Abstract
Measles virus (MV) is a negative strand RNA virus which usually causes acute disease, but in rare cases its persistence in the human brain induces the lethal disease subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE). The transcription of MV and of a defective MV derived from autopsy material of a SSPE case was studied in cultured cells. In the lytic infection the levels of the MV mRNAs decreased progressively with the distance of the six cognate genes from the 3' end of the genome, reflecting transcriptional attenuation at every gene junction. Transcripts covering two or three adjacent genes accounted for up to 20% of single gene transcripts; incidentally the MV intergenic transcription signals were found to be less conserved than the analogous signals of other negative strand RNA viruses. Although the analysed SSPE-derived defective MV showed a localized transcription defect at the phosphoprotein--matrix gene junction (substitution of the mRNAs by readthrough transcripts), the corresponding intergenic 'consensus' sequence and the surrounding nucleotides were not altered. This implies that factor(s) involved in the transcription of this defective SSPE virus fail to recognize this particular signal sequence, a constellation which in this and other cases might be causally related to the development of MV persistence.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alkhatib G., Briedis D. J. The predicted primary structure of the measles virus hemagglutinin. Virology. 1986 Apr 30;150(2):479–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baczko K., Carter M. J., Billeter M., ter Meulen V. Measles virus gene expression in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Virus Res. 1984 Oct;1(7):585–595. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90015-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baczko K., Liebert U. G., Billeter M., Cattaneo R., Budka H., ter Meulen V. Expression of defective measles virus genes in brain tissues of patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):472–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.472-478.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett P. N., Koschel K., Carter M., ter Meulen V. Effect of measles virus antibodies on a measles SSPE virus persistently infected C6 rat glioma cell line. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1411–1421. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini W. J., Englund G., Richardson C. D., Rozenblatt S., Lazzarini R. A. Matrix genes of measles virus and canine distemper virus: cloning, nucleotide sequences, and deduced amino acid sequences. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):408–416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.408-416.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellini W. J., Englund G., Rozenblatt S., Arnheiter H., Richardson C. D. Measles virus P gene codes for two proteins. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):908–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.908-919.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter M. A., Baczko K., Schmid A., Ter Meulen V. Cloning of DNA corresponding to four different measles virus genomic regions. Virology. 1984 Jan 15;132(1):147–159. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90099-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter M. J., Willcocks M. M., ter Meulen V. Defective translation of measles virus matrix protein in a subacute sclerosing panencephalitis cell line. Nature. 1983 Sep 8;305(5930):153–155. doi: 10.1038/305153a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
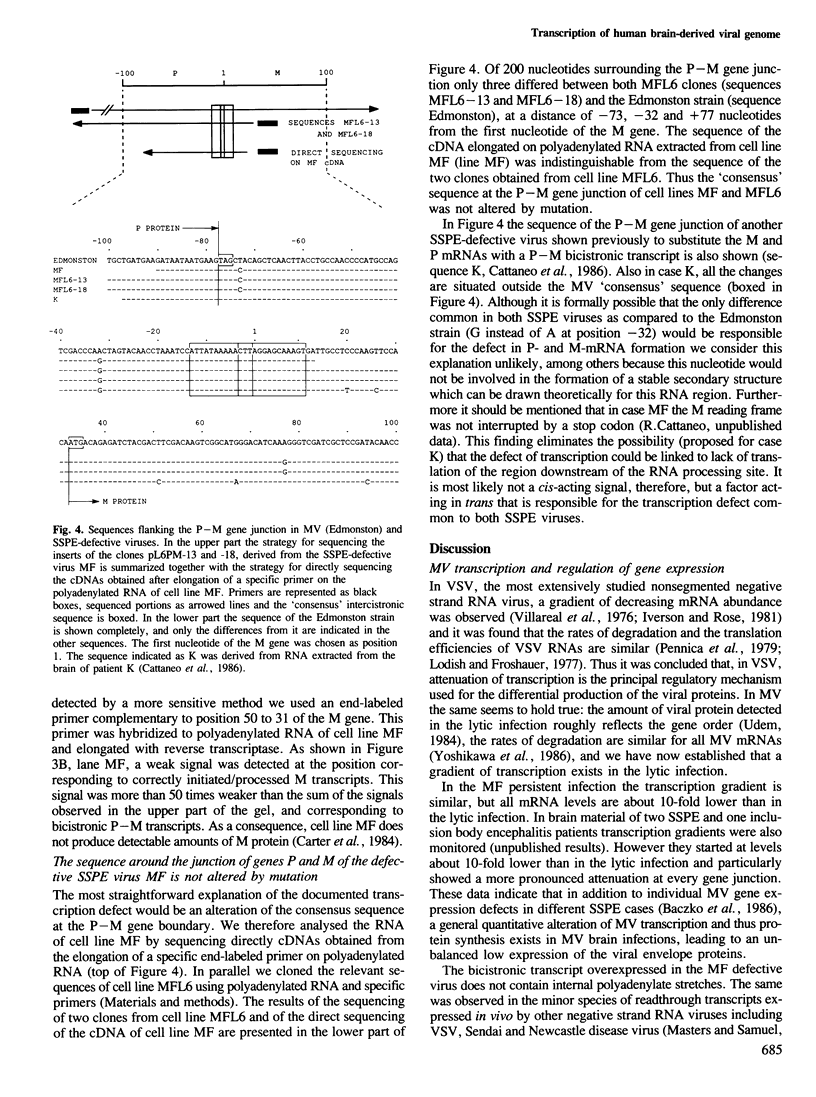
- Cattaneo R., Schmid A., Rebmann G., Baczko K., Ter Meulen V., Bellini W. J., Rozenblatt S., Billeter M. A. Accumulated measles virus mutations in a case of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis: interrupted matrix protein reading frame and transcription alteration. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90433-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Will H., Schaller H. Hepatitis B virus transcription in the infected liver. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2191–2196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domingo E., Martínez-Salas E., Sobrino F., de la Torre J. C., Portela A., Ortín J., López-Galindez C., Pérez-Breña P., Villanueva N., Nájera R. The quasispecies (extremely heterogeneous) nature of viral RNA genome populations: biological relevance--a review. Gene. 1985;40(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling P. C., Blumberg B. M., Kolakofsky D., Cook P., Jotkowitz A., Prineas J. W., Cook S. D. Measles virus nucleic acid sequences in human brain. Virus Res. 1986 Jul;5(1):97–107. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling P. C., Blumberg B. M., Menonna J., Adamus J. E., Cook P., Crowley J. C., Kolakofsky D., Cook S. D. Transcriptional map of the measles virus genome. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1987–1992. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinami R. S., Norrby E., Oldstone M. B. Antigenic modulation induced by monoclonal antibodies: antibodies to measles virus hemagglutinin alters expression of other viral polypeptides in infected cells. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2618–2621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta K. C., Kingsbury D. W. Complete sequences of the intergenic and mRNA start signals in the Sendai virus genome: homologies with the genome of vesicular stomatitis virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3829–3841. