Abstract
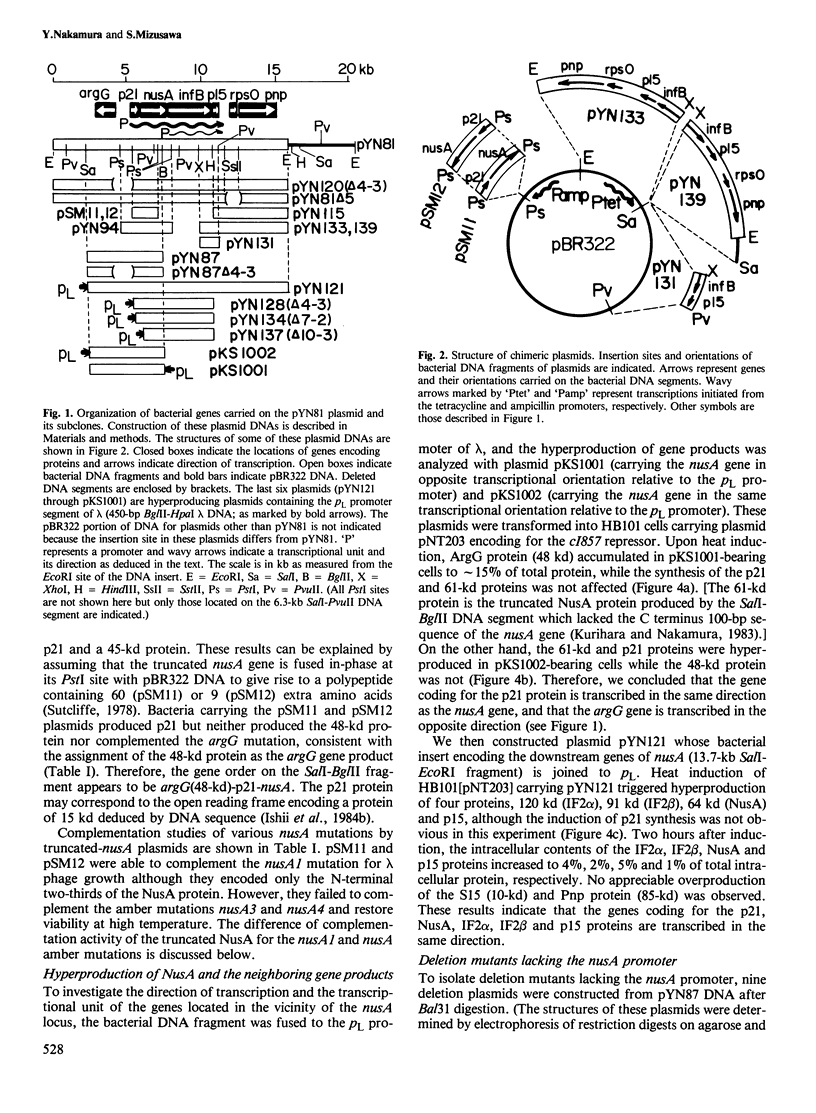
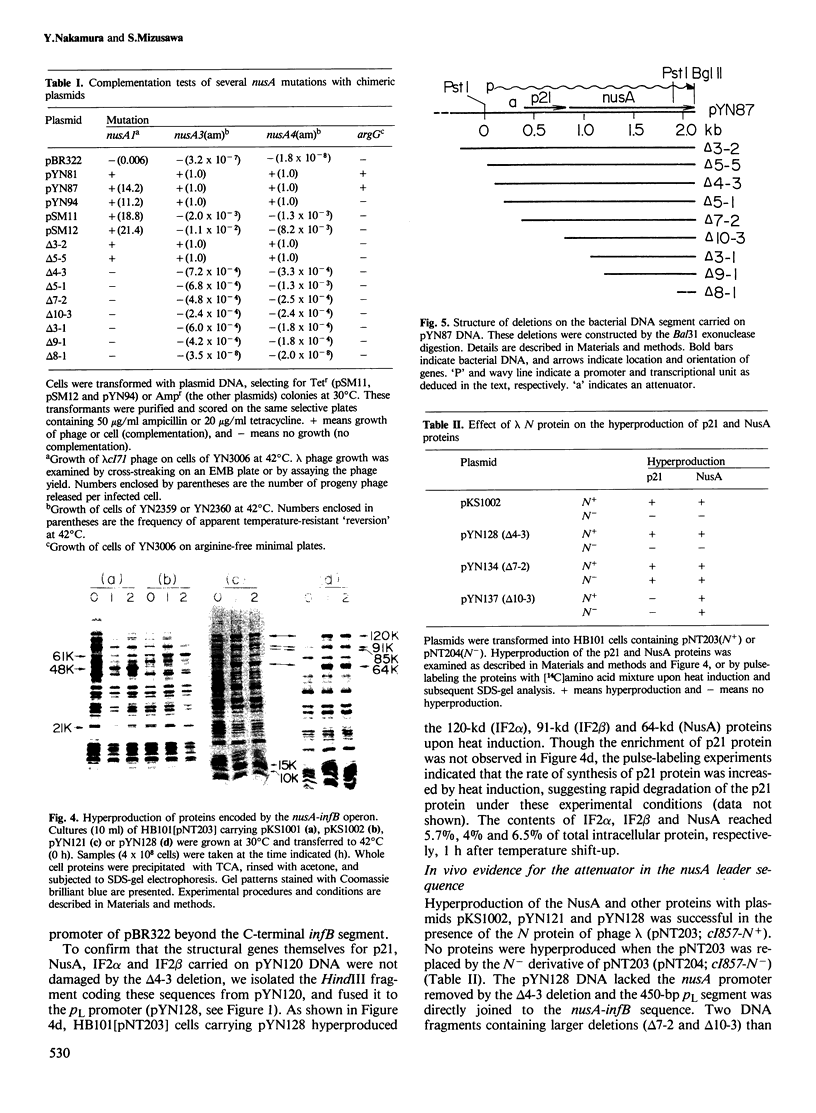
Previous work has shown that the Escherichia coli nusA gene codes for a protein which regulates transcription termination. The 16.0-kb EcoRI DNA fragment that includes the nusA gene, codes for at least eight bacterial proteins of mol. wts. 48 000 (argG), 21 000 (p21), 64 000 (nusA), 120 000 (IF2 alpha)-(infB), 91 000 (IF2 beta)(infB), 15 000 (p15), 10 000 (rpsO) and 85 000 (pnp). We have constructed several deletion and fusion derivatives from this cloned DNA and examined in vivo the structure and expression of these genes. First, the promoter functional in vivo for the nusA gene was mapped at approximately 800 bp upstream of the nusA structural gene. Second, the synthesis of five proteins, p21, NusA, IF2 alpha, IF2 beta (and p15) proteins, was affected by the deletion of the nusA promoter. Third, these same five proteins were hyperproduced after fusion of the DNA fragment to the lambda pL promoter. In addition, subcloning experiments revealed that the p15 gene is expressed by the read-through transcription from the infB gene. These results lead us to conclude that the genes coding for the p21, NusA, InfB (IF2 alpha and IF2 beta), and p15 proteins form a single-transcriptional unit ('nusA-infB operon') in vivo and that rpsO and pnp genes do not belong to the same operon. The in vivo attenuation site of this operon is described.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler H. I., Fisher W. D., Cohen A., Hardigree A. A. MINIATURE escherichia coli CELLS DEFICIENT IN DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):321–326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 7. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Jun;47(2):180–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.2.180-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Greenblatt J., Platt T. Effects of NusA protein on transcription termination in the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):945–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90457-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I., Baron L. S. Genetic characterization of a bacterial locus involved in the activity of the N function of phage lambda. Virology. 1974 Mar;58(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90149-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., McLimont M., Hanly S. Termination of transcription by nusA gene protein of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):215–220. doi: 10.1038/292215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Ihara M., Maekawa T., Nakamura Y., Uchida H., Imamoto F. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned nusA gene and its flanking region of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3333–3342. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Kuroki K., Imamoto F. tRNAMetf2 gene in the leader region of the nusA operon in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):409–413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Chamberlin M. J. Pausing and termination of transcription within the early region of bacteriophage T7 DNA in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2777–2786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Chamberlin M. J. Pausing and attenuation of in vitro transcription in the rrnB operon of E. coli. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):523–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90394-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung H., Spears C., Weissbach H. Purification and properties of a soluble factor required for the deoxyribonucleic acid-directed in vitro synthesis of beta-galactosidase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1556–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurihara T., Nakamura Y. Cloning of the nusA gene of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(2):189–195. doi: 10.1007/BF00330639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata T., Horiuchi T. Isolation and characterization of a temperature-sensitive amber suppressor mutant of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1973;123(1):77–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00282991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y. Hybrid plasmid carrying Escherichia coli genes for the primase (dnaG) and RNA polymerase sigma factor (rpoD); gene organization and control of their expression. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;178(3):487–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00337853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Osawa T., Yura T. Intragenic localization of amber and temperature-sensitive rpoD mutations affecting RNA polymerase sigma factor of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;189(2):193–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00337803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Uchida H. Isolation of conditionally lethal amber mutations affecting synthesis of the nusA protein of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(2):196–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00330640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumbridge J. A., Howe J. G., Springer M., Touati-Schwartz D., Hershey J. W., Grunberg-Manago M. Cloning and mapping of a gene for translational initiation factor IF2 in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5033–5037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumbridge J. A., Springer M. Organization of the Escherichia coli chromosome around the genes for translation initiation factor IF2 (infB) and a transcription termination factor (nusA). J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):227–243. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portier C., Migot C., Grumberg-Manago M. Cloning of E. coli pnp gene from an episome. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(2):298–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00270632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portier C. Physical localisation and direction of transcription of the structural gene for Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S15. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90164-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Uchida H. Initiation of the DNA replication of bacteriophage lambda in Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarucki-Schulz T., Jerez C., Goldberg G., Kung H. F., Huang K. H., Brot N., Weissbach H. DNA-directed in vitro synthesis of proteins involved in bacterial transcription and translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6115–6119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




