Abstract
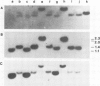
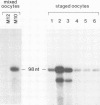
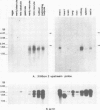
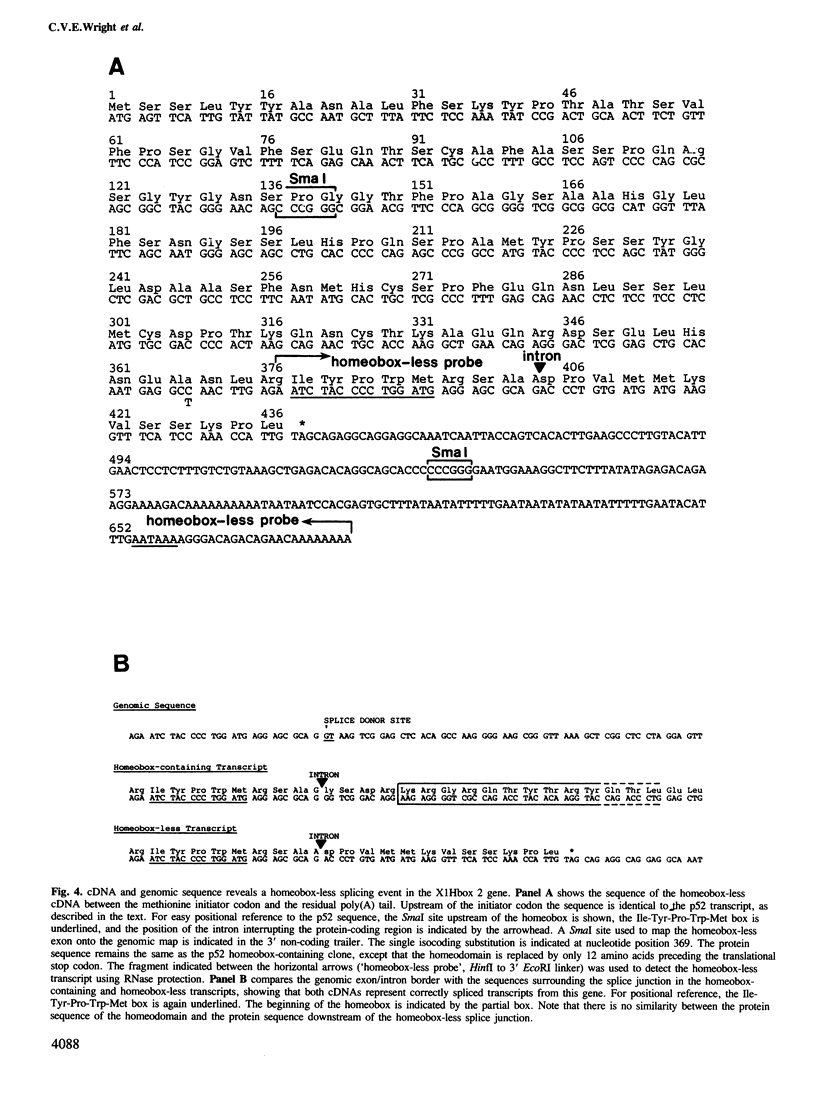
A cDNA clone (p52) that contains all the protein-coding region from the maternally expressed XlHbox 2 locus of the frog Xenopus laevis has been isolated and sequenced. A probe containing the exon preceding the homeobox detected transcripts which arise from a splicing event in which the homeobox-containing exon is replaced by another exon lying 5' to it in the genome. Both the homeobox-containing and homeobox-less splicing event occur in the same tissues, with the homeobox-less RNA representing the minority of mRNA from this gene. There may therefore be a function for two types of transcript, and hence protein, from this locus. This phenomenon may not be exclusive to the XlHbox 2 gene of Xenopus, but might occur more generally in other homeobox-containing genes. The protein deduced from the homeobox-containing cDNA is significantly similar to the yeast mating type factor a1 (MAT-a1) gene product. In addition to the previously described homology of the homeodomains, the amino-terminal domains of XlHbox 2 and MAT-a1 are similar to each other; thus essentially all of the MAT-a1 protein corresponds to some part of the XlHbox 2 protein. In the case of XlHbox 2, the protein coded for by the homeoboxless mRNA would contain all of the non-homeobox homology to yeast MAT-a1.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amara S. G., Jonas V., Rosenfeld M. G., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):240–244. doi: 10.1038/298240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awgulewitsch A., Utset M. F., Hart C. P., McGinnis W., Ruddle F. H. Spatial restriction in expression of a mouse homoeo box locus within the central nervous system. 1986 Mar 27-Apr 2Nature. 320(6060):328–335. doi: 10.1038/320328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bopp D., Burri M., Baumgartner S., Frigerio G., Noll M. Conservation of a large protein domain in the segmentation gene paired and in functionally related genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1033–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90818-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bürglin T. R. SEQGEL: a versatile and comfortable DNA editor which supports a special keyboard and a speech synthesizer. Comput Appl Biosci. 1986 Jun;2(2):99–101. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/2.2.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco A. E., Malacinski G. M. Localization of Xenopus homoeo-box gene transcripts during embryogenesis and in the adult nervous system. Dev Biol. 1987 May;121(1):69–81. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco A. E., McGinnis W., Gehring W. J., De Robertis E. M. Cloning of an X. laevis gene expressed during early embryogenesis coding for a peptide region homologous to Drosophila homeotic genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):409–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90371-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavener D. R. Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1353–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Voss S. D., Chowdhury K., Gruss P. Structural analysis of murine genes containing homoeo box sequences and their expression in embryonal carcinoma cells. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):713–718. doi: 10.1038/314713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colberg-Poley A. M., Voss S. D., Chowdhury K., Stewart C. L., Wagner E. F., Gruss P. Clustered homeo boxes are differentially expressed during murine development. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):39–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRobertis E. M., Fritz A., Goetz J., Martin G., Mattaj I. W., Salo E., Smith G. D., Wright C., Zeller R. The Xenopus homeo boxes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:271–275. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The Drosophila developmental gene, engrailed, encodes a sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):630–635. doi: 10.1038/318630a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolecki G. J., Wannakrairoj S., Lum R., Wang G., Riley H. D., Carlos R., Wang A., Humphreys T. Stage-specific expression of a homeo box-containing gene in the non-segmented sea urchin embryo. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):925–930. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
