Abstract
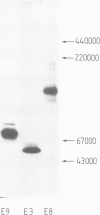
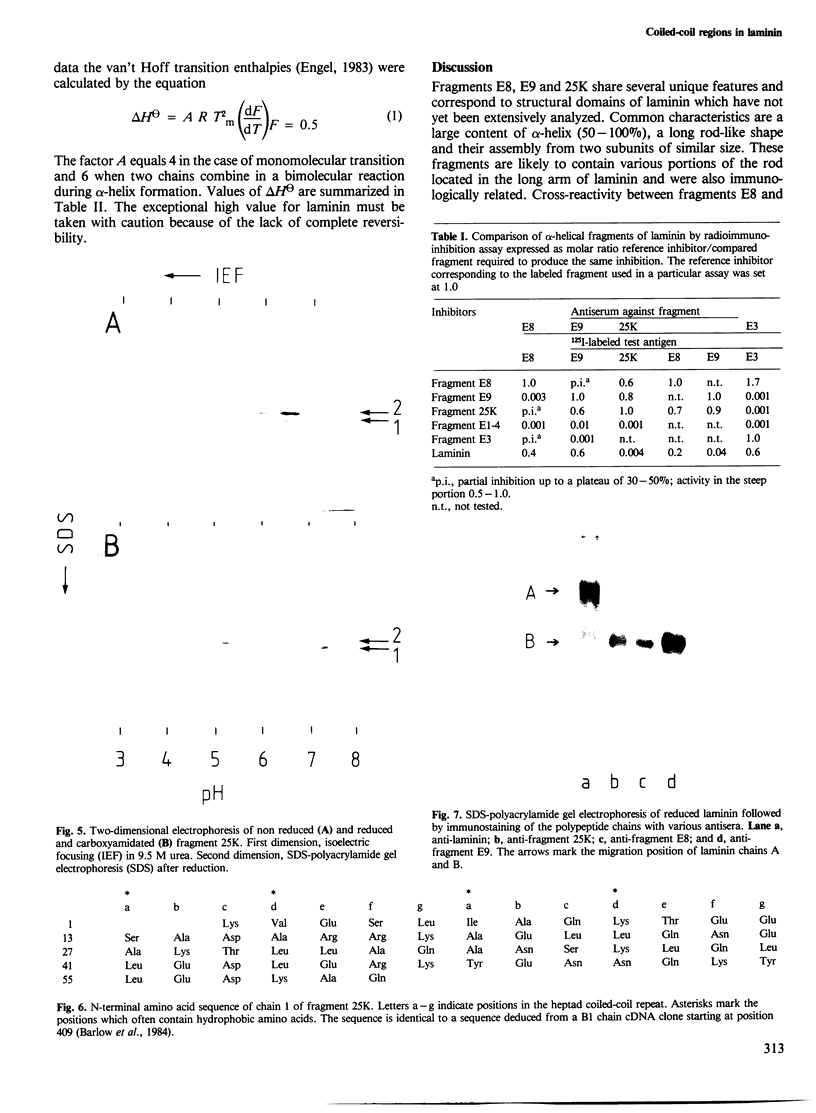
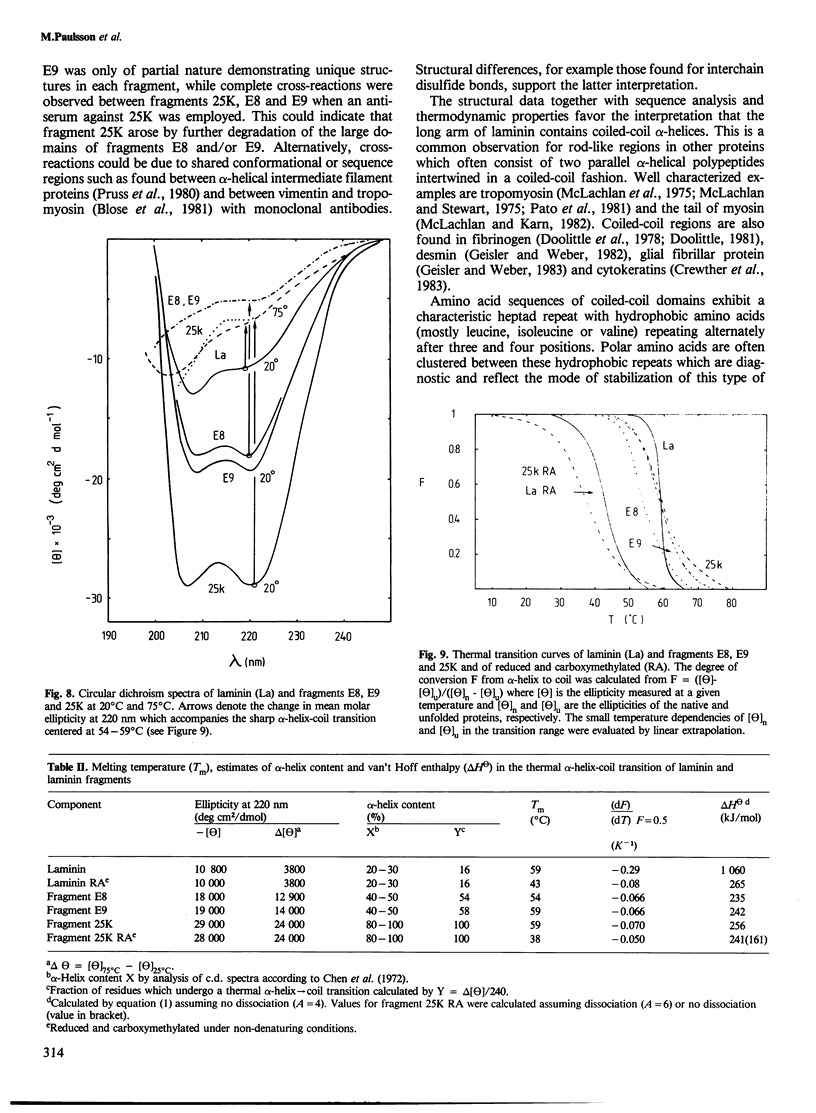
Three new laminin fragments, E8, E9 and 25K with mol. wt. 50 000-280 000, were prepared from a limited elastase digest of laminin and from tissue extracts. They were similar with respect to their rod-like structure, a high alpha-helix content, the assembly from two chain segments and immunological cross-reactivity. Two of the fragments (E8 and E9) possess in addition globular domains which lack alpha-helices. Chemical, immunological and physical data together with sequence analysis strongly indicate that the alpha-helical segments are assembled in coiled-coil structures which are located in the rod of the long arm of laminin. These data give new insights into the overall structure of the protein.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlow D. P., Green N. M., Kurkinen M., Hogan B. L. Sequencing of laminin B chain cDNAs reveals C-terminal regions of coiled-coil alpha-helix. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2355–2362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blose S. H., Matsumura F., Lin J. J. Structure of vimentin 10-nm filaments probed with a monoclonal antibody that recognizes a common antigenic determinant on vimentin and tropomyosin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 1):455–463. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Yang J. T., Martinez H. M. Determination of the secondary structures of proteins by circular dichroism and optical rotatory dispersion. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 24;11(22):4120–4131. doi: 10.1021/bi00772a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung A. E., Jaffe R., Freeman I. L., Vergnes J. P., Braginski J. E., Carlin B. Properties of a basement membrane-related glycoprotein synthesized in culture by a mouse embryonal carcinoma-derived cell line. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. R., Kurkinen M., Taylor A., Hogan B. L. Studies on the biosynthesis of laminin by murine parietal endoderm cells. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep;119(1):189–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. R., MacQueen H. A. Subunits of laminin are differentially synthesized in mouse eggs and early embryos. Dev Biol. 1983 Apr;96(2):467–471. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Goldbaum D. M., Doolittle L. R. Designation of sequences involved in the "coiled-coil" interdomainal connections in fibrinogen: constructions of an atomic scale model. J Mol Biol. 1978 Apr 5;120(2):311–325. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziadek M., Richter H., Schachner M., Timpl R. Monoclonal antibodies used as probes for the structural organization of the central region of fibronectin. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 8;155(2):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80629-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar D., Timpl R., Thoenen H. The heparin-binding domain of laminin is responsible for its effects on neurite outgrowth and neuronal survival. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1463–1468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J., Odermatt E., Engel A., Madri J. A., Furthmayr H., Rohde H., Timpl R. Shapes, domain organizations and flexibility of laminin and fibronectin, two multifunctional proteins of the extracellular matrix. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90326-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Amino acid sequence data on glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFA); implications for the subdivision of intermediate filaments into epithelial and non-epithelial members. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2059–2063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01700.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of chicken muscle desmin provides a common structural model for intermediate filament proteins. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1649–1656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C. C., Dietzschold B. Structural analysis of three subunits of laminin from teratocarcinoma-derived parietal endoderm cells. Dev Biol. 1983 Aug;98(2):385–391. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90367-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottspeich F. Identification of the phenylthiohydantoin derivatives of amino acids by high pressure liquid chromatography, using a ternary, isocratic solvent system. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1980 Dec;361(12):1829–1834. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1980.361.2.1829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Karn J. Periodic charge distributions in the myosin rod amino acid sequence match cross-bridge spacings in muscle. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):226–231. doi: 10.1038/299226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Stewart M., Smillie L. B. Sequence repeats in alpha-tropomyosin. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 25;98(2):281–291. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D., Stewart M. Tropomyosin coiled-coil interactions: evidence for an unstaggered structure. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 25;98(2):293–304. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott U., Odermatt E., Engel J., Furthmayr H., Timpl R. Protease resistance and conformation of laminin. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Mar;123(1):63–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pato M. D., Mak A. S., Smillie L. B. Fragments of rabbit striated muscle alpha-tropomyosin. I. Preparation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):593–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potekhin S. A., Privalov P. L. Co-operative blocks in tropomyosin. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 15;159(3):519–535. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provencher S. W., Glöckner J. Estimation of globular protein secondary structure from circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 6;20(1):33–37. doi: 10.1021/bi00504a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao C. N., Margulies I. M., Tralka T. S., Terranova V. P., Madri J. A., Liotta L. A. Isolation of a subunit of laminin and its role in molecular structure and tumor cell attachment. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9740–9744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Burke B. E., Branton D. The molecular structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. Biophysical and electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):303–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson C. A., Ritchie P. A. Conformational transitions in the subfragment-2 region of myosin. Biochemistry. 1980 Nov 11;19(23):5371–5375. doi: 10.1021/bi00564a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R. Antibodies to collagens and procollagens. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):472–498. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82079-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Dziadek M., Fujiwara S., Nowack H., Wick G. Nidogen: a new, self-aggregating basement membrane protein. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Dec 15;137(3):455–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Johansson S., van Delden V., Oberbäumer I., Hök M. Characterization of protease-resistant fragments of laminin mediating attachment and spreading of rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8922–8927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timpl R., Rohde H., Robey P. G., Rennard S. I., Foidart J. M., Martin G. R. Laminin--a glycoprotein from basement membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9933–9937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsong T. Y., Karr T., Harrington W. F. Rapid helix--coil transitions in the S-2 region of myosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1109–1113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M. Cell surface interactions with extracellular materials. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:761–799. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]