Abstract
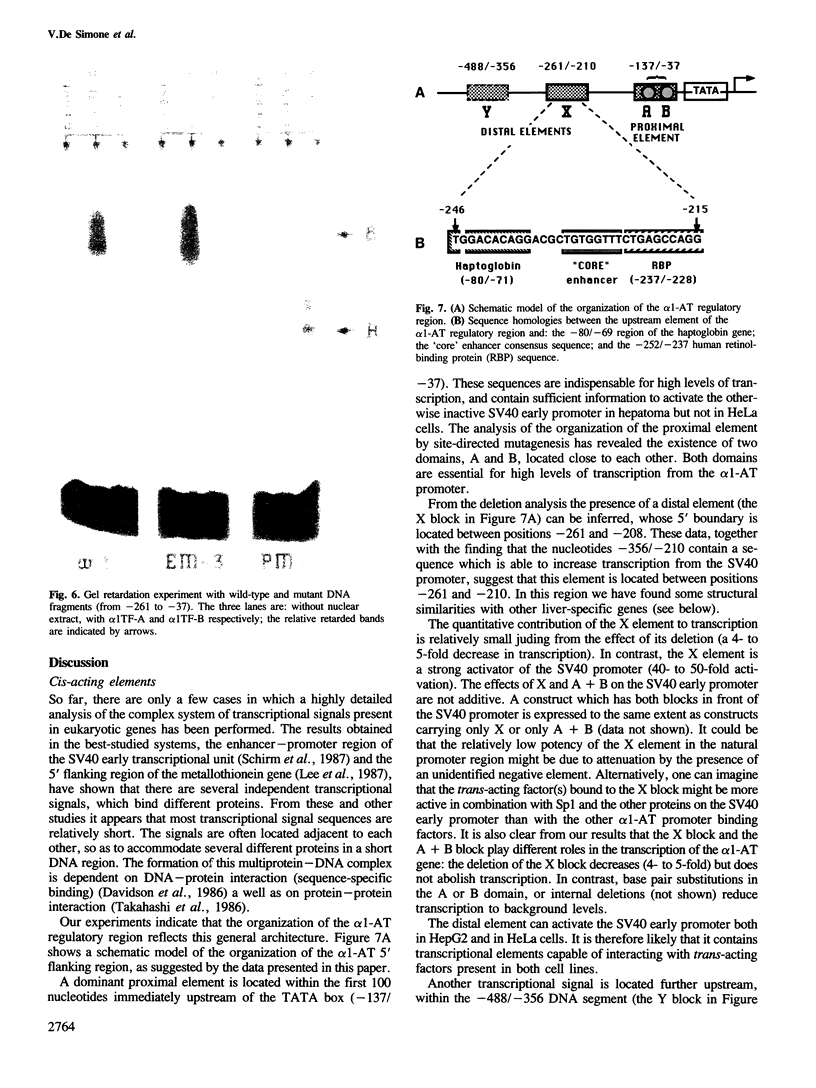
The 5' flanking region of the human alpha 1-antitrypsin (alpha 1-AT) gene contains cis-acting signals for liver-specific expression and, when fused to a reporter gene, is able to drive the expression of this gene specifically in liver cells. Here we report the results of a functional dissection of the alpha 1-AT regulatory region. The expression of the bacterial chloramphenicol-transacetylase (CAT) gene, fused to a set of alpha 1-AT 5' flanking regions shortened by progressive deletions or mutated by base pair substitutions, has been compared by transfection in HepG2 (hepatocyte) and HeLa (non-hepatocyte) human cell lines. A minimal tissue-specific element has been identified between the nucleotides -137 and -37 (from the transcriptional start site). This DNA segment activates the heterologous SV40 promoter in hepatoma cell lines but not in HeLa cells. This element contains at least two regions referred to as the A (-125/-100) and B (-84/-70) domains, both essential for transcription. There are at least two other regulatory domains located upstream of the 'minimal element'; the most active of these is located between positions -261 and -210 from the cap site. These upstream elements activate the heterologous SV40 early promoter both in hepatoma cell lines and in HeLa cells. Upon fractionation of rat liver nuclear extracts two proteins have been identified, alpha 1TF-A and alpha 1TF-B, which bind specifically to the A and B domains respectively. Transcriptionally inactive A and B domain mutants are not able to bind these proteins.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensi G., Raugei G., Klefenz H., Cortese R. Structure and expression of the human haptoglobin locus. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):119–126. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02325.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Dente L., Cortese R. Cell-specific expression of a transfected human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):531–540. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colantuoni V., Pirozzi A., Blance C., Cortese R. Negative control of liver-specific gene expression: cloned human retinol-binding protein gene is repressed in HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):631–636. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04801.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Onofrio C., Colantuoni V., Cortese R. Structure and cell-specific expression of a cloned human retinol binding protein gene: the 5'-flanking region contains hepatoma specific transcriptional signals. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):1981–1989. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03881.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Fromental C., Augereau P., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Cell-type specific protein binding to the enhancer of simian virus 40 in nuclear extracts. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):544–548. doi: 10.1038/323544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Ciliberto G., Cortese R. Structure of the human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein gene: sequence homology with other human acute phase protein genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 11;13(11):3941–3952. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.11.3941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Pizza M. G., Metspalu A., Cortese R. Structure and expression of the genes coding for human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2289–2296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02503.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. E., Krumlauf R., Camper S. A., Brinster R. L., Tilghman S. M. Diversity of alpha-fetoprotein gene expression in mice is generated by a combination of separate enhancer elements. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):53–58. doi: 10.1126/science.2432657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey G. D., Povey S., Bygrave A. E., Lovell-Badge R. H. Species- and tissue-specific expression of human alpha 1-antitrypsin in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):161–171. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles B. B., Howe C. C., Aden D. P. Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines secrete the major plasma proteins and hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1980 Jul 25;209(4455):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.6248960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Haslinger A., Karin M., Tjian R. Activation of transcription by two factors that bind promoter and enhancer sequences of the human metallothionein gene and SV40. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):368–372. doi: 10.1038/325368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliviero S., Morrone G., Cortese R. The human haptoglobin gene: transcriptional regulation during development and acute phase induction. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1905–1912. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02450.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirm S., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. The SV40 enhancer can be dissected into multiple segments, each with a different cell type specificity. Genes Dev. 1987 Mar;1(1):65–74. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sifers R. N., Carlson J. A., Clift S. M., DeMayo F. J., Bullock D. W., Woo S. L. Tissue specific expression of the human alpha-1-antitrypsin gene in transgenic mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1459–1475. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Matthes H., Wildeman A., Zenke M., Chambon P. Requirement of stereospecific alignments for initiation from the simian virus 40 early promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):121–126. doi: 10.1038/319121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., London I. M. Mapping of DNase I-hypersensitive sites in the upstream DNA of human embryonic epsilon-globin gene in K562 leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2718–2722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Chambon P. Short and long range activation by the SV40 enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5589–5608. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








