Abstract
The hemagglutinin of influenza virus (HA), an acid-activated membrane fusion protein, is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum and transported through the Golgi complex to the cell surface of infected cells as an uncleaved, fusion-incompetent precursor, HA0. The mature, proteolytically activated HA is known to undergo a rapid, irreversible, acid-induced conformational change which mediates membrane fusion and virus penetration. On the basis of antigenic modifications and the acquisition of trypsin susceptibility, we demonstrate here that HA0, while unable to cause fusion, is acid sensitive. It undergoes irreversible conformational changes quite similar to those of HA at mildly acidic pH (pH less than 6.0). The ectodomain of HA0 does not, however, acquire hydrophobic properties and the changes occur in a less concerted manner (the pH dependence is much broader and the rate of conversion slower). These differences are likely to account for the inability of acid-treated HA0 to trigger membrane fusion. It was shown, moreover, that HA0 acquired its acid-sensitive properties immediately following trimerization in the endoplasmic reticulum. Since HA0 did not convert to the acid form at any point during its intracellular transport, we concluded that the trans-Golgi compartment, known to be more acidic than the cytosol and involved in constitutive membrane transport, is not likely to have a pH less than 6.0.
Full text
PDF
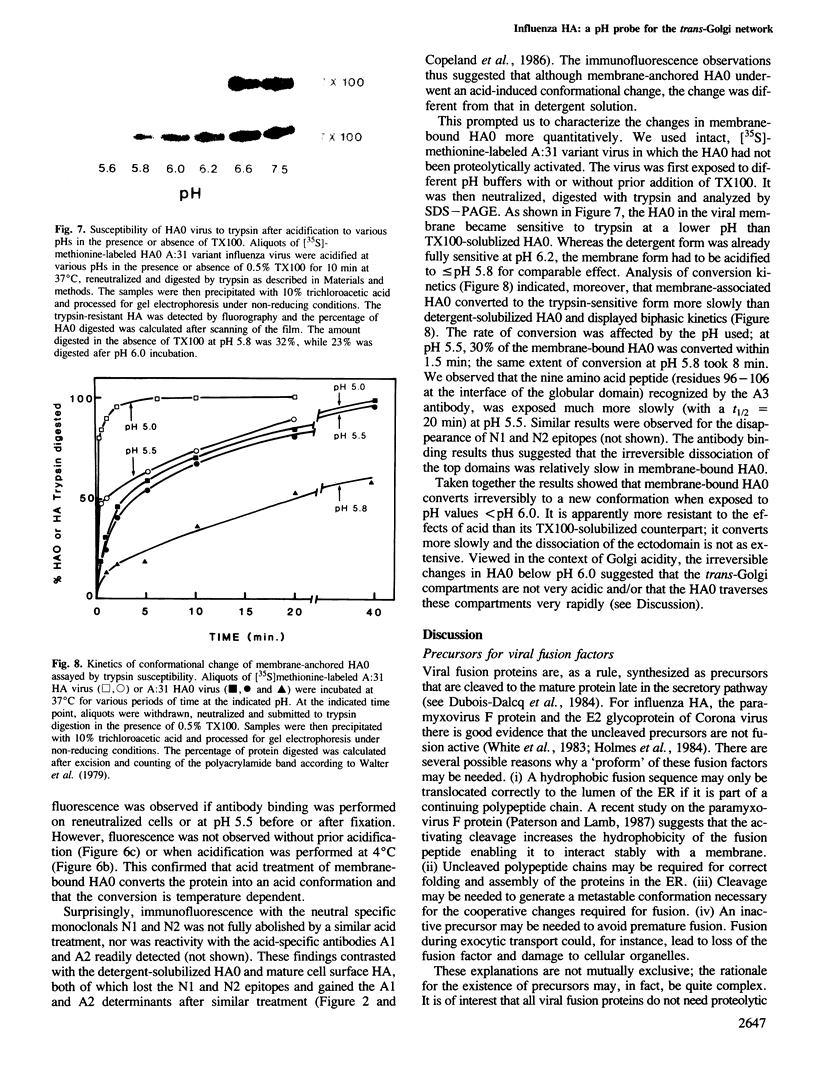



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G., Pathak R. K. Vesicles and cisternae in the trans Golgi apparatus of human fibroblasts are acidic compartments. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann J. E., Singer S. J. Immunoelectron microscopic studies of the intracellular transport of the membrane glycoprotein (G) of vesicular stomatitis virus in infected Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1777–1787. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand C. M., Skehel J. J. Crystalline antigen from the influenza virus envelope. Nat New Biol. 1972 Aug 2;238(83):145–147. doi: 10.1038/newbio238145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bächi T., Gerhard W., Yewdell J. W. Monoclonal antibodies detect different forms of influenza virus hemagglutinin during viral penetration and biosynthesis. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):307–313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.307-313.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland C. S., Doms R. W., Bolzau E. M., Webster R. G., Helenius A. Assembly of influenza hemagglutinin trimers and its role in intracellular transport. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1179–1191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crimmins D. L., Mehard W. B., Schlesinger S. Physical properties of a soluble form of the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus at neutral and acidic pH. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 6;22(25):5790–5796. doi: 10.1021/bi00294a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels R. S., Douglas A. R., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Analyses of the antigenicity of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH optimum for virus-mediated membrane fusion. J Gen Virol. 1983 Aug;64(Pt 8):1657–1662. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-8-1657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Gething M. J., Henneberry J., White J., Helenius A. Variant influenza virus hemagglutinin that induces fusion at elevated pH. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):603–613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.603-613.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Helenius A. Quaternary structure of influenza virus hemagglutinin after acid treatment. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):833–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.833-839.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Helenius A., White J. Membrane fusion activity of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. The low pH-induced conformational change. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2973–2981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxsey S. J., Sambrook J., Helenius A., White J. An efficient method for introducing macromolecules into living cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):19–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle C., Sambrook J., Gething M. J. Analysis of progressive deletions of the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains of influenza hemagglutinin. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1193–1204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Doms R. W., York D., White J. Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: site-specific mutagenesis of the hemagglutinin of influenza virus. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):11–23. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Construction of influenza haemagglutinin genes that code for intracellular and secreted forms of the protein. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):598–603. doi: 10.1038/300598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman J., Croen K., Kelly S., Al-Awqati Q. Golgi membranes contain an electrogenic H+ pump in parallel to a chloride conductance. J Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;97(4):1303–1308. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.4.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K. The trans Golgi network: sorting at the exit site of the Golgi complex. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):438–443. doi: 10.1126/science.2945253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay A. J. Studies on the formation of the influenza virus envelope. Virology. 1974 Aug;60(2):398–418. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90335-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., McCaslin D. R., Fries E., Tanford C. Properties of detergents. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:734–749. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R. T., Rott R., Klenk H. D. Influenza viruses cause hemolysis and fusion of cells. Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):243–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. C., Nestorowicz A. Antigenic determinants of influenza virus hemagglutinin. XI. Conformational changes detected by monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1985 Aug;145(1):72–83. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Pathways of protein secretion in eukaryotes. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):25–32. doi: 10.1126/science.2994224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Rott R., Orlich M., Blödorn J. Activation of influenza A viruses by trypsin treatment. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):426–439. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90284-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenk H. D., Wöllert W., Rott R., Scholtissek C. Association of influenza virus proteins with cytoplasmic fractions. Virology. 1974 Jan;57(1):28–41. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowitz S. G., Choppin P. W. Enhancement of the infectivity of influenza A and B viruses by proteolytic cleavage of the hemagglutinin polypeptide. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):440–454. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90285-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S. Ammonium chloride slows transport of the influenza virus hemagglutinin but does not cause mis-sorting in a polarized epithelial cell line. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15172–15178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Simons K. Reduced temperature prevents transfer of a membrane glycoprotein to the cell surface but does not prevent terminal glycosylation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Simons K. Sorting of an apical plasma membrane glycoprotein occurs before it reaches the cell surface in cultured epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2131–2139. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S. The sorting of proteins to the plasma membrane in epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2565–2568. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse H., Scholtissek C., Klenk H. D. Temperature-sensitive mutants of fowl plague virus defective in the intracellular transport of the hemagglutinin. Virus Res. 1986 Aug;5(2-3):293–305. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestorowicz A., Laver G., Jackson D. C. Antigenic determinants of influenza virus haemagglutinin. X. A comparison of the physical and antigenic properties of monomeric and trimeric forms. J Gen Virol. 1985 Aug;66(Pt 8):1687–1695. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-8-1687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson R. G., Lamb R. A. Ability of the hydrophobic fusion-related external domain of a paramyxovirus F protein to act as a membrane anchor. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):441–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90195-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins A. R., Oliver C., Bateman J. L., Krag S. S., Galloway C. J., Mellman I. A single mutation in Chinese hamster ovary cells impairs both Golgi and endosomal functions. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1296–1308. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Paskiet K. T., Salas P. J., Bard E. Intracellular transport of influenza virus hemagglutinin to the apical surface of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):308–319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruigrok R. W., Cremers A. F., Beyer W. E., de Ronde-Verloop F. M. Changes in the morphology of influenza particles induced at low pH. Arch Virol. 1984;82(3-4):181–194. doi: 10.1007/BF01311162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruigrok R. W., Wrigley N. G., Calder L. J., Cusack S., Wharton S. A., Brown E. B., Skehel J. J. Electron microscopy of the low pH structure of influenza virus haemagglutinin. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):41–49. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04175.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste J., Kuismanen E. Pre- and post-Golgi vacuoles operate in the transport of Semliki Forest virus membrane glycoproteins to the cell surface. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A. L., Strous G. J., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of acidic intracellular compartments in hepatoma cells. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):899–904. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Bayley P. M., Brown E. B., Martin S. R., Waterfield M. D., White J. M., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. Changes in the conformation of influenza virus hemagglutinin at the pH optimum of virus-mediated membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M. Perturbation of vesicular traffic with the carboxylic ionophore monensin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1026–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Jackson R. C., Marcus M. M., Lingappa V. R., Blobel G. Tryptic dissection and reconstitution of translocation activity for nascent presecretory proteins across microsomal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1795–1799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Brown L. E., Jackson D. C. Changes in the antigenicity of the hemagglutinin molecule of H3 influenza virus at acidic pH. Virology. 1983 Apr 30;126(2):587–599. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(83)80015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Helenius A., Gething M. J. Haemagglutinin of influenza virus expressed from a cloned gene promotes membrane fusion. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):658–659. doi: 10.1038/300658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Helenius A. pH-dependent fusion between the Semliki Forest virus membrane and liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3273–3277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kielian M., Helenius A. Membrane fusion proteins of enveloped animal viruses. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 May;16(2):151–195. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Niman H. L., Houghten R. A., Cherenson A. R., Connolly M. L., Lerner R. A. The structure of an antigenic determinant in a protein. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90412-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3 A resolution. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):366–373. doi: 10.1038/289366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gerhard W., Bachi T. Monoclonal anti-hemagglutinin antibodies detect irreversible antigenic alterations that coincide with the acid activation of influenza virus A/PR/834-mediated hemolysis. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):239–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.239-248.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Schneider D. L. The bioenergetics of Golgi apparatus function: evidence for an ATP-dependent proton pump. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):620–625. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90825-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]