Abstract
In spite of the large amount of genetic data obtained on the X chromosome and of the availability of many cloned sequences little is known about the physical map of this chromosome. The construction of large-scale restriction maps is now possible with pulsed field gel methods and data has recently been obtained in the region of band Xq28. We present here results of physical mapping in the Xq27 region, i.e. proximal to the fragile site at Xq27.3 associated with mental retardation, and show physical linkage between the coagulation factor IX gene and the mcf.2 transforming sequence recently localized to Xq27. Our data also indicate partial methylation of some sites in this region, and locate several 'HTF islands', i.e. CpG-rich, unmethylated sequences, containing several sites for 'rare cutter' enzymes, which are believed to be associated with expressed 'housekeeping' genes.
Full text
PDF

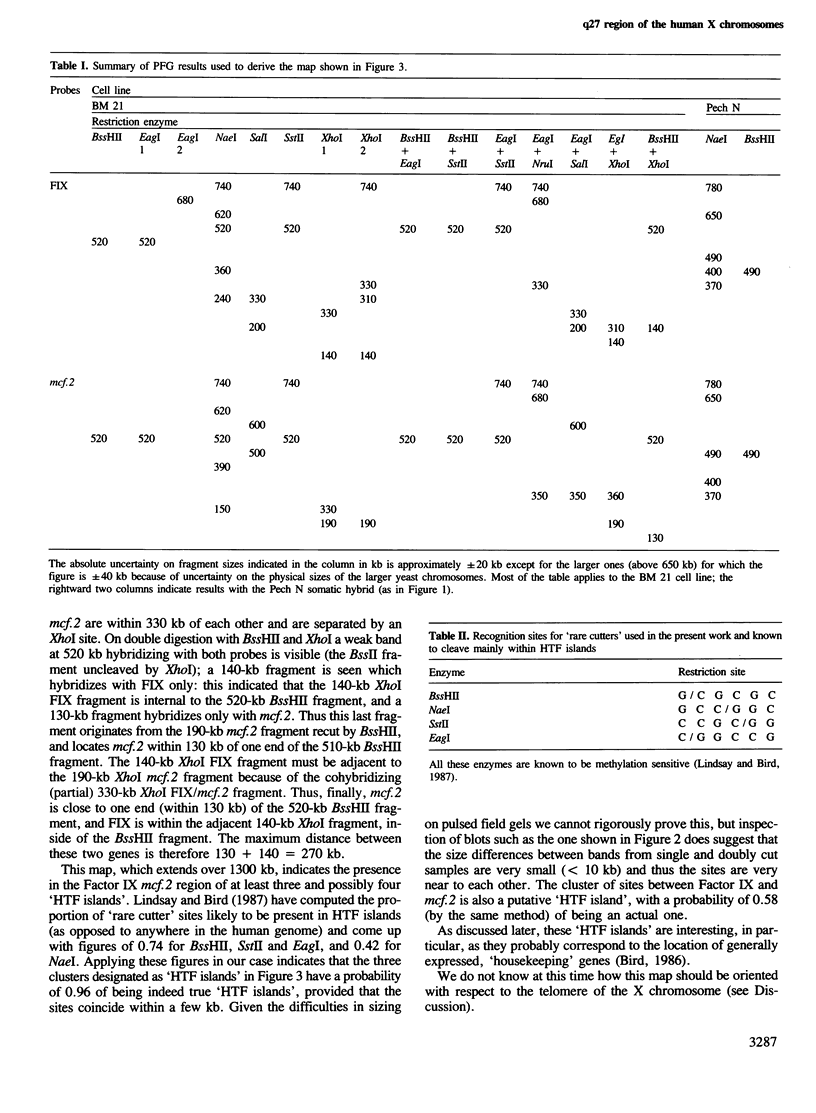
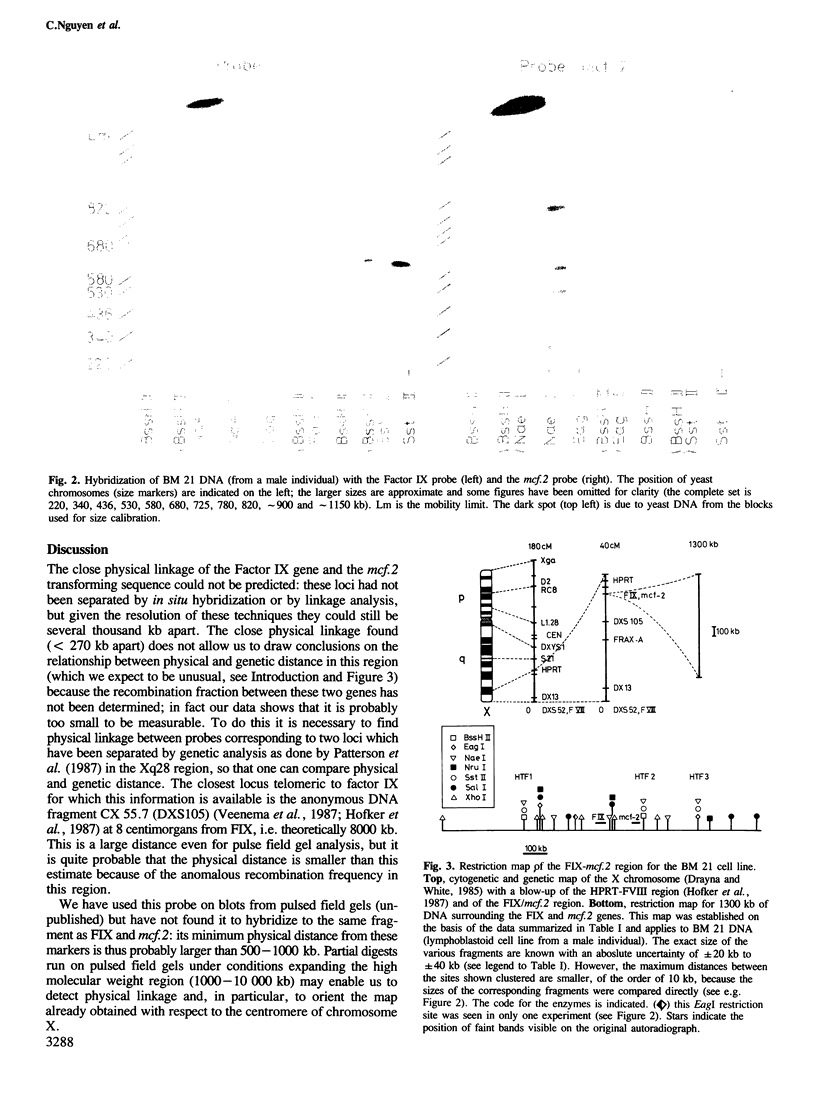

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Bird A. P. Long-range restriction site mapping of mammalian genomic DNA. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):477–481. doi: 10.1038/322477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerino G., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Jaye M., Mandel J. L. Close linkage of fragile X-mental retardation syndrome to haemophilia B and transmission through a normal male. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):701–704. doi: 10.1038/306701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. An electrophoretic karyotype for yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3756–3760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from yeast by orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5647–5664. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., George D., Filby G., Halliday J. L., Leversha M., Webb G., Danks D. M. Linkage analysis of X-linked mental retardation with and without fragile-X using factor IX gene probe. Lancet. 1984 Aug 11;2(8398):349–349. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92715-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen C. R., Hubberman P., Kaslow D. C., Migeon B. R. Comparison of factor IX methylation on human active and inactive X chromosomes: implications for X inactivation and transcription of tissue-specific genes. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2223–2229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04488.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., White R. The genetic linkage map of the human X chromosome. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):753–758. doi: 10.1126/science.4059909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P. N., Davies K. E., Ropers H. H. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of the X and Y Chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):296–352. doi: 10.1159/000132178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S., Bird A. P. Use of restriction enzymes to detect potential gene sequences in mammalian DNA. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):336–338. doi: 10.1038/327336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi T., Mattei M. G., Oberlè I., Planche J., Imbert J., Pelassy C., Birg F., Birnbaum D. Localization of the mcf.2 transforming sequence to the X chromosome. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1301–1307. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson M., Kenwrick S., Thibodeau S., Faulk K., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Davies K. E. Mapping of DNA markers close to the fragile site on the human X chromosome at Xq27.3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2639–2651. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland G. R. The fragile X chromosome. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;81:107–143. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62336-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