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta K. C., Kingsbury D. W. Polytranscripts of Sendai virus do not contain intervening polyadenylate sequences. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):102–109. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90186-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T., Gantz D., Eble B., Walker D., Stowring L., Ventura P., Blum H., Wietgrefe S., Zupancic M., Tourtellotte W. Natural history of restricted synthesis and expression of measles virus genes in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3020–3024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase A. T., Ventura P., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Tourtellotte W. W. Measles virus nucleotide sequences: detection by hybridization in situ. Science. 1981 May 8;212(4495):672–675. doi: 10.1126/science.7221554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall W. W., Choppin P. W. Evidence for lack of synthesis of the M polypeptide of measles virus in brain cells in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):443–447. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser S. L., Aubert C., Burks J. S., Kerr C., Lyon-Caen O., de The G., Brahic M. Analysis of human T-lymphotrophic virus sequences in multiple sclerosis tissue. Nature. 1986 Jul 10;322(6075):176–177. doi: 10.1038/322176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman R. C., Adler S., Lazzarini R. A., Colonno R. J., Banerjee A. K., Westphal H. Intervening polyadenylate sequences in RNA transcripts of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):587–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90027-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman R. C., Schubert M., Keene J. D., Lazzarini R. A. Polycistronic vesicular stomatitis virus RNA transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4662–4665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J., Spindler K., Horodyski F., Grabau E., Nichol S., VandePol S. Rapid evolution of RNA genomes. Science. 1982 Mar 26;215(4540):1577–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.7041255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson L. E., Rose J. K. Localized attenuation and discontinuous synthesis during vesicular stomatitis virus transcription. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):477–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpas A., Kämpf U., Sidèn A., Koch M., Poser S. Lack of evidence for involvement of known human retroviruses in multiple sclerosis. Nature. 1986 Jul 10;322(6075):177–178. doi: 10.1038/322177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., DeFreitas E. C., Harper M. E., Sandberg-Wollheim M., Sheremata W. A., Robert-Guroff M., Saxinger C. W., Feinberg M. B., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Multiple sclerosis and human T-cell lymphotropic retroviruses. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):154–160. doi: 10.1038/318154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzsch V., Hall W. W., Nagashima K., ter Meulen V. Biological and biochemical characterization of a latent subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) virus infection in tissue culture. J Med Virol. 1977;1(2):139–154. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890010207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebert U. G., Baczko K., Budka H., ter Meulen V. Restricted expression of measles virus proteins in brains from cases of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2435–2444. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. H., Thormar H. Absence of M protein in a cell-associated subacute sclerosing panencephalitis virus. Nature. 1980 Jun 12;285(5765):490–492. doi: 10.1038/285490a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Froshauer S. Rates of initiation of protein synthesis by two purified species of vesicular stomatitis virus messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):8804–8811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Hayes E. C., Zweerink H. J. Cells infected with a cell-associated subacute sclerosing panencephalitis virus do not express M protein. Virology. 1981 Jan 30;108(2):515–520. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90460-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters P. S., Samuel C. E. Detection of in vivo synthesis of polycistronic mRNAs of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virology. 1984 Apr 30;134(2):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. A., Perrault J. Poliovirus genome RNA hybridizes specifically to higher eukaryotic rRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):6797–6816. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.6797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. A., Perrault J. RNA virus genomes hybridize to cellular rRNAs and to each other. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):917–921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.917-921.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. D., Balfour H. H., Jr Measles control: so near and yet so far. Prog Med Virol. 1985;31:1–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. M., Rakestraw K. M. Sequence of the Sendai virus L gene: open reading frames upstream of the main coding region suggest that the gene may be polycistronic. Virology. 