has a molecular weight of 39 x 106 and a GC content of 65%. A packaging model accounting for the partial circular permutation and terminal redundancy of øH DNA is suggested. Partial homology of øH DNA with the DNA of H. halobium, predominantly with the AT-rich satellite DNA, was observed. The presence of minor restriction fragments of øH DNA which could be removed by purification of phage from single plaques suggests the existence of phage variants with rearranged DNA. A strain of H. halobium containing øH DNA was isolated which is resistant to infection by phage øH.
Keywords: archaebacteria, virus, genome organization, DNA packaging
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E., Hespell R. B., Gibson J., Maniloff J., Dyer T. A., Wolfe R. S., Balch W. E., Tanner R. S., Magrum L. J. The phylogeny of prokaryotes. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):457–463. doi: 10.1126/science.6771870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman R. B., Bertani G. Heat denaturation of P2 bacteriophage DNA: compositional heterogeneity. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):533–549. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90378-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson E. N., Jackson D. A., Deans R. J. EcoRI analysis of bacteriophage P22 DNA packaging. J Mol Biol. 1978 Jan 25;118(3):365–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The determination of the molecular weight of ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophresis. The effects of changes in conformation. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):131–138. doi: 10.1042/bj1130131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. L., McCarthy B. J. Characterization of the deoxyribonucleic acid of various strains of halophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.248-254.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer F., Weidinger G., Goebel W. Characterization of plasmids in halobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):369–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.369-374.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer F., Weidinger G., Goebel W. Genetic variability in Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):375–381. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.375-381.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. pBR322 restriction map derived from the DNA sequence: accurate DNA size markers up to 4361 nucleotide pairs long. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2721–2728. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torsvik T., Dundas I. D. Bacteriophage of Halobacterium salinarium. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):680–681. doi: 10.1038/248680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wais A. C., Kon M., MacDonald R. E., Stollar B. D. Salt-dependent bacteriophage infecting Halobacterium cutirubrum and H. halobium. Nature. 1975 Jul 24;256(5515):314–315. doi: 10.1038/256314a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidinger G., Klotz G., Goebel W. A large plasmid from Halobacterium halobium carrying genetic information for gas vacuole formation. Plasmid. 1979 Jul;2(3):377–386. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]