Abstract
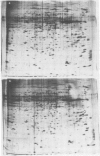
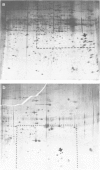
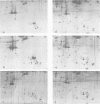
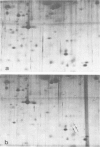
The protein content of various Drosophila imaginal discs was analysed by two-dimensional electrophoresis followed by silver-staining. Three proteins, identified as tropomyosins α and β and actin I, are more abundant in the metathoracic discs (haltere and third leg) than in the mesothoracic discs (wing and second leg). In the case of the wing disc, these proteins are probably contributed by the adepithelial (muscle precursor) cells, as indicated by their non-uniform localisation within the disc. Mutations in the bithorax complex have no effect on the difference between second and third leg discs. We conclude that there is a segmental difference in the protein content of homologous discs, that this difference is probably localized in the adepithelial cells, and that it is not under the direct control of known alleles of the bithorax complex.
Keywords: bithorax complex, Drosophila, imaginal discs, contractile proteins, segmental determination
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Daubas P., Caput D., Buckingham M., Gros F. A comparison between the synthesis of contractile proteins and the accumulation of their translatable mRNAs during calf myoblast differentiation. Dev Biol. 1981 May;84(1):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R. M., Adler P. N. Protein synthesis and accumulation in Drosophila melanogaster imaginal discs: identification of a protein with a nonrandom spatial distribution. Dev Biol. 1982 Feb;89(2):273–286. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence P. A. Cell lineage of the thoracic muscles of Drosophila. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):493–503. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90166-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis E. B. A gene complex controlling segmentation in Drosophila. Nature. 1978 Dec 7;276(5688):565–570. doi: 10.1038/276565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morata G., Lawrence P. A. Homoeotic genes, compartments and cell determination in Drosophila. Nature. 1977 Jan 20;265(5591):211–216. doi: 10.1038/265211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers M. E., Shearn A. Patterns of protein synthesis in imaginal discs of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):915–921. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Drosophila genome organization: conserved and dynamic aspects. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:219–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storti R. V., Horovitch S. J., Scott M. P., Rich A., Pardue M. L. Myogenesis in primary cell cultures from Drosophila melanogaster: protein synthesis and actin heterogeneity during development. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):589–598. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieschaus E., Gehring W. Clonal analysis of primordial disc cells in the early embryo of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1976 Jun;50(2):249–263. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90150-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]