Abstract
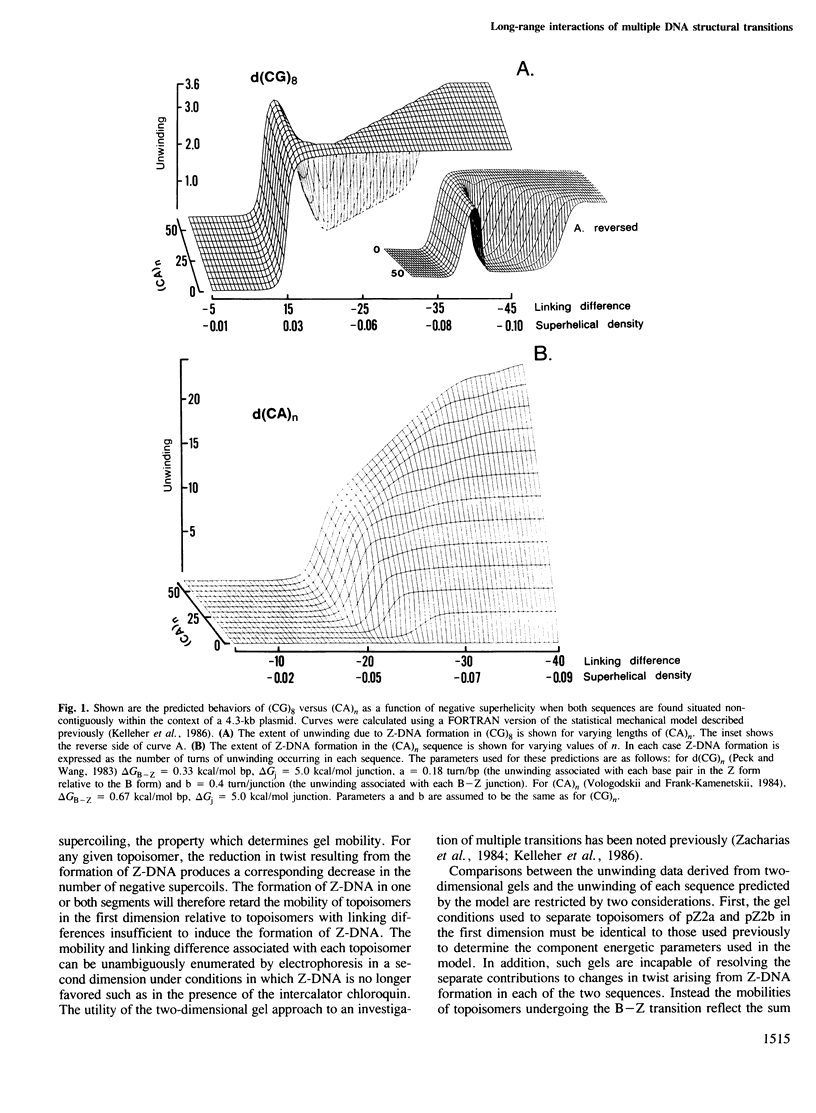
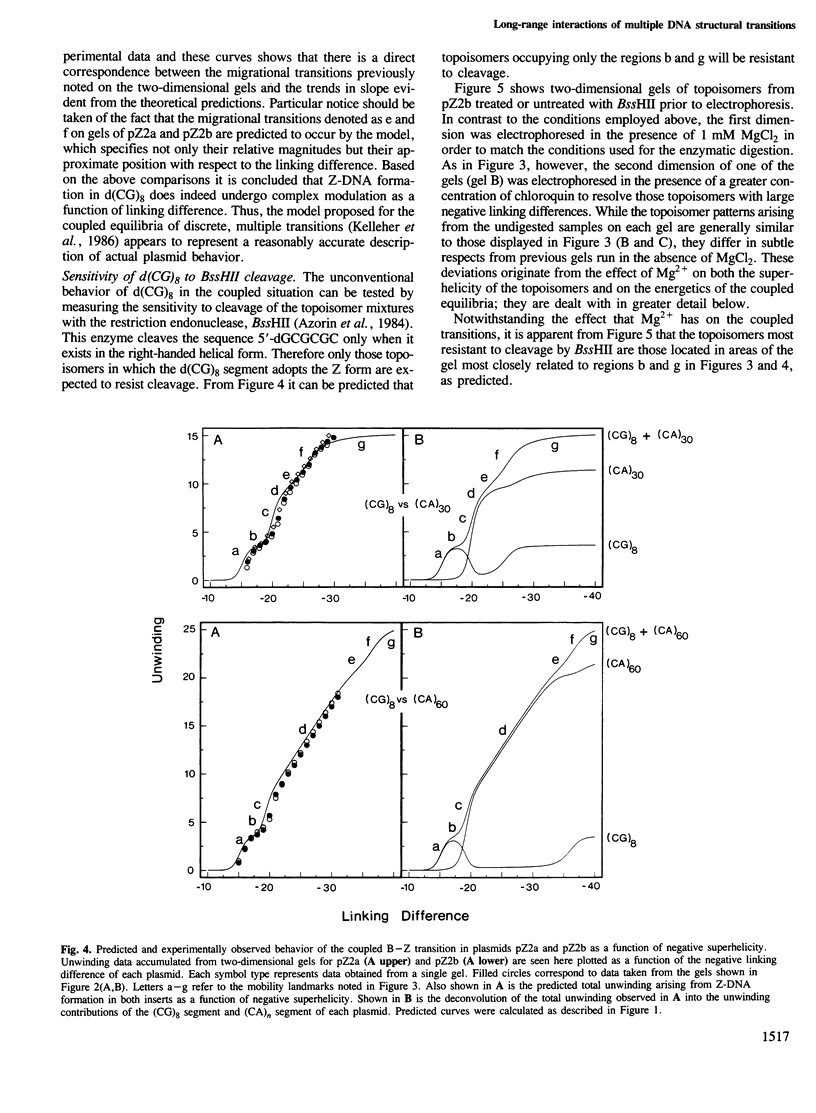
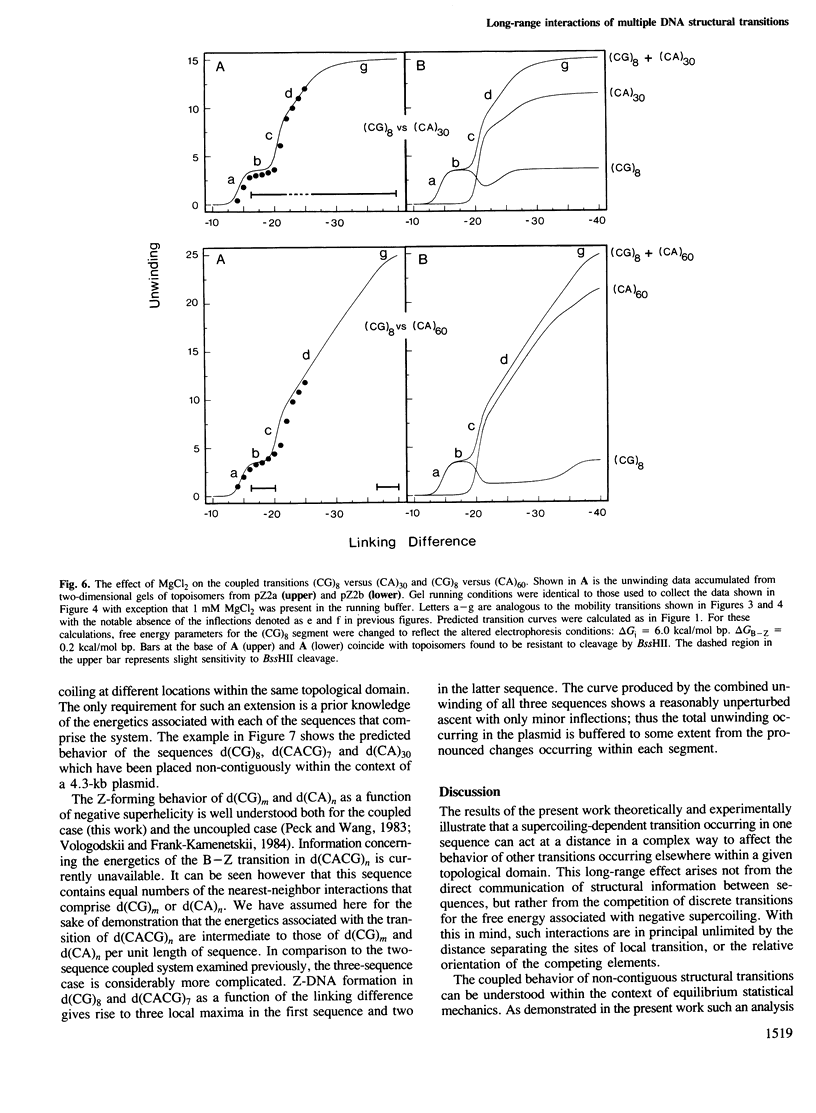
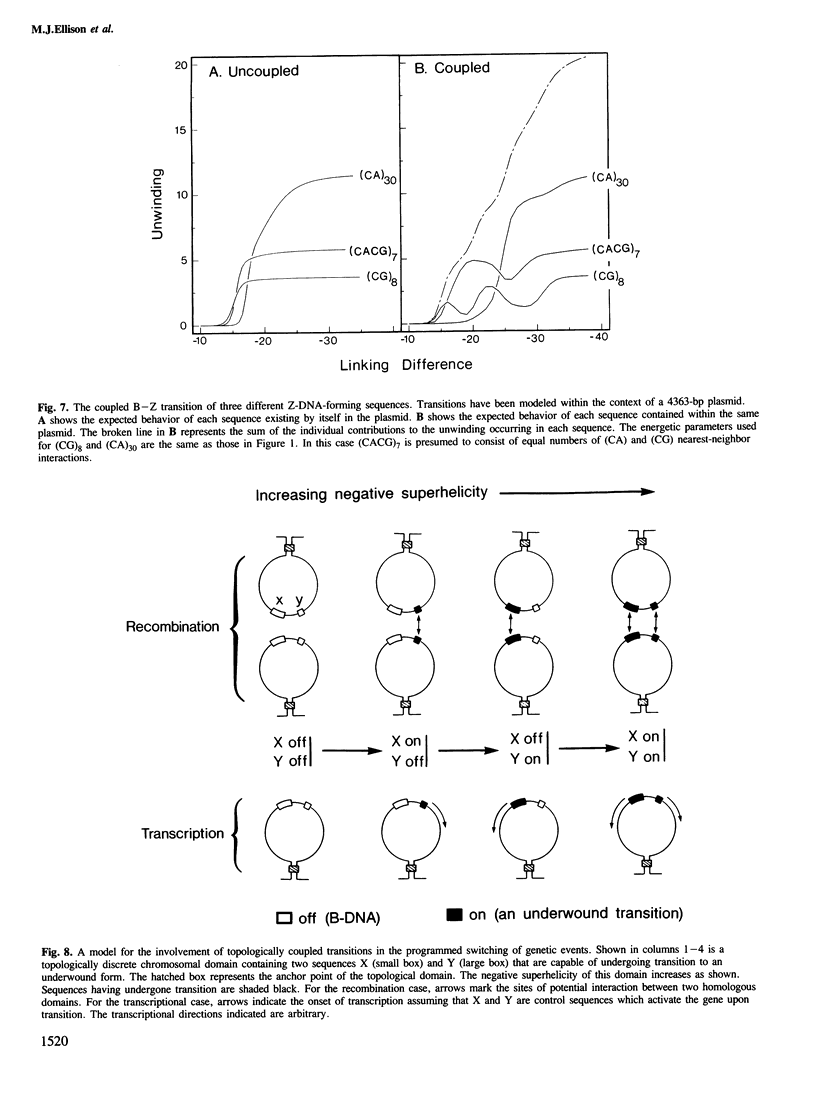
Local DNA conformations that are underwound with respect to the right-handed B form are favored in negatively supercoiled DNA. However, when multiple transitional events co-exist within a common topological domain, they must compete with one another for the available free energy of negative supercoiling. Recently we developed a general theoretical model capable of predicting the behavior at equilibrium of defined sequences in a variety of competitive situations. In the present work we have applied this theory to predict the formation of Z-DNA as a function of superhelicity in stretches of d(CG)m and d(CA)n when they are forced to compete with one another in the same plasmid. The observed behavior of these competing sequences is in close accord with theoretical predictions. These results indicate that sequences separated by large distances can effect the transitional behavior of each other in a complex manner which is independent of the relative orientation of the participating segments. The pattern of transitional events is strongly dependent on levels of DNA supercoiling, ambient conditions and on the nature and number of the sequences involved. Although in the present work we apply the model specifically to the Z-DNA conformational transition, the results of this study may have general relevance to a variety of biological processes in which the helical repeat of DNA is reversibly altered, including the initial steps in transcription, replication and recombination.