Abstract
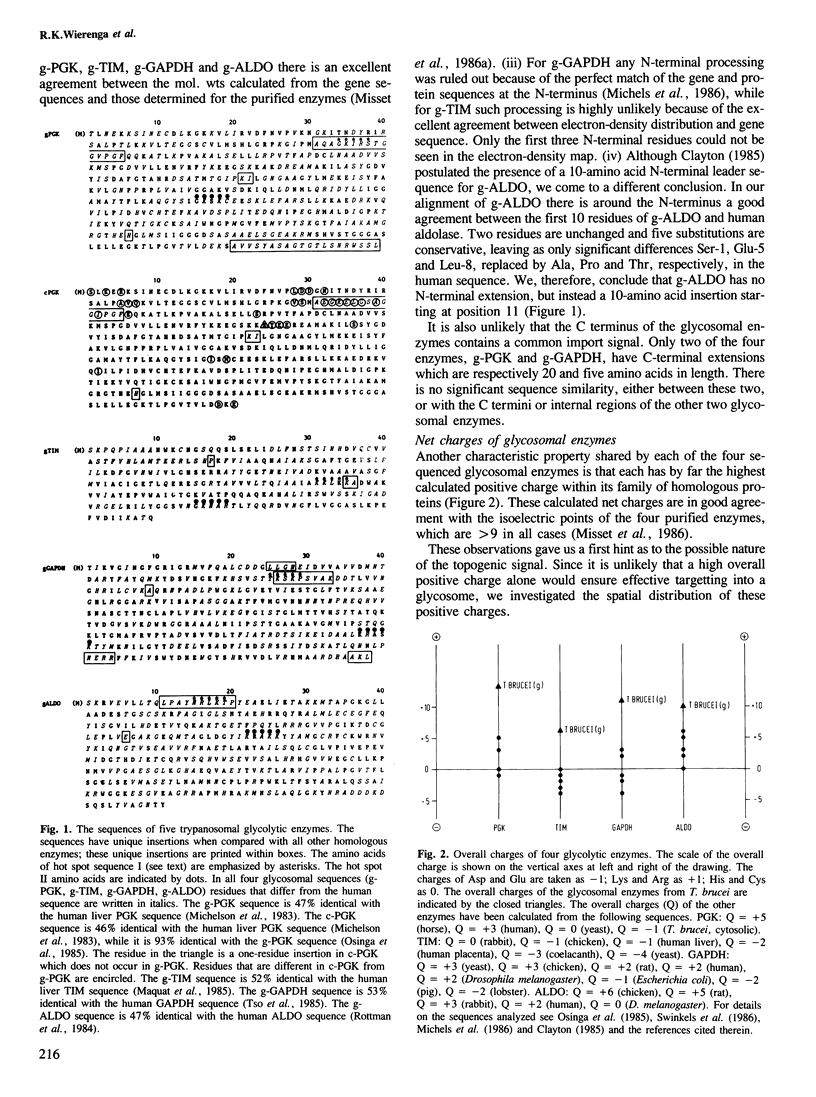
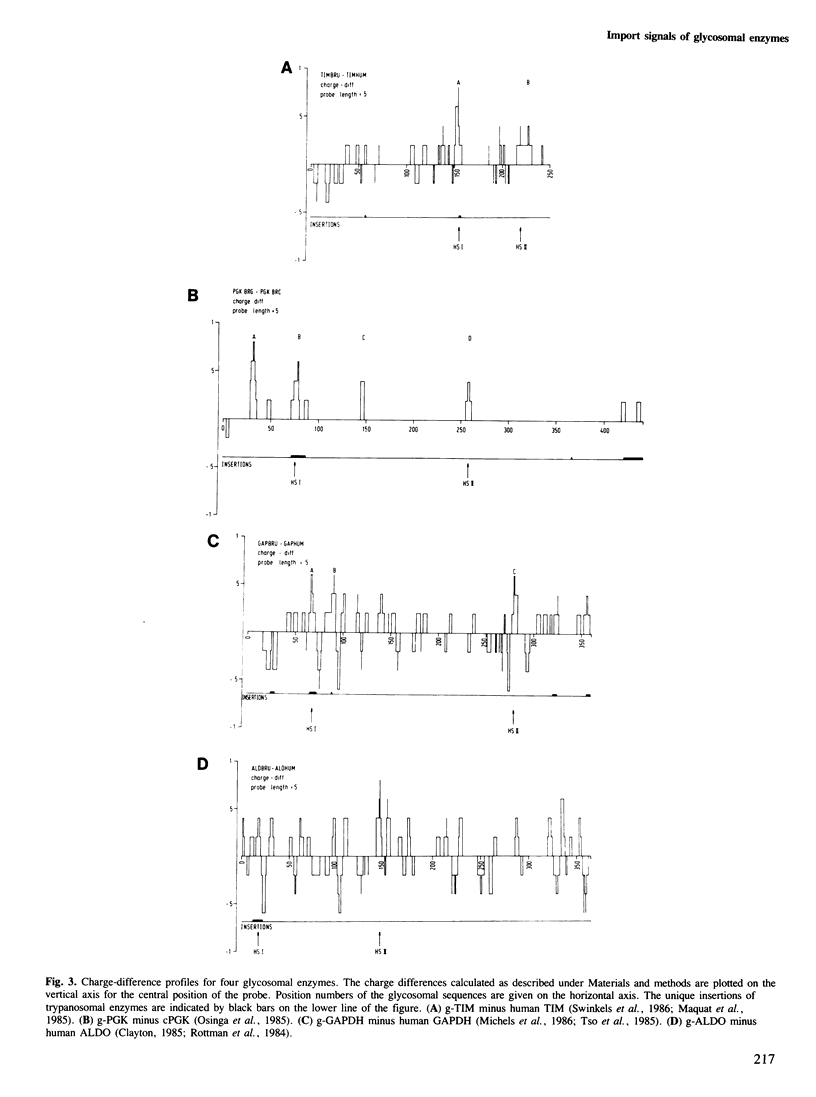
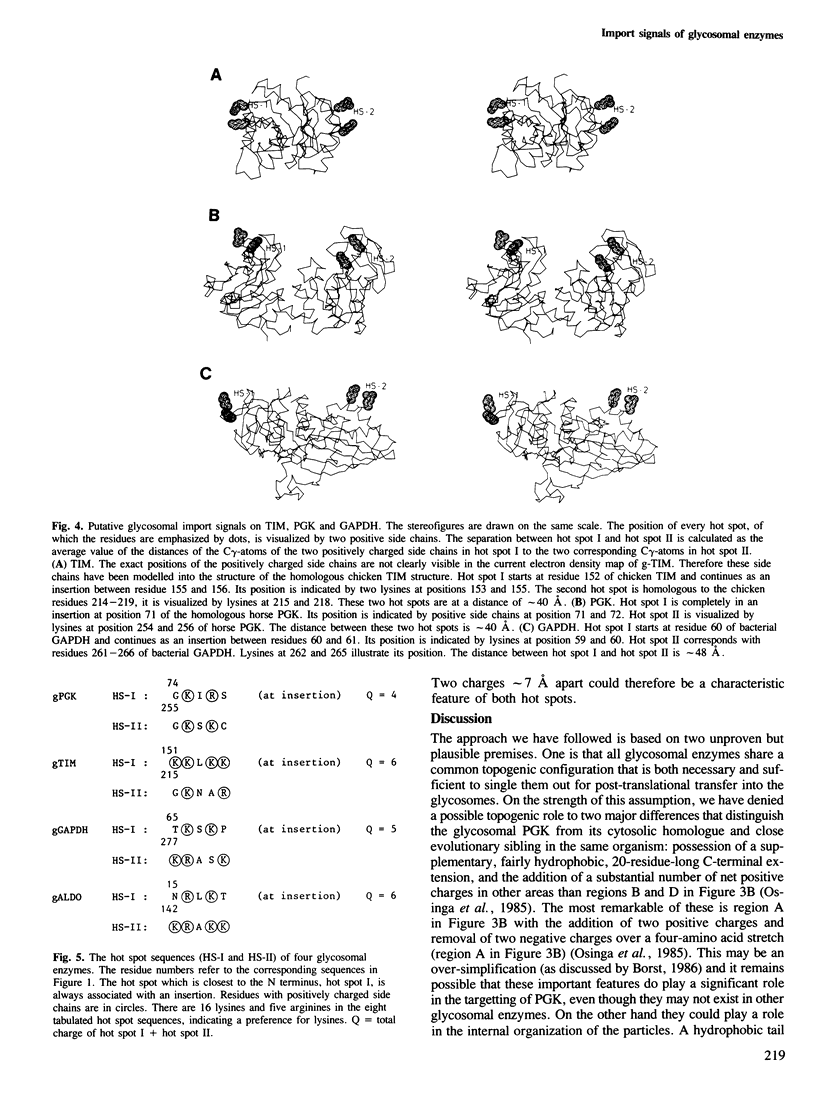
In Trypanosoma brucei, a major pathogenic protozoan parasite of Central Africa, a number of glycolytic enzymes present in the cytosol of other organisms are uniquely segregated in a microbody-like organelle, the glycosome, which they are believed to reach post-translationally after being synthesized by free ribosomes in the cytosol. In a search for possible topogenic signals responsible for import into glycosomes we have compared the amino acid sequences of four glycosomal enzymes: triosephosphate isomerase (TIM), glyceraldehyde-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) and aldolase (ALDO), with each other and with their cytosolic counterparts. Each of these enzymes contains a marked excess of positive charges, distributed in two or more clusters along the polypeptide chain. Modelling of the three-dimensional structures of TIM, PGK and GAPDH using the known structural coordinates of homologous enzymes from other organisms indicates that all three may have in common two 'hot spots' about 40 A apart, which themselves include a pair of basic amino acid residues separated by a distance of about 7 A. The sequence of glycosomal ALDO, for which no three-dimensional information is available, is compatible with the presence of the same configuration on the surface of this enzyme. We propose that this feature plays an essential role in the import of enzymes into glycosomes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alber T., Banner D. W., Bloomer A. C., Petsko G. A., Phillips D., Rivers P. S., Wilson I. A. On the three-dimensional structure and catalytic mechanism of triose phosphate isomerase. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Jun 26;293(1063):159–171. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aman R. A., Kenyon G. L., Wang C. C. Cross-linking of the enzymes in the glycosome of Trypanosoma brucei. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6966–6973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banner D. W., Bloomer A. C., Petsko G. A., Phillips D. C., Pogson C. I., Wilson I. A., Corran P. H., Furth A. J., Milman J. D., Offord R. E. Structure of chicken muscle triose phosphate isomerase determined crystallographically at 2.5 angstrom resolution using amino acid sequence data. Nature. 