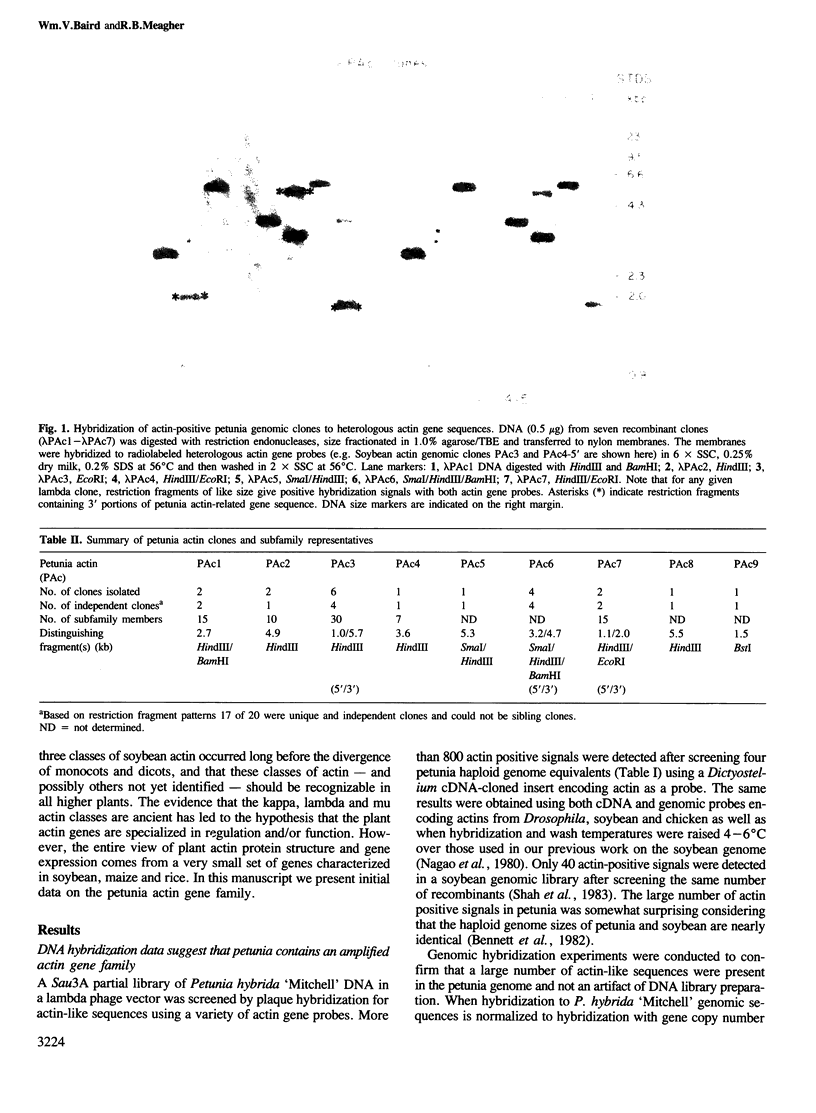
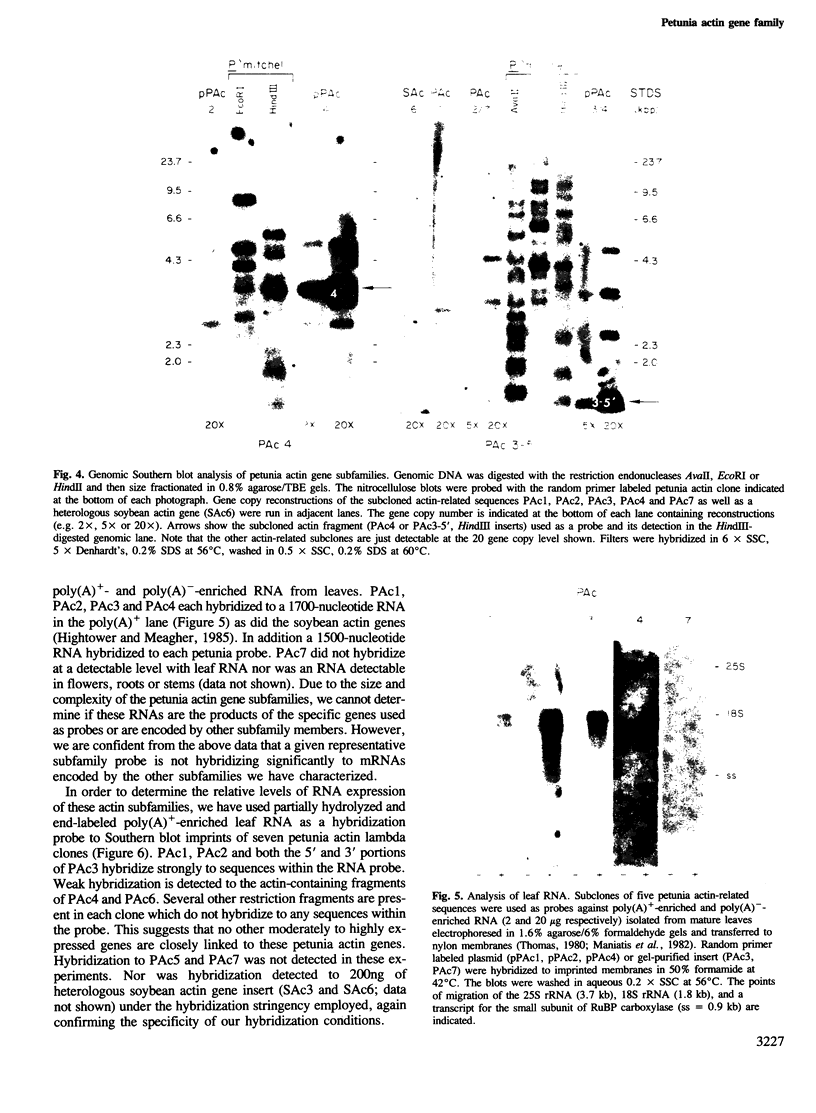
Abstract
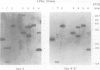
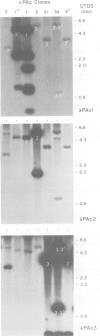
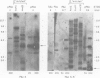
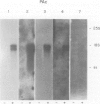
We have shown by several independent criteria that actin is encoded by a very large and complex superfamily of genes in Petunia. Several cDNA and genomic probes encoding actins from diverse organisms (Dictyostelium, Drosophila, chicken and soybean) hybridize to hundreds of restriction fragments in the petunia genome. Actin-hybridizing sequences were isolated from a petunia genomic library at a rate of at least 200 per genome equivalent. Twenty randomly selected actin-hybridizing clones were characterized in more detail. DNA sequence data from four representative and highly divergent clones, PAc2, PAc3, PAc4 and PAc7, demonstrate that these actin-like sequences are related to functional actin genes. Intron positions typical of other known plant actin genes are conserved in these clones. Four of six clones analyzed (PAc1, PAc2, PAc3, PAc4) hybridize to leaf mRNA of the same size (1.7 kb) as that reported for other plant actin mRNAs and to a slightly smaller mRNA species (1.5 kb). Five distinct subfamilies of actin-related genes were characterized which varied in size from a few members to several dozen members. It is clear from our data that other actin gene subfamilies must also exist within the genome. Possible mechanisms of actin gene amplification and genome turnover are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Retroviruses and retrotransposons: the role of reverse transcription in shaping the eukaryotic genome. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):481–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. D., Smith J. B. Nuclear dna amounts in angiosperms. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 May 27;274(933):227–274. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1976.0044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Chang K. S., Schwartz R. J. Novel chicken actin gene: third cytoplasmic isoform. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1151–1162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. A colony bank containing synthetic Col El hybrid plasmids representative of the entire E. coli genome. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condit C., Hagen T. J., McKnight T. D., Meagher R. B. Characterization and preliminary mapping of cauliflower mosaic virus transcripts. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90172-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cupples C. G., Pearlman R. E. Isolation and characterization of the actin gene from Tetrahymena thermophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5160–5164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean C., Elzen P., Tamaki S., Dunsmuir P., Bedbrook J. Differential expression of the eight genes of the petunia ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit multi-gene family. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3055–3061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donn G., Tischer E., Smith J. A., Goodman H. M. Herbicide-resistant alfalfa cells: an example of gene amplification in plants. J Mol Appl Genet. 1984;2(6):621–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunsmuir P., Smith S. M., Bedbrook J. The major chlorophyll a/b binding protein of petunia is composed of several polypeptides encoded by a number of distinct nuclear genes. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(3):285–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckenrode V. K., Arnold J., Meagher R. B. Comparison of the nucleotide sequence of soybean 18S rRNA with the sequences of other small-subunit rRNAs. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(3):259–269. doi: 10.1007/BF02102358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Files J. G., Carr S., Hirsh D. Actin gene family of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 5;164(3):355–375. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Bond B. J., Hershey N. D., Mixter K. S., Davidson N. The actin genes of Drosophila: protein coding regions are highly conserved but intron positions are not. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90506-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Kindle K. L., Davidson N., Kindle K. L. The actin genes of Drosophila: a dispersed multigene family. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):365–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90511-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Seidel R. Molecular cloning of the actin gene from yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 11;8(5):1043–1059. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.5.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms C., Graham M. Y., Dutchik J. E., Olson M. V. A new method for purifying lambda DNA from phage lysates. DNA. 1985 Feb;4(1):39–49. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower R. C., Meagher R. B. Divergence and differential expression of soybean actin genes. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):1–8. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02309.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower R. C., Meagher R. B. The molecular evolution of actin. Genetics. 1986 Sep;114(1):315–332. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.1.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns M. A., Mottinger J., Freeling M. A low copy number, copia-like transposon in maize. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1093–1101. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03745.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindle K. L., Firtel R. A. Identification and analysis of Dictyostelium actin genes, a family of moderately repeated genes. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):763–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90262-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koes R. E., Spelt C. E., Reif H. J., van den Elzen P. J., Veltkamp E., Mol J. N. Floral tissue of Petunia hybrida (V30) expresses only one member of the chalcone synthase multigene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5229–5239. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariani B. D., Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in a single cell cycle in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1901–1910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeown M., Taylor W. C., Kindle K. L., Firtel R. A., Bender W., Davidson N. Multiple, heterogeneous actin genes in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):789–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90264-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Alonso S., Guénet J. L., Buckingham M. E. Number and organization of actin-related sequences in the mouse genome. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 15;167(1):77–101. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao R. T., Shah D. M., Eckenrode V. K., Meagher R. B. Multigene family of actin-related sequences isolated from a soybean genomic library. DNA. 1981;1(1):1–9. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1981.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellen W., Gallwitz D. Actin genes and actin messenger RNA in Acanthamoeba castellanii. Nucleotide sequence of the split actin gene I. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 25;159(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng S. Y., Gunning P., Eddy R., Ponte P., Leavitt J., Shows T., Kedes L. Evolution of the functional human beta-actin gene and its multi-pseudogene family: conservation of noncoding regions and chromosomal dispersion of pseudogenes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2720–2732. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gunning P., Blau H., Kedes L. Human actin genes are single copy for alpha-skeletal and alpha-cardiac actin but multicopy for beta- and gamma-cytoskeletal genes: 3' untranslated regions are isotype specific but are conserved in evolution. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1783–1791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada I., Schmid C. W. Primate evolution of the alpha-globin gene cluster and its Alu-like repeats. J Mol Biol. 1986 Dec 20;192(4):693–709. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedl T., Dove W. F. Mendelian analysis of the organization of actin sequences in Physarum polycephalum. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep;160(1):41–57. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller R. H., McAllister L. B., Crain W. R., Jr, Durica D. S., Posakony J. W., Thomas T. L., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Organization and expression of multiple actin genes in the sea urchin. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;1(7):609–628. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.7.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. J., Rothblum K. N. Gene switching in myogenesis: differential expression of the chicken actin multigene family. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4122–4129. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. M., Hightower R. C., Meagher R. B. Complete nucleotide sequence of a soybean actin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1022–1026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. M., Hightower R. C., Meagher R. B. Genes encoding actin in higher plants: intron positions are highly conserved but the coding sequences are not. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):111–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. M., Horsch R. B., Klee H. J., Kishore G. M., Winter J. A., Tumer N. E., Hironaka C. M., Sanders P. R., Gasser C. S., Aykent S., Siegel N. R., Rogers S. G., Fraley R. T. Engineering herbicide tolerance in transgenic plants. Science. 1986 Jul 25;233(4762):478–481. doi: 10.1126/science.233.4762.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Wessler S., Fedoroff N. Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soares M. B., Schon E., Henderson A., Karathanasis S. K., Cate R., Zeitlin S., Chirgwin J., Efstratiadis A. RNA-mediated gene duplication: the rat preproinsulin I gene is a functional retroposon. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2090–2103. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Gene amplification. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:447–491. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Vegetative Dictyostelium cells containing 17 actin genes express a single major actin. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):475–477. doi: 10.1038/284475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanin E. F. Processed pseudogenes: characteristics and evolution. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:253–272. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E., Quintrell N., Ortiz S. Retroviruses as mutagens: insertion and excision of a nontransforming provirus alter expression of a resident transforming provirus. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B. Thalassemia revisited. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):7–9. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang R., Lis J., Wu R. Elution of DNA from agarose gels after electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:176–182. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]