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azorin F., Hahn R., Rich A. Restriction endonucleases can be used to study B-Z junctions in supercoiled DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5714–5718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. A., Sekimizu K., Funnell B. E., Kornberg A. Extensive unwinding of the plasmid template during staged enzymatic initiation of DNA replication from the origin of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90537-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behe M., Felsenfeld G. Effects of methylation on a synthetic polynucleotide: the B--Z transition in poly(dG-m5dC).poly(dG-m5dC). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1619–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. J. Statistical mechanical analysis of competing conformational transitions in superhelical DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):219–227. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham C. J. Theoretical analysis of competitive conformational transitions in torsionally stressed DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):43–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90324-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depew D. E., Wang J. C. Conformational fluctuations of DNA helix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison M. J., Feigon J., Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Wang A. H., Habener J. F., Rich A. An assessment of the Z-DNA forming potential of alternating dA-dT stretches in supercoiled plasmids. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 17;25(12):3648–3655. doi: 10.1021/bi00360a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison M. J., Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Wang A. H., Habener J. F., Rich A. Sequence-dependent energetics of the B-Z transition in supercoiled DNA containing nonalternating purine-pyrimidine sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8320–8324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. The organisation of chromatin loops: characterization of a scaffold attachment site. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):511–518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:879–910. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. Facile transition of poly[d(TG) x d(CA)] into a left-handed helix in physiological conditions. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):632–634. doi: 10.1038/302632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. The in-vivo occurrence of Z DNA. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Dec;1(3):593–609. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. Transition of a cloned d(AT)n-d(AT)n tract to a cruciform in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4343–4363. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
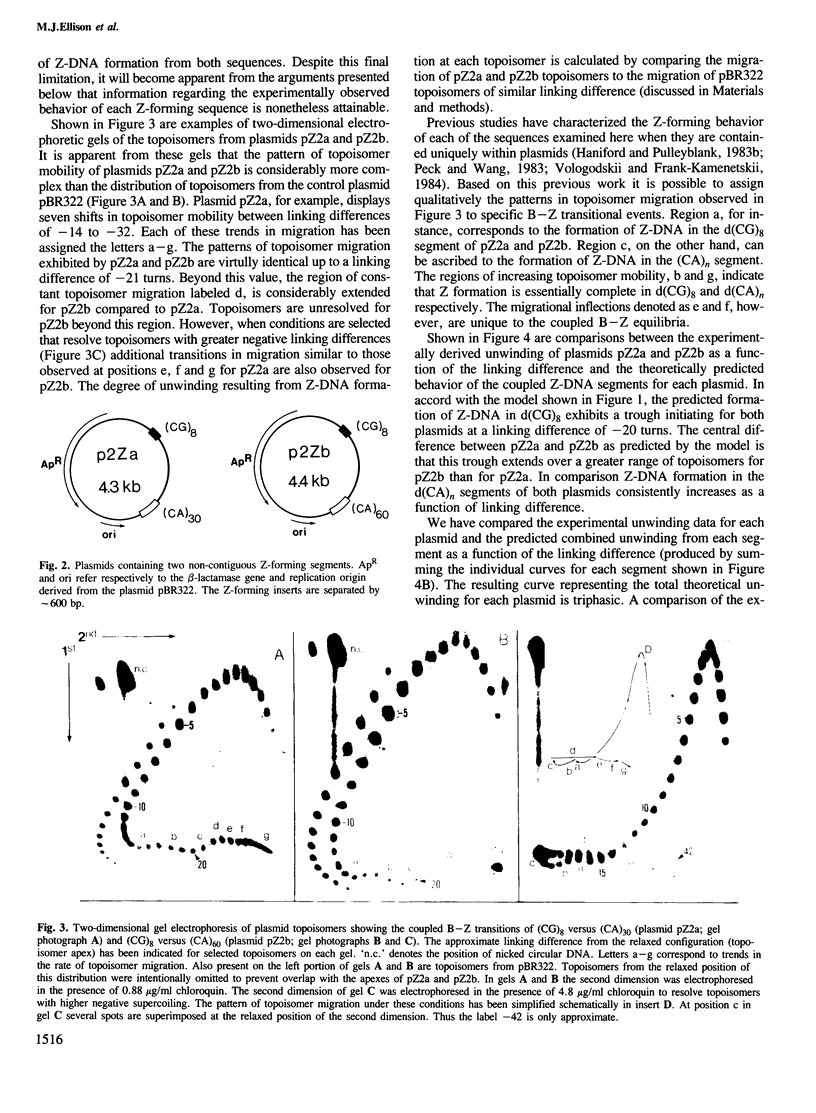
- Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Ellison M. J., Ho P. S., Rich A. Competitive behavior of multiple, discrete B-Z transitions in supercoiled DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6342–6346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E. B., Angelides K. J., Holloman W. K. Left-handed DNA and the synaptic pairing reaction promoted by Ustilago rec1 protein. