Abstract
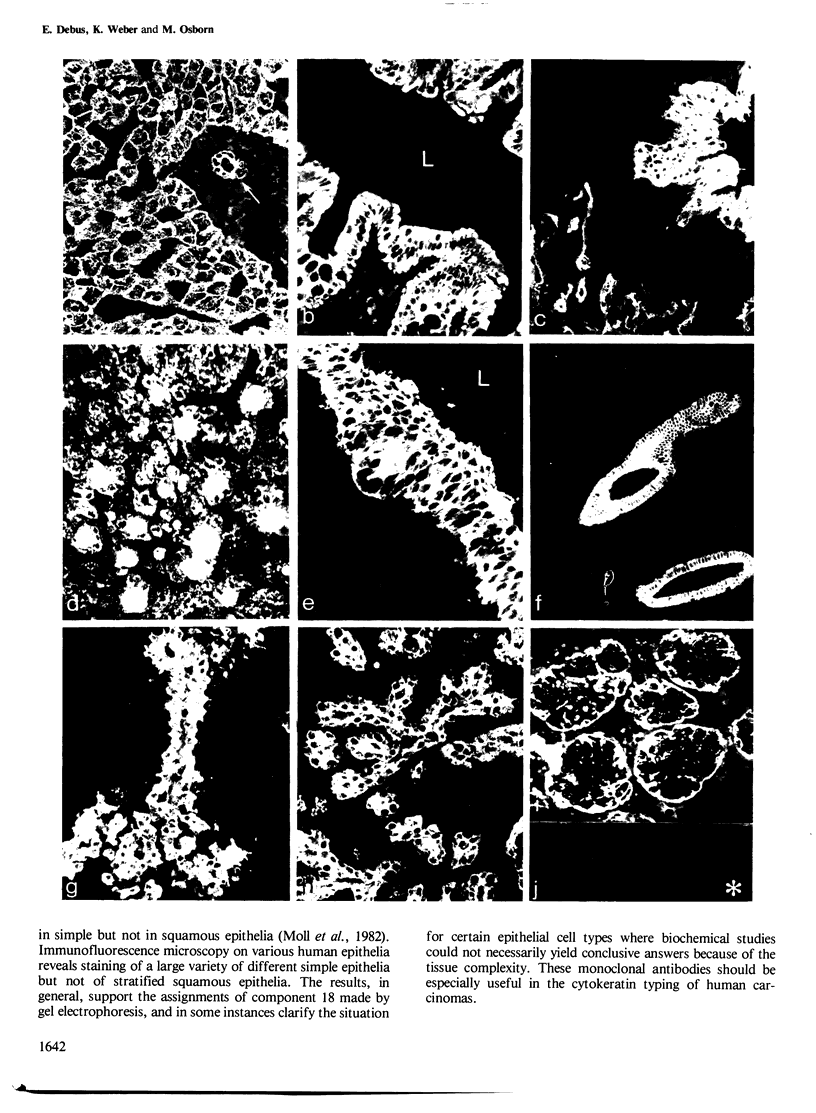
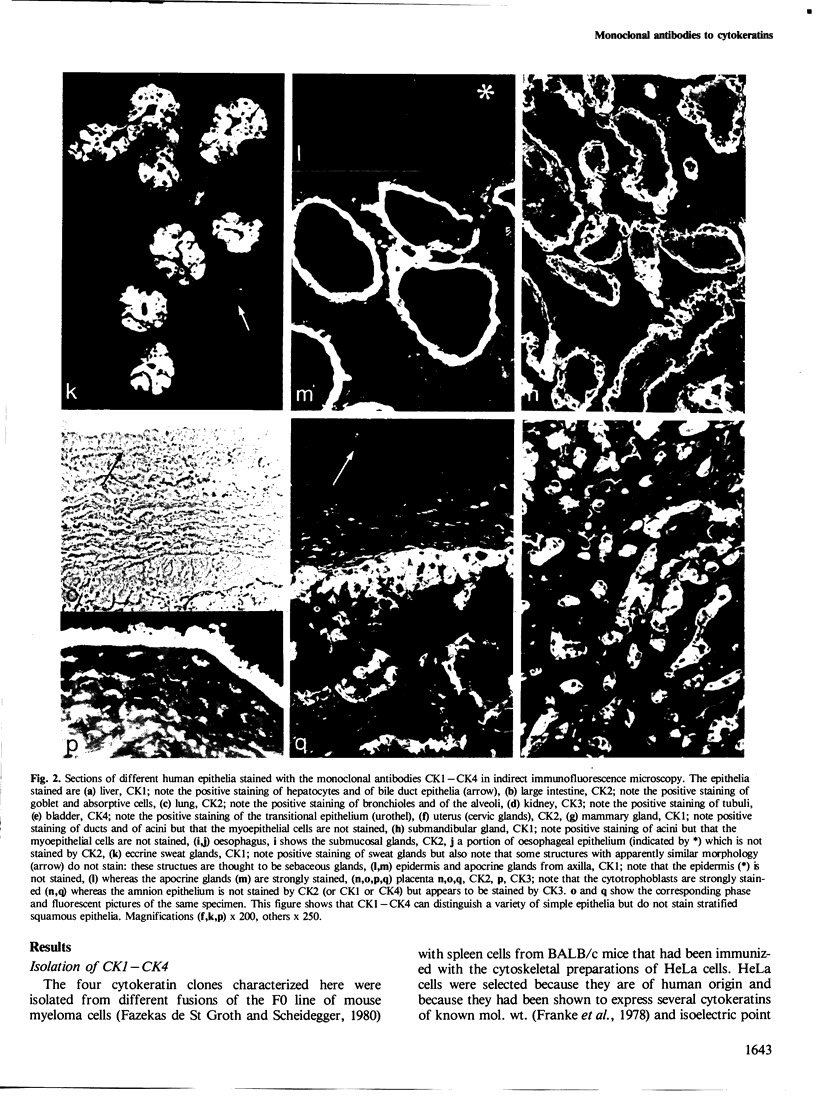
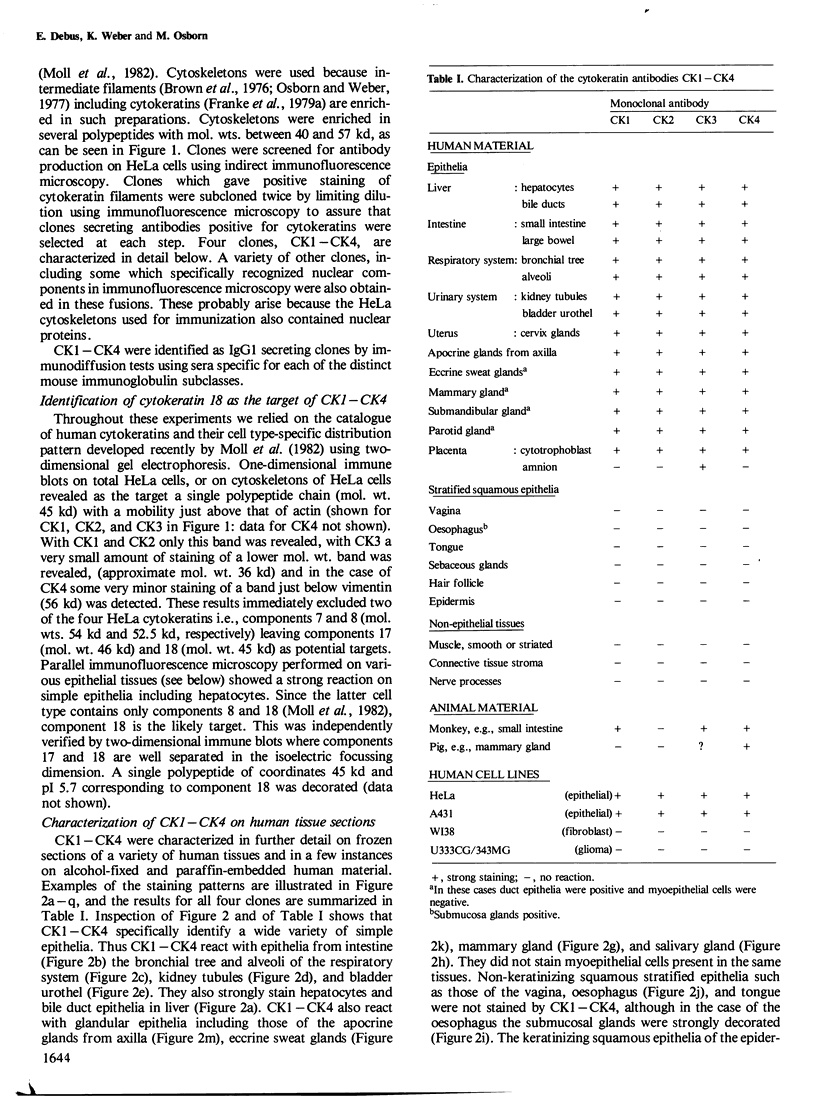
Four monoclonal antibodies designated CK1 - CK4 were obtained from fusions of mouse myeloma F0 cells with spleen cells from BALB/c mice immunized with cytoskeletal preparations made by treatment of human HeLa cells with non-ionic detergents. These IgG1 type antibodies all recognize, in immune blots, cytokeratin 18 (45 kd, pI 5.7) in the catalogue of 19 human cytokeratin species developed by Moll et al. (1982). Immunofluorescence microscopy on human material shows that CK1 - CK4 stain a wide variety of simple epithelia (e.g., intestine, respiratory and urinary systems, liver, glandular epithelia) but do not stain stratified squamous epithelia (e.g., oesophagus, epidermis) or non-epithelial cells. The immunofluorescence results, developed mainly by gel electrophoresis, support the concept of cytokeratin divergence in different epithelia and clarify, for cytokeratin 18, some unsolved problems posed by high tissue complexity. CK2 appears specific for human, CK1 and CK3 for primates, while CK4 shows broad cross-species reactivity. Thus, CK1 - CK4 appear to be valuable tools for cytokeratin typing and initial experiments also suggest that they can be used to further subdivide human tumours of epithelial origin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmannsberger M., Osborn M., Hölscher A., Schauer A., Weber K. The distribution of keratin type intermediate filaments in human breast cancer. An immunohistological study. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1981;37(3):277–284. doi: 10.1007/BF02892576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmannsberger M., Osborn M., Treuner J., Hölscher A., Weber K., Shauer A. Diagnosis of human childhood rhabdomyosarcoma of antibodies to desmin, the structural protein of muscle specific intermediate filaments. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1982;39(2):203–215. doi: 10.1007/BF02892848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmannsberger M., Weber K., Hölscher A., Schauer A., Osborn M. Antibodies to intermediate filaments as diagnostic tools: human gastrointestinal carcinomas express prekeratin. Lab Invest. 