Abstract
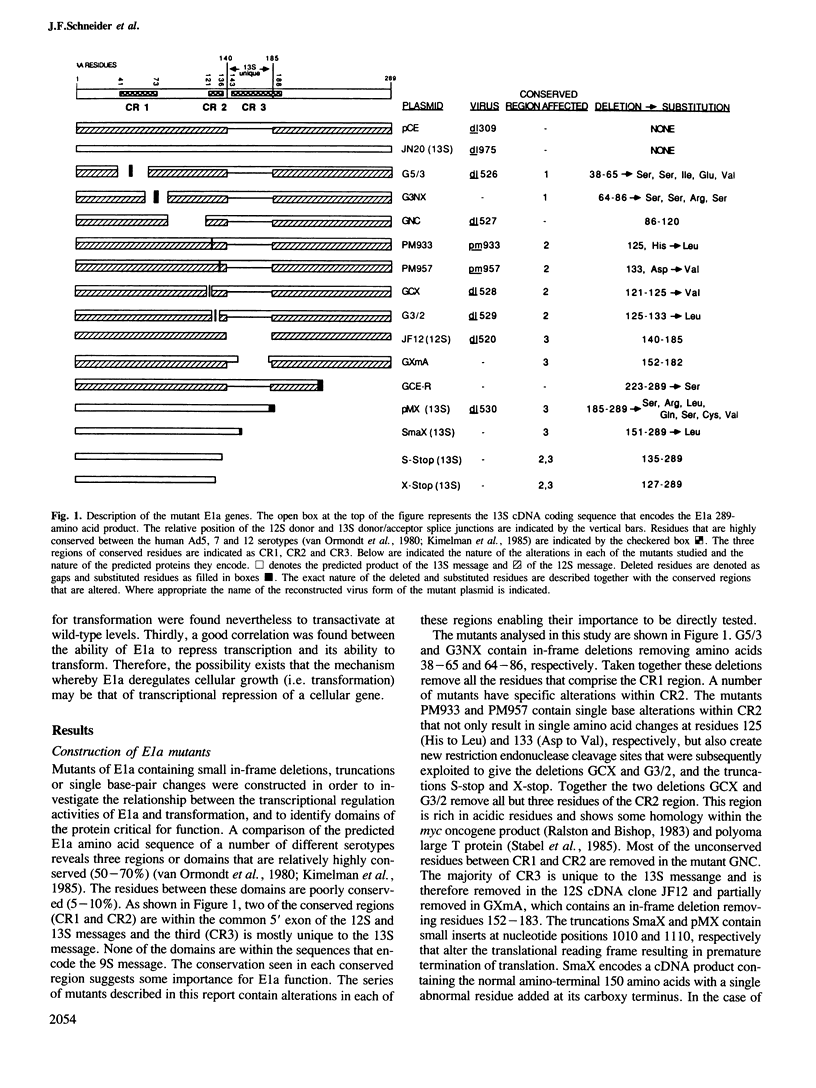
To determine whether the transcription regulatory activities of the adenoviral E1a gene play a role in its ability to transform primary cells we have constructed an extensive series of mutations within the E1a gene. The mutants have been characterized for their ability to transactivate the adenoviral early promoters, repress the transcriptional stimulation of the polyoma virus enhancer, establish primary baby rat kidney cells in culture and cooperate with the activated Ha-ras oncogene in morphologically transforming these cells. The mutant phenotypes reveal that: (i) the two transcription regulatory activities of E1a are separable since essential protein domains map within different regions of the protein; (ii) transactivation is unlikely to contribute significantly to E1a-mediated transformation since several isolated mutants lost the ability to transactivate but were nevertheless efficient at transformation; and (iii) both establishment and oncogene cooperation are linked to enhancer repression suggesting that E1a transforms cells by the repression of a cellular enhancer.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J. Adenovirus promoters and E1A transactivation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:45–79. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Chambon P. Adenovirus-2 E1A products repress enhancer-induced stimulation of transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):608–612. doi: 10.1038/312608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite A. W., Murray J. D., Bellett A. J. Alterations to controls of cellular DNA synthesis by adenovirus infection. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):331–340. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.331-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlock L. R., Jones N. C. Transformation-defective mutant of adenovirus type 5 containing a single altered E1a mRNA species. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):657–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.657-664.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G. Adenovirus 2 Ip+ locus codes for a 19 kd tumor antigen that plays an essential role in cell transformation. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):759–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn G. M., Ricciardi R. P. Adenovirus 5 early region 1A host range mutants hr3, hr4, and hr5 contain point mutations which generate single amino acid substitutions. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):66–74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.66-74.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Harrison T., Williams J. Defective transforming capacity of adenovirus type 5 host-range mutants. Virology. 1978 May 1;86(1):10–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley K. P., Overhauser J., Babiss L. E., Ginsberg H. S., Jones N. C. Transformation properties of type 5 adenovirus mutants that differentially express the E1A gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5734–5738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Chambon P. Repression of the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer by the adenovirus-2 E1A products. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1391–1394. doi: 10.1126/science.2999984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines J. C., Ray D. S. Construction and characterization of new coliphage M13 cloning vectors. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houweling A., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J. Partial transformation of primary rat cells by the leftmost 4.5% fragment of adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao H. T., Nevins J. R. Transcriptional activation and subsequent control of the human heat shock gene during adenovirus infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2058–2065. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Miller J. S., Porter D., Roberts B. E. E1a regions of the human adenoviruses and of the highly oncogenic simian adenovirus 7 are closely related. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):399–409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.399-409.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchingman G. R., Westphal H. The structure of adenovirus 2 early nuclear and cytoplasmic RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 15;137(1):23–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Identification of a cellular transcription factor involved in E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M., Green M. R. An adenovirus E1a protein region required for transformation and transcriptional repression. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90704-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Boswell D. R. Confidence limits for homology in protein or gene sequences. The c-myc oncogene and adenovirus E1a protein. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 5;185(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90181-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Grodzicker T., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Zerler B. Lytic and transforming functions of individual products of the adenovirus E1A gene. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):765–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.765-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Zerler B., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. Identification of separate domains in the adenovirus E1A gene for immortalization activity and the activation of virus early genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3470–3480. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Induction of the synthesis of a 70,000 dalton mammalian heat shock protein by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perricaudet M., Akusjärvi G., Virtanen A., Pettersson U. Structure of two spliced mRNAs from the transforming region of human subgroup C adenoviruses. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):694–696. doi: 10.1038/281694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston R., Bishop J. M. The protein products of the myc and myb oncogenes and adenovirus E1a are structurally related. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):803–806. doi: 10.1038/306803a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Hen R., Borrelli E., Leff T., Chambon P. Far upstream sequences are required for efficient transcription from the adenovirus-2 E1A transcription unit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8735–8745. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Weinberg R. A. Isolation of a transforming sequence from a human bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Kegler D. M., Ziff E. B. Vector expression of adenovirus type 5 E1a proteins: evidence for E1a autoregulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2684–2696. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Eng C. Y., Berk A. J. An adenovirus early region 1A protein is required for maximal viral DNA replication in growth-arrested human cells. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):742–750. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.742-750.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabel S., Argos P., Philipson L. The release of growth arrest by microinjection of adenovirus E1A DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2329–2336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. W., Ziff E. B. Repression of insulin gene expression by adenovirus type 5 E1a proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1164–1170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Ziff E. B. HeLa cell beta-tubulin gene transcription is stimulated by adenovirus 5 in parallel with viral early genes by an E1a-dependent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2792–2801. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Cloning of a DNA fragment from the left-hand terminus of the adenovirus type 2 genome and its use in site-directed mutagenesis. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):171–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.171-180.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Akusjärvi G. Adenovirus 2 early region 1A stimulates expression of both viral and cellular genes. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):789–794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Eb A. J., Mulder C., Graham F. L., Houweling A. Transformation with specific fragments of adenovirus DNAs. I. Isolation of specific fragments with transforming activity of adenovirus 2 and 5 DNA. Gene. 1977;2(3-4):115–132. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress transcription from the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. L., Jones N. C. E1A control of gene expression is mediated by sequences 5' to the transcriptional starts of the early viral genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1222–1234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. The action of oncogenes in the cytoplasm and nucleus. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):770–776. doi: 10.1126/science.2997917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberg G., Shenk T. Dissection of overlapping functions within the adenovirus type 5 E1A gene. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1907–1912. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu B. J., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C., Morimoto R. I. The E1A 13S product of adenovirus 5 activates transcription of the cellular human HSP70 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2994–2999. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerler B., Moran B., Maruyama K., Moomaw J., Grodzicker T., Ruley H. E. Adenovirus E1A coding sequences that enable ras and pmt oncogenes to transform cultured primary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):887–899. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ormondt H., Maat J., Dijkema R. Comparison of nucleotide sequences of the early E1a regions for subgroups A, B and C of human adenoviruses. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):63–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]