Abstract
Varying lengths of the hamster desmin and vimentin promoter regions were fused to the bacterial chloramphenicol acetyl-transferase gene. These constructs were transfected into two different myogenic cell lines, T984 and C2C12. In both cell lines an increase in endogenous desmin expression takes place upon myogenesis. A region between -89 and +25 bp relative to the desmin transcription initiation site directs high-level tissue- and stage-specific expression upon in vitro myogenesis. At the myoblast stage, C2C12 cells appeared to express both desmin and vimentin, whereas in T984 myoblasts only vimentin expression was detected. Although vimentin is expressed during all stages of myogenesis, a strong decrease in vimentin expression occurs during differentiation of C2C12 cells. Vimentin--CAT constructs followed the endogenous expression pattern, showing that this down-regulation is mediated by 5' flanking sequences. Vimentin promoter activity is modulated by at least two separate regions, both in myogenic and in non-myogenic cell lines.
Full text
PDF

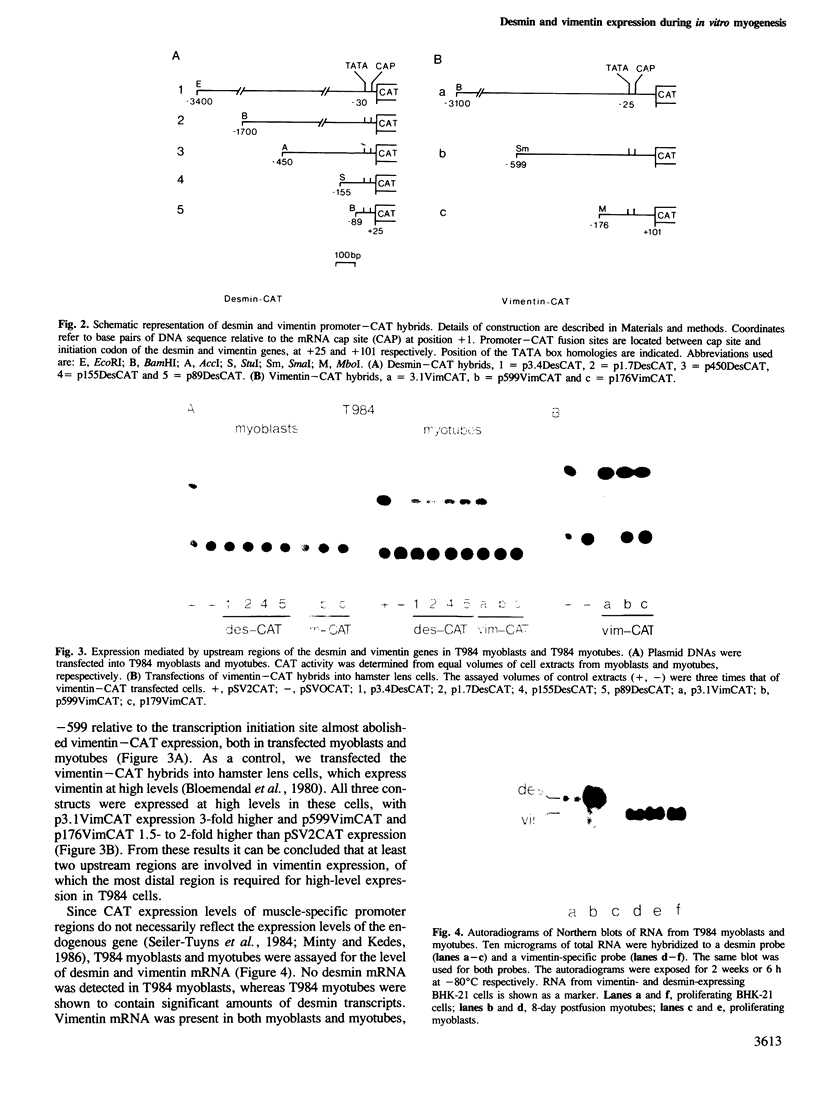
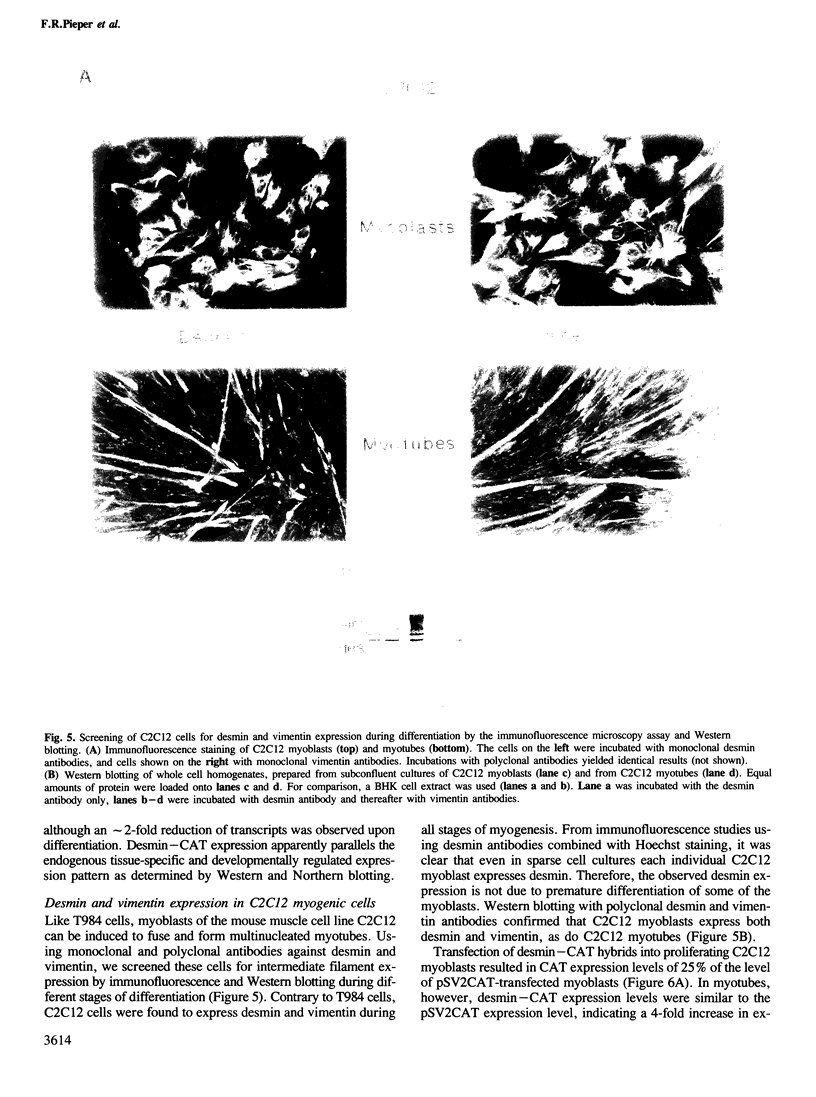




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader B. L., Magin T. M., Hatzfeld M., Franke W. W. Amino acid sequence and gene organization of cytokeratin no. 19, an exceptional tail-less intermediate filament protein. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1865–1875. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bains W., Ponte P., Blau H., Kedes L. Cardiac actin is the major actin gene product in skeletal muscle cell differentiation in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1449–1453. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. S., Fellini S. A., Toyama Y., Holtzer H. Redistribution of intermediate filament subunits during skeletal myogenesis and maturation in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):577–584. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Grichnik J. M., Gossett L. M., Schwartz R. J. Delimitation and characterization of cis-acting DNA sequences required for the regulated expression and transcriptional control of the chicken skeletal alpha-actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2462–2475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M., Chiu C. P., Webster C. Cytoplasmic activation of human nuclear genes in stable heterocaryons. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1171–1180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90300-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M., Pavlath G. K., Hardeman E. C., Chiu C. P., Silberstein L., Webster S. G., Miller S. C., Webster C. Plasticity of the differentiated state. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):758–766. doi: 10.1126/science.2414846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blikstad I., Lazarides E. Vimentin filaments are assembled from a soluble precursor in avian erythroid cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1803–1808. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broers J. L., Carney D. N., Klein Rot M., Schaart G., Lane E. B., Vooijs G. P., Ramaekers F. C. Intermediate filament proteins in classic and variant types of small cell lung carcinoma cell lines: a biochemical and immunochemical analysis using a panel of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1986 Jul;83:37–60. doi: 10.1242/jcs.83.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capetanaki Y. G., Ngai J., Flytzanis C. N., Lazarides E. Tissue-specific expression of two mRNA species transcribed from a single vimentin gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capetanaki Y. G., Ngai J., Lazarides E. Characterization and regulation in the expression of a gene coding for the intermediate filament protein desmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6909–6913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caravatti M., Minty A., Robert B., Montarras D., Weydert A., Cohen A., Daubas P., Buckingham M. Regulation of muscle gene expression. The accumulation of messenger RNAs coding for muscle-specific proteins during myogenesis in a mouse cell line. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep;160(1):59–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90131-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dlugosz A. A., Tapscott S. J., Holtzer H. Effects of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate on the differentiation program of embryonic chick skeletal myoblasts. Cancer Res. 1983 Jun;43(6):2780–2789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. Z., Chaudhary N., Blobel G. cDNA sequencing of nuclear lamins A and C reveals primary and secondary structural homology to intermediate filament proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Lazarides E. The synthesis and distribution of desmin and vimentin during myogenesis in vitro. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90408-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Desmin and vimentin coexist at the periphery of the myofibril Z disc. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1053–1063. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grichnik J. M., Bergsma D. J., Schwartz R. J. Tissue restricted and stage specific transcription is maintained within 411 nucleotides flanking the 5' end of the chicken alpha-skeletal actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1683–1701. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardeman E. C., Chiu C. P., Minty A., Blau H. M. The pattern of actin expression in human fibroblast x mouse muscle heterokaryons suggests that human muscle regulatory factors are produced. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90373-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Duran S., Lin Z. X., Weber K., Holtzer H. Titin and myosin, but not desmin, are linked during myofibrillogenesis in postmitotic mononucleated myoblasts. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2185–2196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzer H., Forry-Schaudies S., Dlugosz A., Antin P., Dubyak G. Interactions between IFs, microtubules, and myofibrils in fibrogenic and myogenic cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:106–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakob H., Buckingham M. E., Cohen A., Dupont L., Fiszman M., Jacob F. A skeletal muscle cell line isolated from a mouse teratocarcinoma undergoes apparently normal terminal differentiation in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jul;114(2):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90499-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., Chamberlain J. S., Buskin J. N., Johnson J. E., Hauschka S. D. Transcriptional regulation of the muscle creatine kinase gene and regulated expression in transfected mouse myoblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2855–2864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Luciw P. A., Tjian R. Activation of the AIDS retrovirus promoter by the cellular transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):755–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3008338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorcano J. L., Magin T. M., Franke W. W. Cell type-specific expression of bovine keratin genes as demonstrated by the use of complementary DNA clones. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 15;176(1):21–37. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90380-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny S. F., Emerson C. P., Jr Differentiation, not determination, regulates muscle gene activation: transfection of troponin I genes into multipotential and muscle lineages of 10T1/2 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2423–2432. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments: a chemically heterogeneous, developmentally regulated class of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:219–250. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilienbaum A., Legagneux V., Portier M. M., Dellagi K., Paulin D. Vimentin gene: expression in human lymphocytes and in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2809–2814. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchuk D., McCrohon S., Fuchs E. Complete sequence of a gene encoding a human type I keratin: sequences homologous to enhancer elements in the regulatory region of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1609–1613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melloul D., Aloni B., Calvo J., Yaffe D., Nudel U. Developmentally regulated expression of chimeric genes containing muscle actin DNA sequences in transfected myogenic cells. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):983–990. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Blau H., Kedes L. Two-level regulation of cardiac actin gene transcription: muscle-specific modulating factors can accumulate before gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2137–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Garrett N., Gurdon J. B. Upstream sequences required for tissue-specific activation of the cardiac actin gene in Xenopus laevis embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3185–3193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Lazarides E. Posttranslational control of membrane-skeleton (ankyrin and alpha beta-spectrin) assembly in early myogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1726–1735. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngai J., Capetanaki Y. G., Lazarides E. Differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells results in the rapid repression of vimentin gene expression. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):306–314. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngai J., Capetanaki Y. G., Lazarides E. Expression of the genes coding for the intermediate filament proteins vimentin and desmin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:144–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Greenberg D., Ordahl C. P., Saxel O., Neuman S., Yaffe D. Developmentally regulated expression of a chicken muscle-specific gene in stably transfected rat myogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3106–3109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Geisler N., Shaw G., Sharp G., Weber K. Intermediate filaments. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):413–429. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., Egberts W. V., Hendriks W., Quax-Jeuken Y., Bloemendal H. The structure of the vimentin gene. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., van den Broek L., Egberts W. V., Ramaekers F., Bloemendal H. Characterization of the hamster desmin gene: expression and formation of desmin filaments in nonmuscle cells after gene transfer. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):327–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Puts J. J., Moesker O., Kant A., Huysmans A., Haag D., Jap P. H., Herman C. J., Vooijs G. P. Antibodies to intermediate filament proteins in the immunohistochemical identification of human tumours: an overview. Histochem J. 1983 Jul;15(7):691–713. doi: 10.1007/BF01002988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramaekers F. C., Puts J. J., Moesker O., Kant A., Vooijs G. P., Jap P. H. Intermediate filaments in malignant melanomas. Identification and use as marker in surgical pathology. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):635–643. doi: 10.1172/JCI110810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid E., Osborn M., Rungger-Brändle E., Gabbiani G., Weber K., Franke W. W. Distribution of vimentin and desmin filaments in smooth muscle tissue of mammalian and avian aorta. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Feb;137(2):329–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Eldridge J. D., Paterson B. M. Expression and regulation of chicken actin genes introduced into mouse myogenic and nonmyogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2980–2984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M. Tissue-specific and developmentally regulated expression of a chimeric actin-globin gene in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2624–2631. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberstein L., Webster S. G., Travis M., Blau H. M. Developmental progression of myosin gene expression in cultured muscle cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1075–1081. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90707-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Steven A. C., Roop D. R. The molecular biology of intermediate filaments. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T., Maher P. A., Singer S. J. Distributions of vimentin and desmin in developing chick myotubes in vivo. I. Immunofluorescence study. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):1961–1972. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weydert A., Barton P., Harris A. J., Pinset C., Buckingham M. Developmental pattern of mouse skeletal myosin heavy chain gene transcripts in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):121–129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90762-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Saxel O. A myogenic cell line with altered serum requirements for differentiation. Differentiation. 1977;7(3):159–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1977.tb01507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Saxel O. Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):725–727. doi: 10.1038/270725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehner Z. E., Paterson B. M. The chicken vimentin gene: aspects of organization and transcription during myogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;455:79–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]