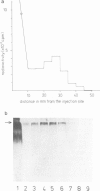
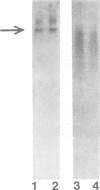
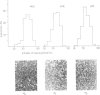
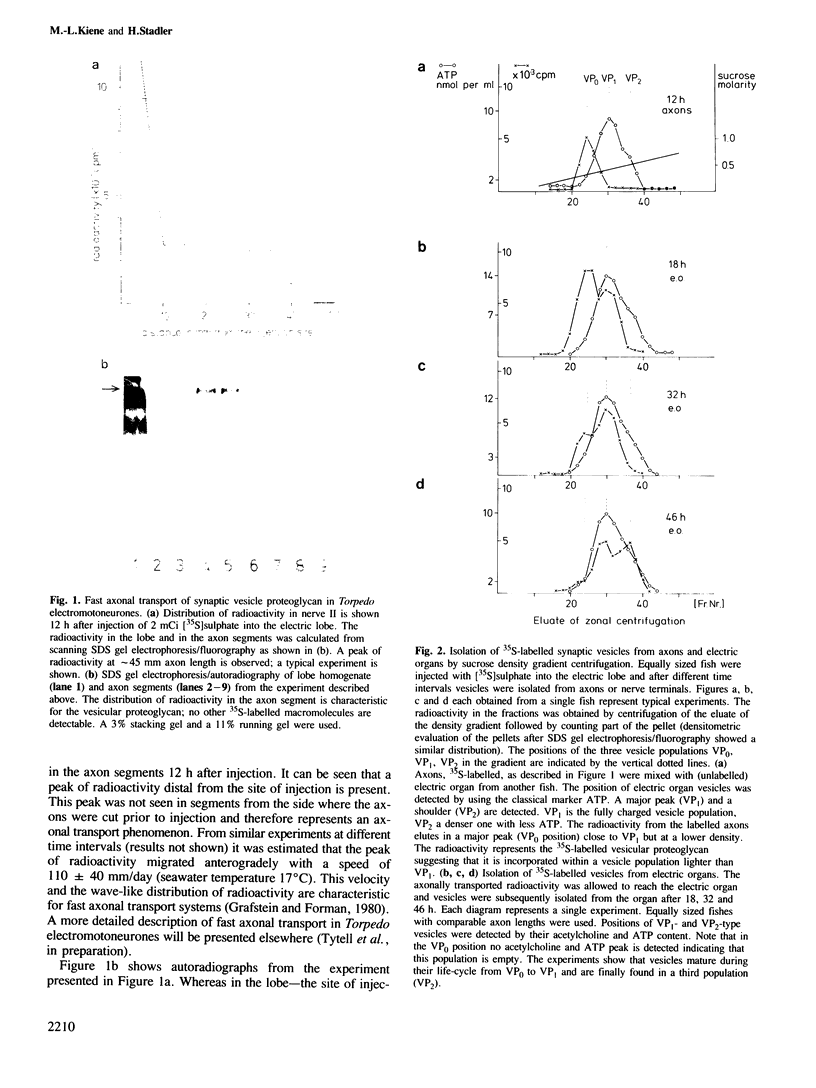
Abstract
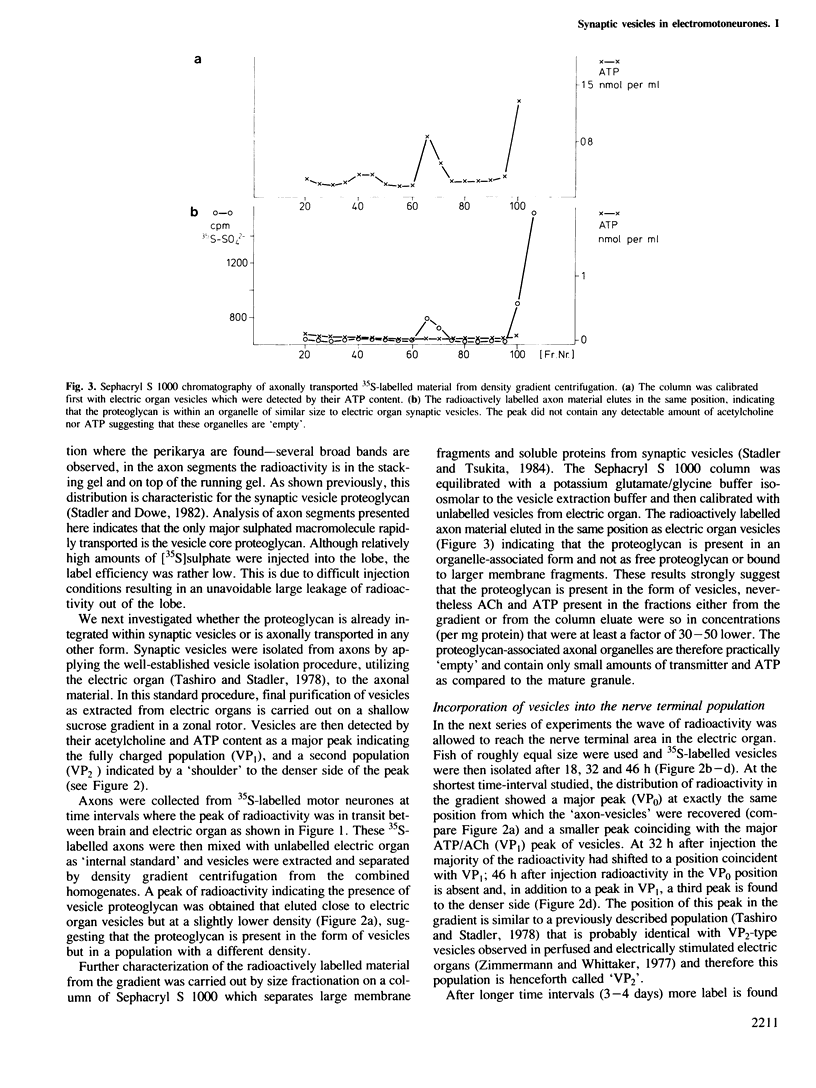
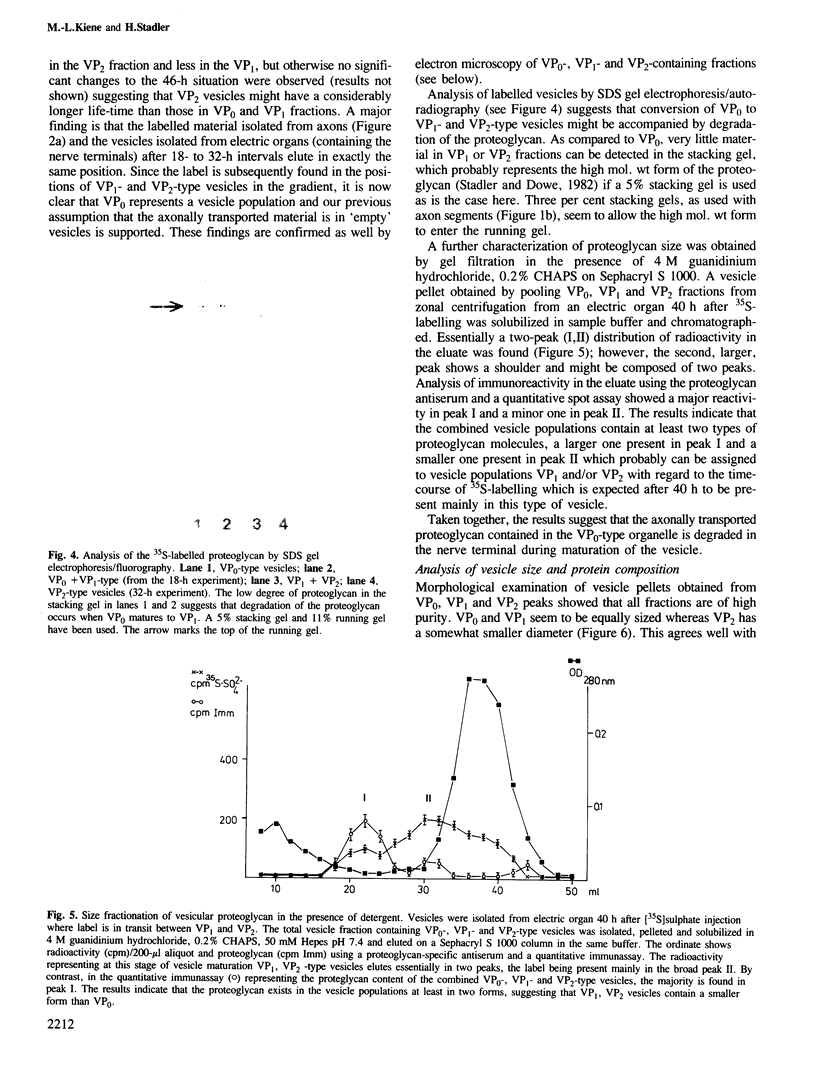
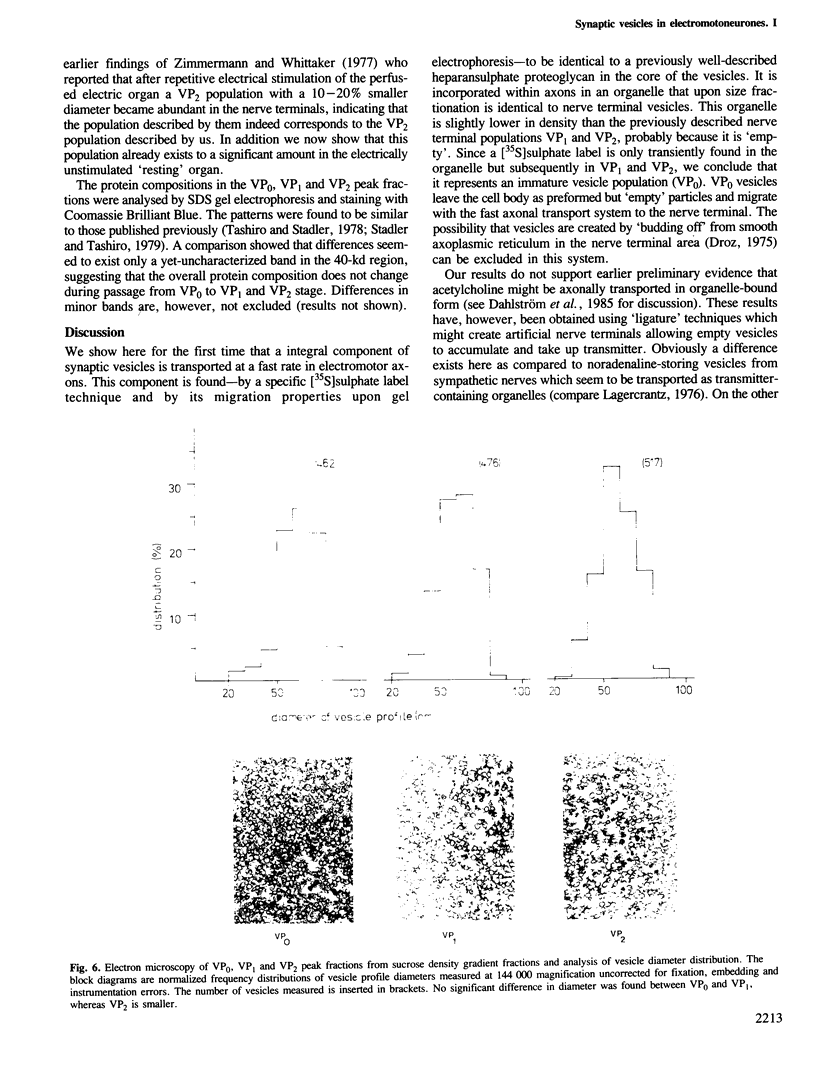
We were able by using an in vivo pulse-label technique to trace part of the life cycle of a secretory organelle, the acetylcholine-storing synaptic vesicle from electromotoneurones of Torpedo marmorata. This technique uses [35S]sulphate incorporation into the cell bodies of the electromotoneurones which results in radioactive labelling of a synaptic vesicle heparansulphate proteoglycan--a major core component. Vesicles are anterogradely transported in the axons at a fast rate as 'empty' organelles (VP0 population). In the nerve terminal, maturation of the granule to a population (VP1) fully charged with acetylcholine and ATP occurs. Finally after a longer time interval a change to a third population (VP2) is observed. This population is reduced in diameter as compared to VP0 and VP1 suggesting, in agreement with earlier reports, that it has undergone exo-endocytosis. The changes from VP0 to VP1 and VP2 are accompanied by a degradation of the core proteoglycan as measured by gel filtration of the 35S-labelled compound. The results show that vesicles are axonally transported as preformed organelles, exist in the neurone at least in three different populations and that the nerve terminal is the major site of transmitter uptake.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. D., Metuzals J., Tasaki I., Brady S. T., Gilbert S. P. Fast axonal transport in squid giant axon. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1127–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.6183744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady S. T., Lasek R. J., Allen R. D. Fast axonal transport in extruded axoplasm from squid giant axon. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1129–1131. doi: 10.1126/science.6183745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley K. M., Schweitzer E. S., Miljanich G. P., Clift-O'Grady L., Kushner P. D., Reichardt L. F., Kelly R. B. A synaptic vesicle antigen is restricted to the junctional region of the presynaptic plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7342–7346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson S. S., Kelly R. B. A highly antigenic proteoglycan-like component of cholinergic synaptic vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11082–11091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson S. S., Wagner J. A., Kelly R. B. Purification of synaptic vesicles from elasmobranch electric organ and the use of biophysical criteria to demonstrate purity. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1188–1199. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlström A., Larsson P. A., Carlson S. S., Böj S. Localization and axonal transport of immunoreactive cholinergic organelles in rat motor neurons--an immunofluorescent study. Neuroscience. 1985 Feb;14(2):607–625. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90314-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdall M. J., Boyne A. F., Whittaker V. P. Adenosine triphosphate. A constituent of cholinergic synaptic vesicles. Biochem J. 1974 Apr;140(1):1–12. doi: 10.1042/bj1400001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droz B., Rambourg A., Koenig H. L. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum: structure and role in the renewal of axonal membrane and synaptic vesicles by fast axonal transport. Brain Res. 1975 Jul 25;93(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90282-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füldner H. H., Stadler H. 31P-NMR analysis of synaptic vesicles. Status of ATP and internal pH. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jan;121(3):519–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05817.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafstein B., Forman D. S. Intracellular transport in neurons. Physiol Rev. 1980 Oct;60(4):1167–1283. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.4.1167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlos P., Lee D. A., Stadler H. Characterization of a Mg2+-ATPase and a proton pump in cholinergic synaptic vesicles from the electric organ of Torpedo marmorata. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 2;144(3):441–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Schiebler W., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. III. Its association with synaptic vesicles studied in a highly purified synaptic vesicle preparation. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1374–1388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Schiebler W., Ouimet C., Greengard P. A 38,000-dalton membrane protein (p38) present in synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4137–4141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. T., Walker J. H., Stadler H., Whittaker V. P. Immunohistochemical localization of a synaptic-vesicle antigen in a cholinergic neuron under conditions of stimulation and rest. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;223(1):117–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00221503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagercrantz H. On the composition and function of large dense cored vesicles in sympathetic nerves. Neuroscience. 