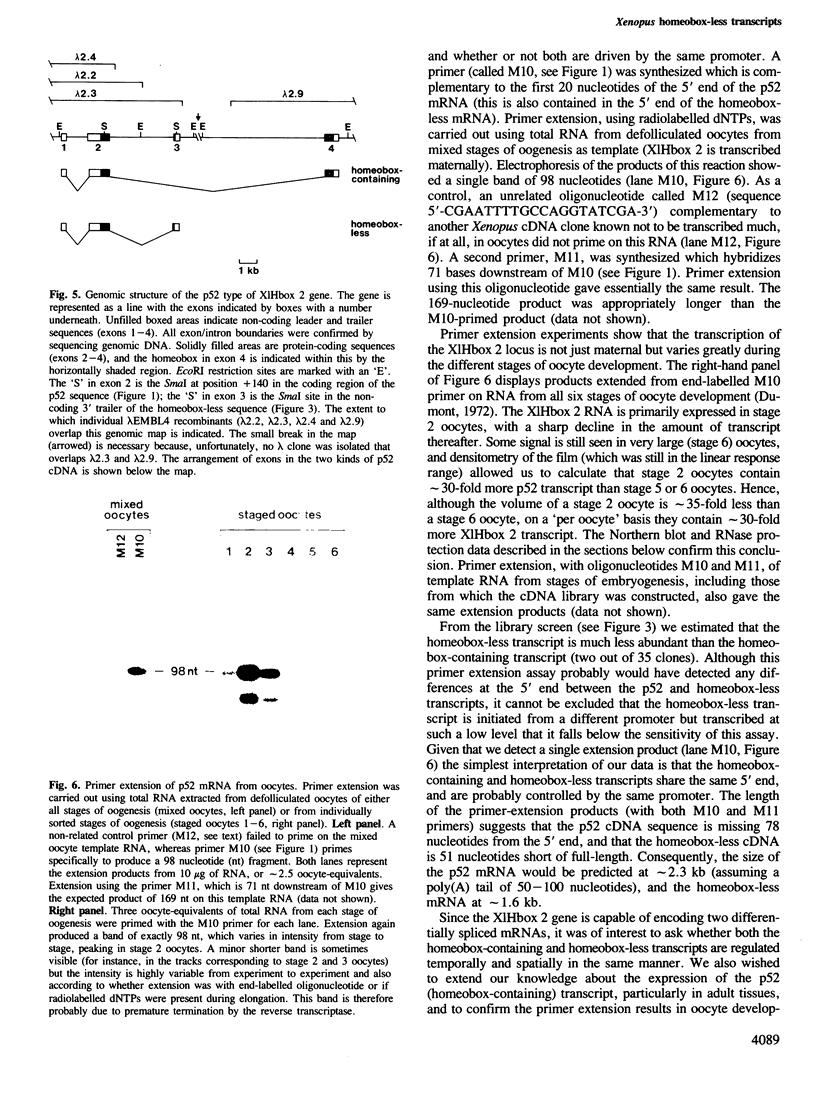
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainsod A., Bogarad L. D., Ruusala T., Lubin M., Crothers D. M., Ruddle F. H. The homeo domain of a murine protein binds 5' to its own homeo box. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9532–9536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fermi G. Three-dimensional fourier synthesis of human deoxyhaemoglobin at 2-5 A resolution: refinement of the atomic model. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 15;97(2):237–256. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frigerio G., Burri M., Bopp D., Baumgartner S., Noll M. Structure of the segmentation gene paired and the Drosophila PRD gene set as part of a gene network. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90516-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. Homeotic genes, the homeobox, and the spatial organization of the embryo. Harvey Lect. 1985 1986;81:153–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Heterogeneity and 5'-terminal structures of the late RNAs of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):813–846. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden L., Schafer U., Rosbash M. Accumulation of individual pA+ RNAs during oogenesis of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):835–844. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90560-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Mohun T. J., Fairman S., Brennan S. All components required for the eventual activation of muscle-specific actin genes are localized in the subequatorial region of an uncleaved amphibian egg. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):139–143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. P., Tabin C. J., Melton D. A. Embryonic expression and nuclear localization of Xenopus homeobox (Xhox) gene products. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1237–1244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04352.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner A. L., Martin G. R. En-1 and En-2, two mouse genes with sequence homology to the Drosophila engrailed gene: expression during embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1987 Mar;1(1):29–38. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R., Holland P. W., McVey J. H., Hogan B. L. Developmental and spatial patterns of expression of the mouse homeobox gene, Hox 2.1. Development. 1987 Apr;99(4):603–617. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.4.603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laughon A., Scott M. P. Sequence of a Drosophila segmentation gene: protein structure homology with DNA-binding proteins. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):25–31. doi: 10.1038/310025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Rubin G. M., Tjian R. Human DNA sequences homologous to a protein coding region conserved between homeotic genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):667–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90261-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Struhl G. A molecular gradient in early Drosophila embryos and its role in specifying the body pattern. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):537–545. doi: 10.1038/324537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. R. Nomenclature for homoeobox-containing genes. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):21–22. doi: 10.1038/325021b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavilio F., Simeone A., Giampaolo A., Faiella A., Zappavigna V., Acampora D., Poiana G., Russo G., Peschle C., Boncinelli E. Differential and stage-related expression in embryonic tissues of a new human homoeobox gene. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):664–668. doi: 10.1038/324664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Garber R. L., Wirz J., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. A homologous protein-coding sequence in Drosophila homeotic genes and its conservation in other metazoans. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):403–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis W., Hart C. P., Gehring W. J., Ruddle F. H. Molecular cloning and chromosome mapping of a mouse DNA sequence homologous to homeotic genes of Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mlodzik M., Fjose A., Gehring W. J. Isolation of caudal, a Drosophila homeo box-containing gene with maternal expression, whose transcripts form a concentration gradient at the pre-blastoderm stage. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2961–2969. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04030.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mlodzik M., Gehring W. J. Expression of the caudal gene in the germ line of Drosophila: formation of an RNA and protein gradient during early embryogenesis. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):465–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90197-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Carrasco A. E., DeRobertis E. M. A homeo-box-containing gene expressed during oogenesis in Xenopus. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenwald W. F., Taylor C. F., Palmer-Hill F. J., Friedrich V., Jr, Tani M., Lazzarini R. A. Expression of a homeo domain protein in noncontact-inhibited cultured cells and postmitotic neurons. Genes Dev. 1987 Jul;1(5):482–496. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.5.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Probst E., Kressmann A., Birnstiel M. L. Expression of sea urchin histone genes in the oocyte of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1979 Dec 15;135(3):709–732. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90173-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebagliati M. R., Weeks D. L., Harvey R. P., Melton D. A. Identification and cloning of localized maternal RNAs from Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):769–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regulski M., McGinnis N., Chadwick R., McGinnis W. Developmental and molecular analysis of Deformed; a homeotic gene controlling Drosophila head development. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):767–777. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04819.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneuwly S., Kuroiwa A., Baumgartner P., Gehring W. J. Structural organization and sequence of the homeotic gene Antennapedia of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):733–739. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04275.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J. C., McGinnis W., Carrasco A. E., De Robertis E. M., Gehring W. J. Fly and frog homoeo domains show homologies with yeast mating type regulatory proteins. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):70–71. doi: 10.1038/310070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroeher V. L., Jorgensen E. M., Garber R. L. Multiple transcripts from the Antennapedia gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4667–4675. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M., Stephenson P. Role of the conserved AAUAAA sequence: four AAUAAA point mutants prevent messenger RNA 3' end formation. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1045–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.6208611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Engelmyer E., Duggal R. N., Gizang-Ginsberg E., Mutter G. L., Ponzetto C., Viviano C., Zakeri Z. F. Isolation of a mouse cDNA coding for a developmentally regulated, testis-specific transcript containing homeo box homology. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1229–1235. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]