1982 May;46(5):520–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. S., Fellini S. A., Croop J. M., Otto J. J., Bryan J., Holtzer H. Differences among 100-A filamentilament subunits from different cell types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4364–4368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S., Levinson W., Spudich J. A. Cytoskeletal elements of chick embryo fibroblasts revealed by detergent extraction. J Supramol Struct. 1976;5(2):119–130. doi: 10.1002/jss.400050203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus E., Flügge G., Weber K., Osborn M. A monoclonal antibody specific for the 200 K polypeptide of the neurofilament triplet. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):41–45. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01121.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodemont H. J., Soriano P., Quax W. J., Ramaekers F., Lenstra J. A., Groenen M. A., Bernardi G., Bloemendal H. The genes coding for the cytoskeletal proteins actin and vimentin in warm-blooded vertebrates. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):167–171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01142.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Appelhans B., Schmid E., Freudenstein C., Osborn M., Weber K. Identification and characterization of epithelial cells in mammalian tissues by immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies to prekeratin. Differentiation. 1979;15(1):7–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb01030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Moll R., Winter S., Schmid E., Engelbrecht I., Denk H., Krepler R., Platzer B. Diversity of cytokeratins. Differentiation specific expression of cytokeratin polypeptides in epithelial cells and tissues. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 25;153(4):933–959. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Grund C., Geiger B. Intermediate filament proteins in nonfilamentous structures: transient disintegration and inclusion of subunit proteins in granular aggregates. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Osborn M., Weber K. Different intermediate-sized filaments distinguished by immunofluorescence microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5034–5038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Weber K., Osborn M. HeLa cells contain intermediate-sized filaments of the prekeratin type. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Jan;118(1):95–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90587-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. Changes in keratin gene expression during terminal differentiation of the keratinocyte. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Kapanci Y., Barazzone P., Franke W. W. Immunochemical identification of intermediate-sized filaments in human neoplastic cells. A diagnostic aid for the surgical pathologist. Am J Pathol. 1981 Sep;104(3):206–216. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Weber K. Proteinchemical characterization of three structurally distinct domains along the protofilament unit of desmin 10 nm filaments. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Plessmann U., Weber K. Related amino acid sequences in neurofilaments and non-neural intermediate filaments. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):448–450. doi: 10.1038/296448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Comparison of the proteins of two immunologically distinct intermediate-sized filaments by amino acid sequence analysis: desmin and vimentin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4120–4123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Fuchs E., Watt F. Differentiated structural components of the keratinocyte. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):293–301. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D., Geisler N., Weber K. A periodic ultrastructure in intermediate filaments. J Mol Biol. 1982 Feb 25;155(2):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90444-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B., Kupfer H., Eshhar Z., Geiger B. Reorganization of arrays of prekeratin filaments during mitosis. Immunofluorescence microscopy with multiclonal and monoclonal prekeratin antibodies. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Aug;134(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90427-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson B. W., Grund C., Winter S., Franke W. W., Illmensee K. Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis. II. Epithelial differentiation and intermediate-sized filaments in early postimplantation embryos. Differentiation. 1981;20(3):203–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1981.tb01177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane E. B., Goodman S. L., Trejdosiewicz L. K. Disruption of the keratin filament network during epithelial cell division. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1365–1372. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane E. B. Monoclonal antibodies provide specific intramolecular markers for the study of epithelial tonofilament organization. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):665–673. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leim R. K., Keith C. H., Leterrier J. F., Trenkner E., Shelanski M. L. Chemistry and biology of neuronal and glial intermediate filaments. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):341–350. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstone L. M., McGuire J. Different polypeptides form the intermediate filaments in bovine hoof and esophageal epithelium and in aortic endothelium. J Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;88(2):312–316. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.2.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Franke W., Weber K. Direct demonstration of the presence of two immunologically distinct intermediate-sized filament systems in the same cell by double immunofluorescence microscopy. Vimentin and cytokeratin fibers in cultured epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Jan;125(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90186-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Geisler N., Shaw G., Sharp G., Weber K. Intermediate filaments. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):413–429. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. The detertent-resistant cytoskeleton of tissue culture cells includes the nucleus and the microfilament bundles. Exp Cell Res. 1977 May;106(2):339–349. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Wantz M. L., Idler W. W. O-phosphoserine content of intermediate filament subunits. Biochemistry. 1982 Jan 5;21(1):177–183. doi: 10.1021/bi00530a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Shih C., Green H. Keratin cytoskeletons in epithelial cells of internal organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2813–2817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng S. C., Jarvinen M. J., Nelson W. G., Huang J. W., Woodcock-Mitchell J., Sun T. T. Correlation of specific keratins with different types of epithelial differentiation: monoclonal antibody studies. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90234-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Geisler N. The structural relation between intermediate filament proteins in living cells and the alpha-keratins of sheep wool. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1155–1160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]