1976;1(2):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(76)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. A., Witzemann V. Photoaffinity labeling of a synaptic vesicle specific nucleotide transport system from Torpedo marmorata. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 20;22(26):6123–6130. doi: 10.1021/bi00295a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luqmani Y. A. Nucleotide uptake by isolated cholinergic synaptic vesicles: evidence for a carrier of adenosine 5'-triphosphate. Neuroscience. 1981;6(6):1011–1021. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maret G. E., Fauchère J. L. The prohormone processing activity is enriched in a low-density subpopulation of chromaffin granules. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):258–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80171-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp B. J., Vale R. D., Sheetz M. P., Reese T. S. Single microtubules from squid axoplasm support bidirectional movement of organelles. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):455–462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90160-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler H., Dowe G. H. Identification of a heparan sulphate-containing proteoglycan as a specific core component of cholinergic synaptic vesicles from Torpedo marmorata. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1381–1384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01326.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler H., Fenwick E. M. Cholinergic synaptic vesicles from Torpedo marmorata contain an atractyloside-binding protein related to the mitochondrial ADP/ATP carrier. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Nov 2;136(2):377–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler H., Füldner H. H. Proton NMR detection of acetylcholine status in synaptic vesicles. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):293–294. doi: 10.1038/286293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler H., Kiene M. L. Synaptic vesicles in electromotoneurones. II. Heterogeneity of populations is expressed in uptake properties; exocytosis and insertion of a core proteoglycan into the extracellular matrix. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2217–2221. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02493.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler H., Tashiro T. Isolation of synaptosomal plasma membranes from cholinergic nerve terminals and a comparison of their proteins with those of synaptic vesicles. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;101(1):171–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler H., Tsukita S. Synaptic vesicles contain an ATP-dependent proton pump and show 'knob-like' protrusions on their surface. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3333–3337. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro T., Stadler H. Chemical composition of cholinergic synaptic vesicles from Torpedo marmorata based on improved purification. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct 16;90(3):479–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torri-Tarelli F., Grohovaz F., Fesce R., Ceccarelli B. Temporal coincidence between synaptic vesicle fusion and quantal secretion of acetylcholine. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1386–1399. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukita S., Ishikawa H. The movement of membranous organelles in axons. Electron microscopic identification of anterogradely and retrogradely transported organelles. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):513–530. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. H., Jones R. T., Obrocki J., Richardson G. P., Stadler H. Presynaptic plasma membranes and synaptic vesicles of cholinergic nerve endings demonstrated by means of specific antisera. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;223(1):101–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00221502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. H., Kristjansson G. I., Stadler H. Identification of a synaptic vesicle antigen (Mr 86,000) conserved between Torpedo and rat. J Neurochem. 1986 Mar;46(3):875–881. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb13053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Franke W. W. Identification and localization of synaptophysin, an integral membrane glycoprotein of Mr 38,000 characteristic of presynaptic vesicles. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann H. Vesicle recycling and transmitter release. Neuroscience. 1979;4(12):1773–1804. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann H., Whittaker V. P. Effect of electrical stimulation on the yield and composition of synaptic vesicles from the cholinergic synapses of the electric organ of Torpedo: a combined biochemical, electrophysiological and morphological study. J Neurochem. 1974 Mar;22(3):435–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb07610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann H., Whittaker V. P. Morphological and biochemical heterogeneity of cholinergic synaptic vesicles. Nature. 1977 Jun 16;267(5612):633–635. doi: 10.1038/267633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wedel R. J., Carlson S. S., Kelly R. B. Transfer of synaptic vesicle antigens to the presynaptic plasma membrane during exocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1014–1018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]