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90317-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E. B., Holloman W. K. Homologous pairing of DNA molecules by Ustilago rec1 protein is promoted by sequences of Z-DNA. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kłysik J., Stirdivant S. M., Larson J. E., Hart P. A., Wells R. D. Left-handed DNA in restriction fragments and a recombinant plasmid. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):672–677. doi: 10.1038/290672a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Energetics of B-to-Z transition in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peck L. J., Wang J. C. Transcriptional block caused by a negative supercoiling induced structural change in an alternating CG sequence. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90316-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Haniford D. B., Morgan A. R. A structural basis for S1 nuclease sensitivity of double-stranded DNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):271–280. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Shure M., Tang D., Vinograd J., Vosberg H. P. Action of nicking-closing enzyme on supercoiled and nonsupercoiled closed circular DNA: formation of a Boltzmann distribution of topological isomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4280–4284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., Nordheim A., Wang A. H. The chemistry and biology of left-handed Z-DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:791–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Vinograd J. The number of superhelical turns in native virion SV40 DNA and minicol DNA determined by the band counting method. Cell. 1976 Jun;8(2):215–226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singleton C. K., Klysik J., Stirdivant S. M., Wells R. D. Left-handed Z-DNA is induced by supercoiling in physiological ionic conditions. Nature. 1982 Sep 23;299(5881):312–316. doi: 10.1038/299312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan K. M., Lilley D. M. A dominant influence of flanking sequences on a local structural transition in DNA. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):817–827. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90524-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vologodskii A. V., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D. Left-handed Z form in superhelical DNA: a theoretical study. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1984 Jun;1(6):1325–1333. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1984.10507523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. H., Quigley G. J., Kolpak F. J., Crawford J. L., van Boom J. H., van der Marel G., Rich A. Molecular structure of a left-handed double helical DNA fragment at atomic resolution. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):680–686. doi: 10.1038/282680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharias W., Larson J. E., Kilpatrick M. W., Wells R. D. HhaI methylase and restriction endonuclease as probes for B to Z DNA conformational changes in d(GCGC) sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7677–7692. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Sande J. H., Jovin T. M. Z* DNA, the left-handed helical form of poly[d(G-C)] in MgCl2-ethanol, is biologically active. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):115–120. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]