1975 Jun 19;255(5510):609–614. doi: 10.1038/255609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P. How proteins get into microbodies (peroxisomes, glyoxysomes, glycosomes). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 May 5;866(4):179–203. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(86)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner-Holzach O., Smit J. D. Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic data for fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase from Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11747–11749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Lesk A. M. The relation between the divergence of sequence and structure in proteins. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):823–826. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04288.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E. Structure and regulated expression of genes encoding fructose biphosphate aldolase in Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2997–3003. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04035.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairlamb A. H., Opperdoes F. R., Borst P. New approach to screening drugs for activity against African trypanosomes. Nature. 1977 Jan 20;265(5591):270–271. doi: 10.1038/265270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. T., Opperdoes F. R. The occurrence of glycosomes (microbodies) in the promastigote stage of four major Leishmania species. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1984 Oct;13(2):159–172. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(84)90110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie A. G., Wonacott A. J. Structural evidence for ligand-induced sequential conformational changes in glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 25;178(3):743–772. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90250-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E., Chilcote R., Ryan P. M. Human triosephosphate isomerase cDNA and protein structure. Studies of triosephosphate isomerase deficiency in man. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3748–3753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrett M. Primary structure of 3-phosphoglycerate kinase from horse muscle. II. Amino acid sequence of cyanogen bromide peptides CB1-CB4 and CB6-CB14, sequence of methionine-containing regions, and complete sequence of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10293–10305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michels P. A., Poliszczak A., Osinga K. A., Misset O., Van Beeumen J., Wierenga R. K., Borst P., Opperdoes F. R. Two tandemly linked identical genes code for the glycosomal glyceraldehyde-phosphate dehydrogenase in Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1049–1056. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04321.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Markham A. F., Orkin S. H. Isolation and DNA sequence of a full-length cDNA clone for human X chromosome-encoded phosphoglycerate kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):472–476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misset O., Bos O. J., Opperdoes F. R. Glycolytic enzymes of Trypanosoma brucei. Simultaneous purification, intraglycosomal concentrations and physical properties. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Jun 2;157(2):441–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09687.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misset O., Opperdoes F. R. Simultaneous purification of hexokinase, class-I fructose-bisphosphate aldolase, triosephosphate isomerase and phosphoglycerate kinase from Trypanosoma brucei. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 2;144(3):475–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori N., Singer-Sam J., Riggs A. D. Evolutionary conservation of the substrate-binding cleft of phosphoglycerate kinases. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 18;204(2):313–317. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80835-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nwagwu M., Opperdoes F. R. Regulation of glycolysis in Trypanosoma brucei: hexokinase and phosphofructokinase activity. Acta Trop. 1982 Mar;39(1):61–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oduro K. K., Bowman I. B., Flynn I. W. Trypanosoma brucei: preparation and some properties of a multienzyme complex catalysing part of the glycolytic pathway. Exp Parasitol. 1980 Oct;50(2):240–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(80)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opperdoes F. R. Biochemical peculiarities of trypanosomes, African and South American. Br Med Bull. 1985 Apr;41(2):130–136. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opperdoes F. R., Borst P. Localization of nine glycolytic enzymes in a microbody-like organelle in Trypanosoma brucei: the glycosome. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 15;80(2):360–364. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80476-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osinga K. A., Swinkels B. W., Gibson W. C., Borst P., Veeneman G. H., Van Boom J. H., Michels P. A., Opperdoes F. R. Topogenesis of microbody enzymes: a sequence comparison of the genes for the glycosomal (microbody) and cytosolic phosphoglycerate kinases of Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3811–3817. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04152.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottmann W. H., Tolan D. R., Penhoet E. E. Complete amino acid sequence for human aldolase B derived from cDNA and genomic clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2738–2742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinkels B. W., Gibson W. C., Osinga K. A., Kramer R., Veeneman G. H., van Boom J. H., Borst P. Characterization of the gene for the microbody (glycosomal) triosephosphate isomerase of Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1291–1298. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04358.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sygusch J., Boulet H., Beaudry D. Structure of rabbit muscle aldolase at low resolution. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15286–15290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. B., Berghausen H., Heyworth P., Messenger N., Rees L. J., Gutteridge W. E. Subcellular localization of some glycolytic enzymes in parasitic flagellated protozoa. Int J Biochem. 1980;11(2):117–120. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90243-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Kao T. H., Reece K. S., Wu R. Isolation and characterization of rat and human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs: genomic complexity and molecular evolution of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2485–2502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Carne A. F., Runswick M. J., Bridgen J., Harris J. I. D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Complete amino-acid sequence of the enzyme from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):549–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., Hol W. G., Misset O., Opperdoes F. R. Preliminary crystallographic studies of triosephosphate isomerase from the blood parasite Trypanosoma brucei brucei. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):487–490. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


