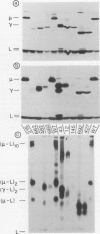
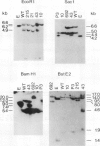
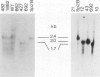
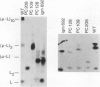
Abstract
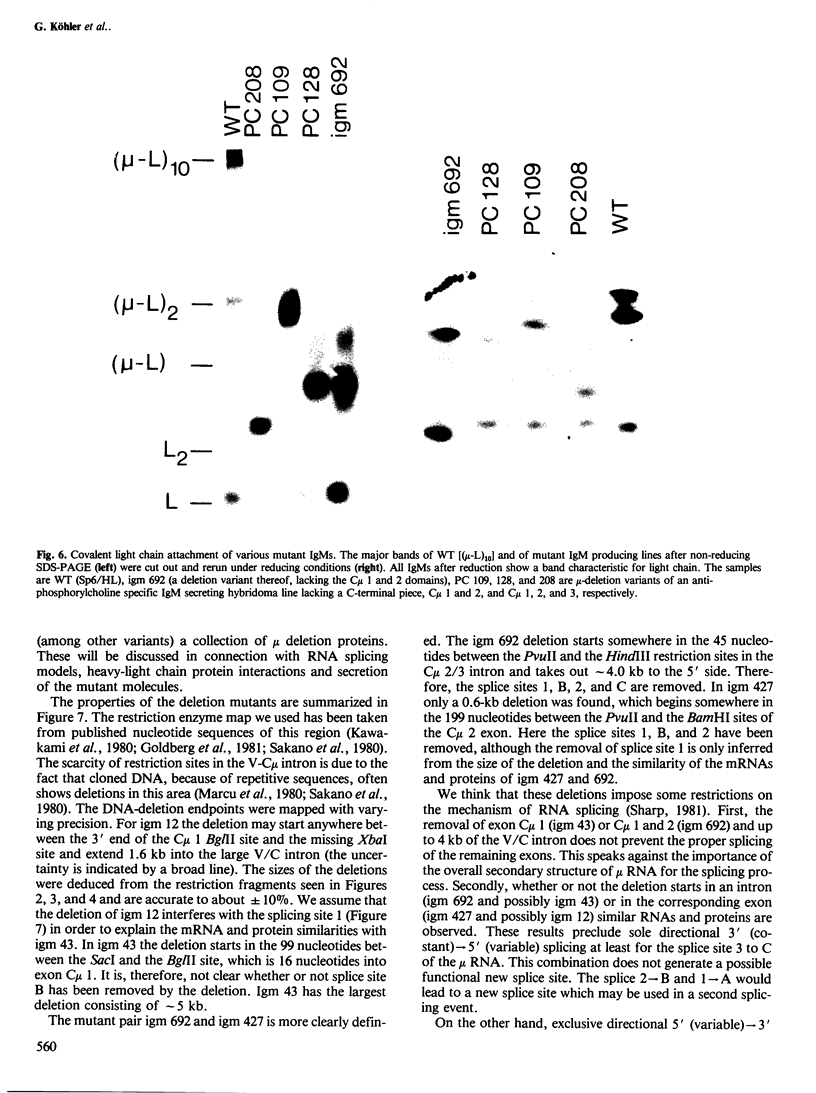
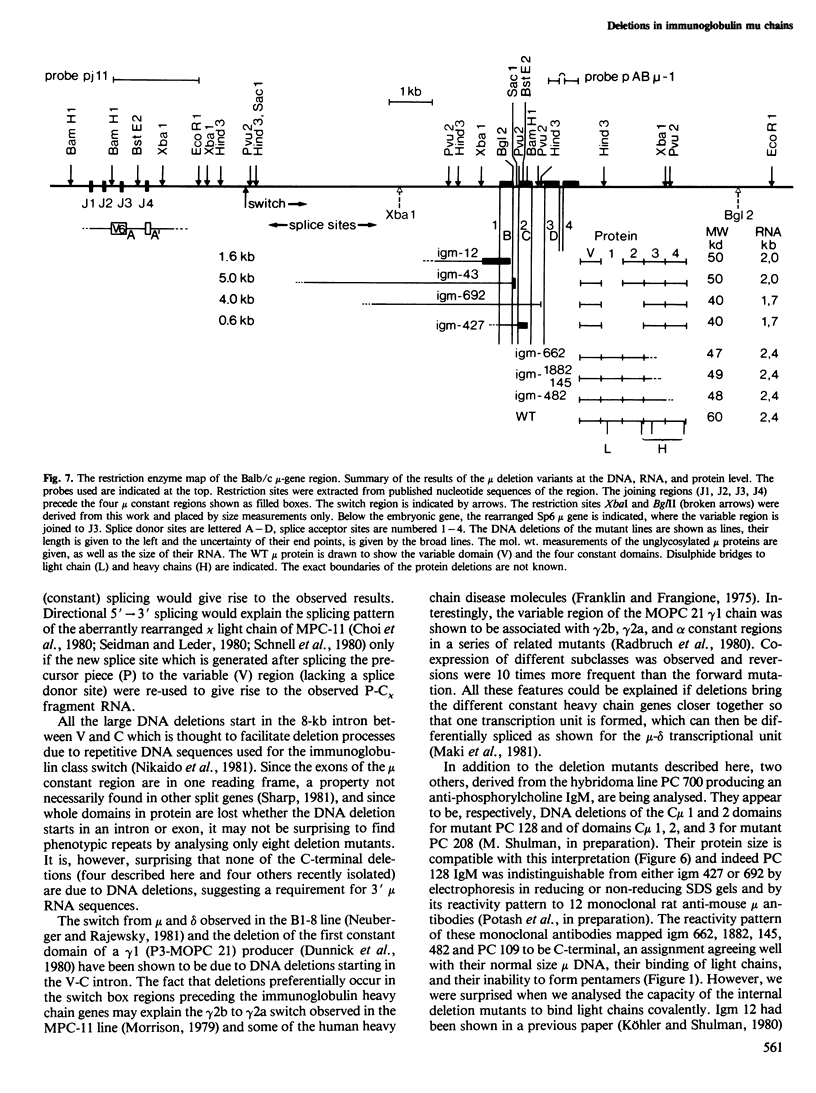
Eight mutant hybridoma lines are described, which synthesize short immunoglobulin mu chains. Four internal deletions were mapped by Southern blot analysis. They are shown to remove DNA from either part or all of the first, and first and second, constant mu exons. The sizes of the deletions range between 0.6 and 5 kb, leaving an equal or unequal number of splice signals. Shorter mu RNA of one size was found irrespective of whether an exon was completely or only partially deleted. These results preclude exclusive 3' (constant region) to 5' (variable region) directional splicing of the mu RNA. No important signals seem to reside in the deleted DNA stretches affecting the transcription or the correct RNA splicing of the remaining exons. The internal mu protein deletions revealed unusual covalent light chain attachment demonstrating functional homology between the first (normally used) and fourth mu constant domain. The other mu protein deletions (10, 11, and 12 kd) involved neither gross DNA nor RNA lesions and are considered to be due to premature chain termination. Since secretion is found in most of the mutant IgM-producing lines, no single one of the four mu constant domains (including the C-terminal one which contains the so-called secretory piece) is necessary for secretion.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Bothwell A. L., Knapp M., Siden E., Mather E., Koshland M., Baltimore D. Synthesis of secreted and membrane-bound immunoglobulin mu heavy chains is directed by mRNAs that differ at their 3' ends. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90615-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altenburger W., Neumaier P. S., Steinmetz M., Zachau H. G. DNA sequence of the constant gene region of the mouse immunoglobulin kappa chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):971–981. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard O., Hozumi N., Tonegawa S. Sequences of mouse immunoglobulin light chain genes before and after somatic changes. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1133–1144. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90041-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell A. L., Paskind M., Reth M., Imanishi-Kari T., Rajewsky K., Baltimore D. Heavy chain variable region contribution to the NPb family of antibodies: somatic mutation evident in a gamma 2a variable region. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):625–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90089-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brack C., Hirama M., Lenhard-Schuller R., Tonegawa S. A complete immunoglobulin gene is created by somatic recombination. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows P., LeJeune M., Kearney J. F. Evidence that murine pre-B cells synthesise mu heavy chains but no light chains. Nature. 1979 Aug 30;280(5725):838–840. doi: 10.1038/280838a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi E., Kuehl M., Wall R. RNA splicing generates a variant light chain from an aberrantly rearranged kappa gene. Nature. 1980 Aug 21;286(5775):776–779. doi: 10.1038/286776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews S., Griffin J., Huang H., Calame K., Hood L. A single VH gene segment encodes the immune response to phosphorylcholine: somatic mutation is correlated with the class of the antibody. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90231-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnick W., Rabbitts T. H., Milstein C. An immunoglobulin deletion mutant with implications for the heavy-chain switch and RNA splicing. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):669–675. doi: 10.1038/286669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Huang H., Davis M., Calame K., Hood L. An immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene is generated from three segments of DNA: VH, D and JH. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):981–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90089-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Rogers J., Davis M., Calame K., Bond M., Wall R., Hood L. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Early P., Rogers J., Davis M., Calame K., Bond M., Wall R., Hood L. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin mu gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90617-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin E. C., Frangione B. Structural variants of human and murine immunoglobulins. Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1975;4:89–126. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8930-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M., Kemp D. J., Tyler B. M., Adams J. M., Cory S. Intervening sequences divide the gene for the constant region of mouse immunoglobulin mu chains into segments, each encoding a domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):554–558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlyn P. H., Gait M. J., Milstein C. Complete sequence of an immunoglobulin mRNA using specific priming and the dideoxynucleotide method of RNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 25;9(18):4485–4494. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.18.4485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengartner H., Meo T., Müller E. Assignment of genes for immunoglobulin kappa and heavy chains to chromosomes 6 and 12 in mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4494–4498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman S., Kornfeld S. Effect of tunicamycin on IgM, IgA, and IgG secretion by mouse plasmacytoma cells. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):990–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami T., Takahashi N., Honjo T. Complete nucleotide sequence of mouse immunoglobulin mu gene and comparison with other immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3933–3945. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehry M., Ewald S., Douglas R., Sibley C., Raschke W., Fambrough D., Hood L. The immunoglobulin mu chains of membrane-bound and secreted IgM molecules differ in their C-terminal segments. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):393–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90476-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kehry M., Sibley C., Fuhrman J., Schilling J., Hood L. E. Amino acid sequence of a mouse immunoglobulin mu chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2932–2936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Hengartner H., Shulman M. J. Immunoglobulin production by lymphocyte hybridomas. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Feb;8(2):82–88. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki R., Roeder W., Traunecker A., Sidman C., Wabl M., Raschke W., Tonegawa S. The role of DNA rearrangement and alternative RNA processing in the expression of immunoglobulin delta genes. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):353–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90325-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Banerji J., Penncavage N. A., Lang R., Arnheim N. 5' flanking region of immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes displays length heterogeneity in germlines of inbred mouse strains. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. The nucleotide sequence of a 5.5-kilobase DNA segment containing the mouse kappa immunoglobulin J and C region genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5116–5120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison S. L. Murine heavy chain disease. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Mar;8(3):194–199. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison S. L. Sequentially derived mutants of the constant region of the heavy chain of murine immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):793–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S., Rajewsky K. Switch from hapten-specific immunoglobulin M to immunoglobulin D secretion in a hybrid mouse cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1138–1142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido T., Nakai S., Honjo T. Switch region of immunoglobulin Cmu gene is composed of simple tandem repetitive sequences. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):845–848. doi: 10.1038/292845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. Isolation of variants of mouse myeloma X63 that express changed immunoglobulin class. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2909–2913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Maki R., Kurosawa Y., Roeder W., Tonegawa S. Two types of somatic recombination are necessary for the generation of complete immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):676–683. doi: 10.1038/286676a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell H., Steinmetz M., Zachau H. G., Schechter I. An unusual translocation of immunoglobulin gene segments in variants of the mouse myeloma MPC11. Nature. 1980 Jul 10;286(5769):170–173. doi: 10.1038/286170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Leder P. A mutant immunoglobulin light chain is formed by aberrant DNA- and RNA-splicing events. Nature. 1980 Aug 21;286(5775):779–783. doi: 10.1038/286779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligmann M., Mihaesco E., Preud'homme J. L., Danon F., Brouet J. C. Heavy chain diseases: current findings and concepts. Immunol Rev. 1979;48:145–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selsing E., Storb U. Somatic mutation of immunoglobulin light-chain variable-region genes. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):47–58. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90230-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Speculations on RNA splicing. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. B lymphocyte differentiation and the control of IgM mu chain expression. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C., Potash M. J., Köhler G. Roles of protein and carbohydrate in glycoprotein processing and secretion. Studies using mutants expressing altered IgM mu chains. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13180–13187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svasti J., Milstein C. The complete amino acid sequence of a mouse kappa light chain. Biochem J. 1972 Jun;128(2):427–444. doi: 10.1042/bj1280427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]