Abstract
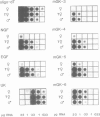
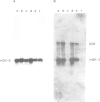
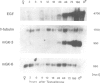
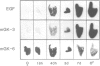
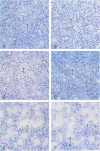
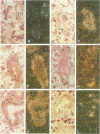
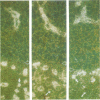
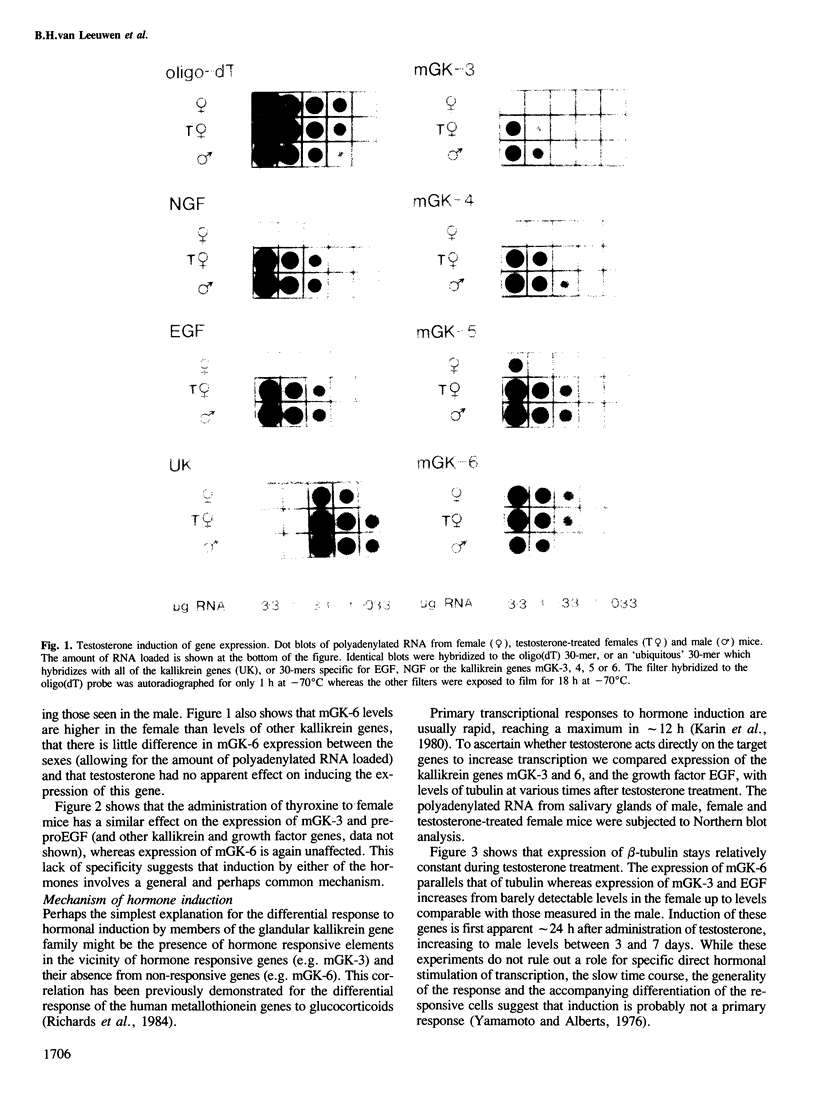
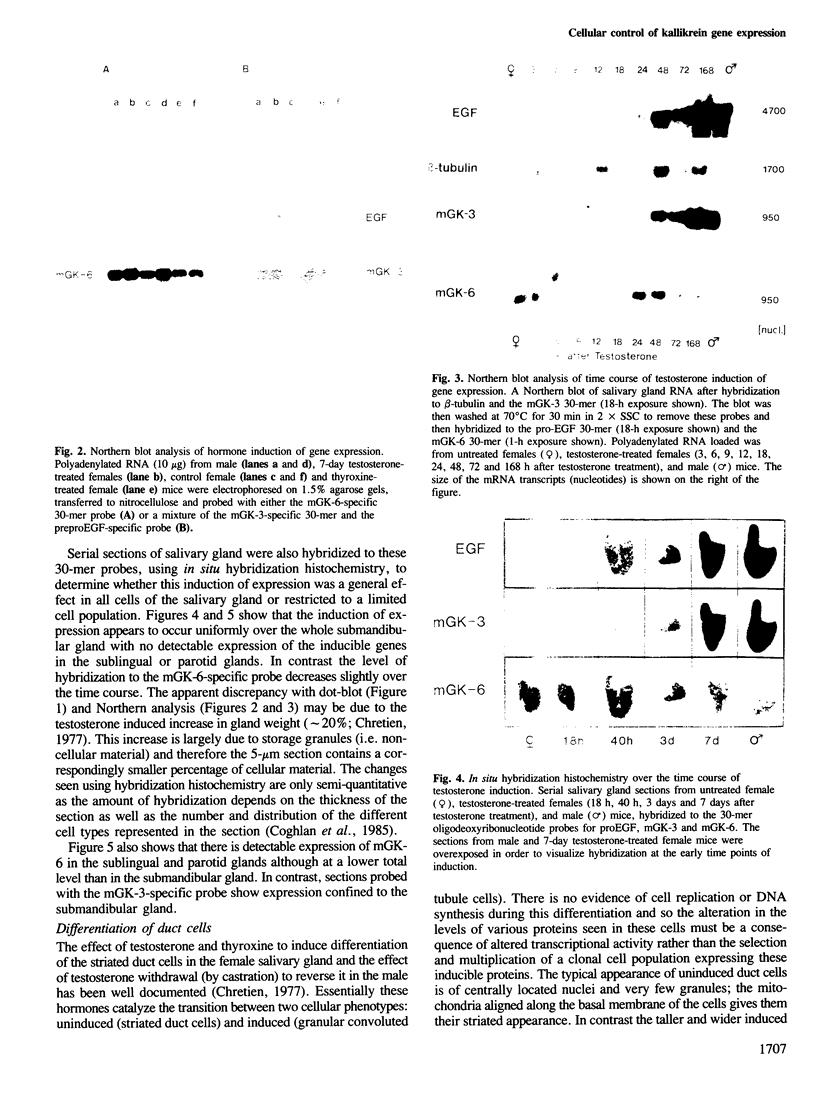
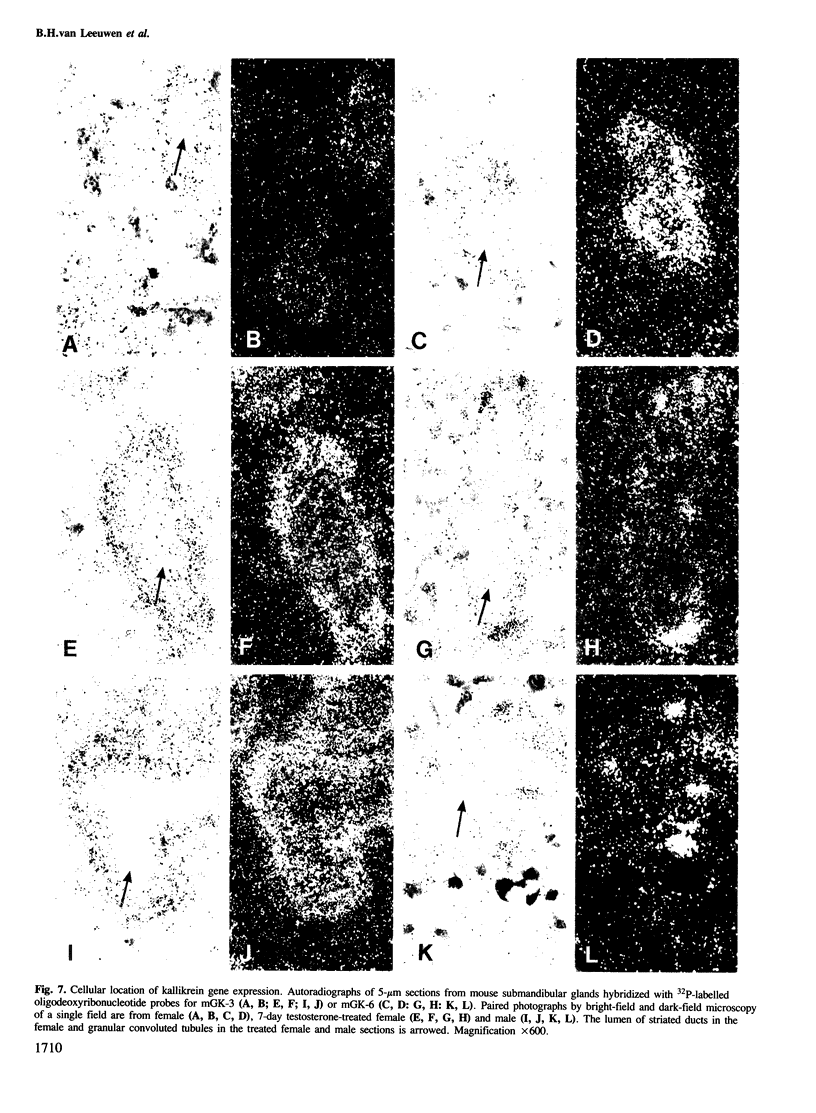
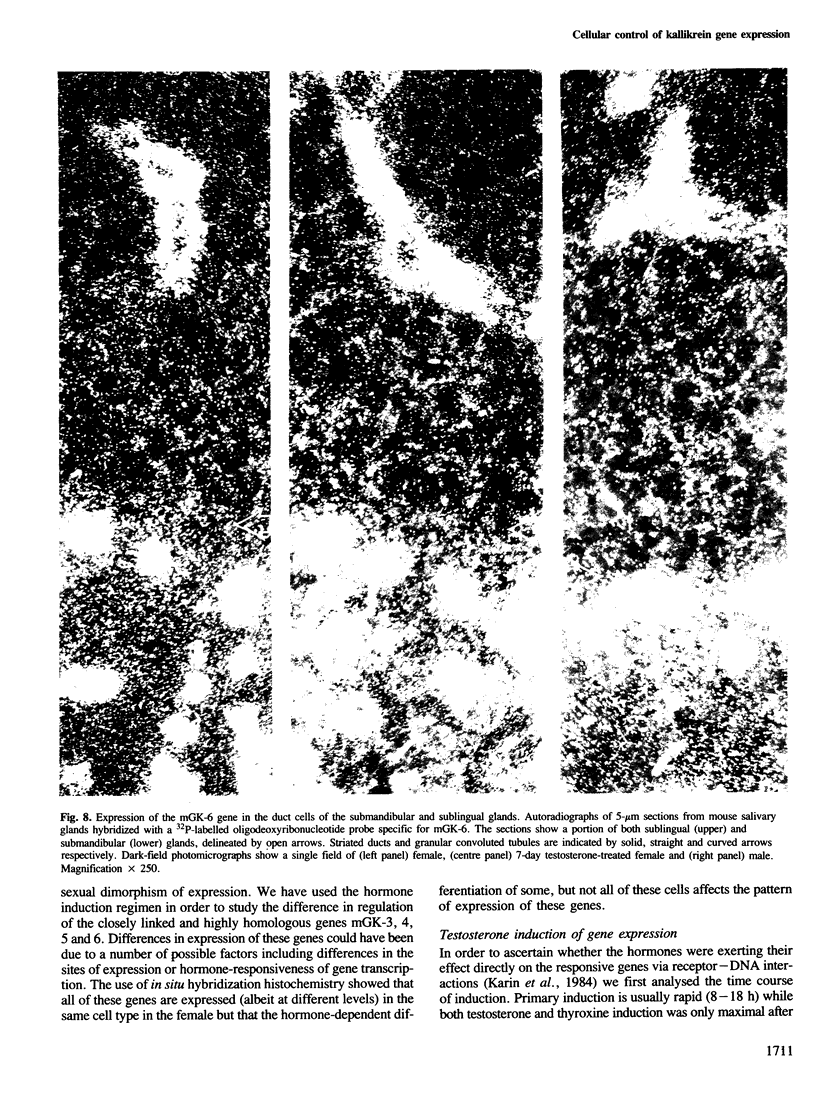
The expression of many mouse kallikrein genes in the salivary gland is sexually dimorphic and inducible in females by administration of testosterone or thyroxine. Induction is slow (3-7 days) and is accompanied by the non-uniform differentiation of the cell type expressing these genes from striated duct (SD) cells (female) to granular convoluted tubule (GCT) cells (male). One kallikrein gene, mGK-6, is expressed at an apparently constant total level in male and female and is not induced by either hormone. In situ hybridization histochemistry shows that all kallikrein genes analyzed exhibit uniform cellular distribution of expression in the SD cells of the female. The hormonally mediated differentiation of some, but not all, of these cells has different effects on kallikrein gene expression--mGK-6 is repressed while other kallikreins are induced--leading to non-uniform distribution of expression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barka T. Biologically active polypeptides in submandibular glands. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Aug;28(8):836–859. doi: 10.1177/28.8.7003006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catanzaro D. F., Mesterovic N., Morris B. J. Studies of the regulation of mouse renin genes by measurement of renin messenger ribonucleic acid. Endocrinology. 1985 Sep;117(3):872–878. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-3-872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J., Margolius H. S. Differential effects of testosterone, thyroxine, and cortisol on rat submandibular gland versus renal kallikrein. Endocrinology. 1983 Dec;113(6):2221–2225. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-6-2221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrétien M. Action of testosterone on the differentiation and secretory activity of a target organ: the submaxillary gland of the mouse. Int Rev Cytol. 1977;50:333–396. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60101-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coghlan J. P., Aldred P., Haralambidis J., Niall H. D., Penschow J. D., Tregear G. W. Hybridization histochemistry. Anal Biochem. 1985 Aug 15;149(1):1–28. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90472-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans B. A., Richards R. I. Genes for the alpha and gamma subunits of mouse nerve growth factor are contiguous. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):133–138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02327.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Andersen R. D., Slater E., Smith K., Herschman H. R. Metallothionein mRNA induction in HeLa cells in response to zinc or dexamethasone is a primary induction response. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):295–297. doi: 10.1038/286295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason A. J., Evans B. A., Cox D. R., Shine J., Richards R. I. Structure of mouse kallikrein gene family suggests a role in specific processing of biologically active peptides. Nature. 1983 May 26;303(5915):300–307. doi: 10.1038/303300a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. I., Heguy A., Karin M. Structural and functional analysis of the human metallothionein-IA gene: differential induction by metal ions and glucocorticoids. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90322-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Selby M., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Bell G. I., Rutter W. J. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the precursor of mouse nerve growth factor. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):538–540. doi: 10.1038/302538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Sanchez-Pescador R., Fong N., Selby M., Rutter W. J., Bell G. I. Structure of a mouse submaxillary messenger RNA encoding epidermal growth factor and seven related proteins. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):236–240. doi: 10.1126/science.6602382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi O., Kurachi H., Oka T. A physiological role of epidermal growth factor in male reproductive function. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):975–977. doi: 10.1126/science.3090686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M. Steroid receptors: elements for modulation of eukaryotic transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:721–746. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Leeuwen B. H., Evans B. A., Tregear G. W., Richards R. I. Mouse glandular kallikrein genes. Identification, structure, and expression of the renal kallikrein gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5529–5535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]