1986 Oct 15;154(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90427-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrby E., Kristensson K., Brzosko W. J., Kapsenberg J. G. Measles virus matrix protein detected by immune fluorescence with monoclonal antibodies in the brain of patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):337–340. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.337-340.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Fujinami R. S., Lampert P. W. Membrane and cytoplasmic changes in virus-infected cells induced by interactions of antiviral antibody with surface viral antigen. Prog Med Virol. 1980;26:45–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Lynch K. R., Cohen P. S., Ennis H. L. Decay of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNAs in vivo. Virology. 1979 Apr 30;94(2):484–487. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90480-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rammohan K. W., McFarland H. F., McFarlin D. E. Induction of subacute murine measles encephalitis by monoclonal antibody to virus haemagglutinin. Nature. 1981 Apr 16;290(5807):588–589. doi: 10.1038/290588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson C., Hull D., Greer P., Hasel K., Berkovich A., Englund G., Bellini W., Rima B., Lazzarini R. The nucleotide sequence of the mRNA encoding the fusion protein of measles virus (Edmonston strain): a comparison of fusion proteins from several different paramyxoviruses. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):508–523. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90212-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rima B. K., Baczko K., Clarke D. K., Curran M. D., Martin S. J., Billeter M. A., ter Meulen V. Characterization of clones for the sixth (L) gene and a transcriptional map for morbilliviruses. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1971–1978. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K. Complete intergenic and flanking gene sequences from the genome of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90515-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenblatt S., Eizenberg O., Ben-Levy R., Lavie V., Bellini W. J. Sequence homology within the morbilliviruses. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):684–690. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.684-690.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenborn E. T., Mierendorf R. C., Jr A novel transcription property of SP6 and T7 RNA polymerases: dependence on template structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6223–6236. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard R. D., Raine C. S., Bornstein M. B., Udem S. A. Rapid degradation restricts measles virus matrix protein expression in a subacute sclerosing panencephalitis cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7913–7917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs M. K., Collins P. L. Human parainfluenza virus type 3: messenger RNAs, polypeptide coding assignments, intergenic sequences, and genetic map. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):646–654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.646-654.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udem S. A., Cook K. A. Isolation and characterization of measles virus intracellular nucleocapsid RNA. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):57–65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.57-65.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udem S. A. Measles virus: conditions for the propagation and purification of infectious virus in high yield. J Virol Methods. 1984 Feb;8(1-2):123–136. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(84)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarreal L. P., Breindl M., Holland J. J. Determination of molar ratios of vesicular stomatitis virus induced RNA species in BHK21 cells. Biochemistry. 1976 Apr 20;15(8):1663–1667. doi: 10.1021/bi00653a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman B. Mechanisms in multiple sclerosis. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):104–105. doi: 10.1038/318104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Fields B. N. Differences between the intracellular polypeptides of measles and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis virus. Nature. 1978 Mar 30;272(5652):458–460. doi: 10.1038/272458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler S. L., Meissner H. C. Measles and SSPE viruses: similarities and differences. Prog Med Virol. 1982;28:65–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde A., Morrison T. Structural and functional characterization of Newcastle disease virus polycistronic RNA species. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):71–76. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.71-76.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa Y., Mizumoto K., Yamanouchi K. Characterization of messenger RNAs of measles virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2807–2812. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young K. K., Heineke B. E., Wechsler S. L. M protein instability and lack of H protein processing associated with nonproductive persistent infection of HeLa cells by measles virus. Virology. 1985 Jun;143(2):536–545. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90392-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Meulen V., Carter M. J. Measles virus persistency and disease. Prog Med Virol. 1984;30:44–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]