Abstract
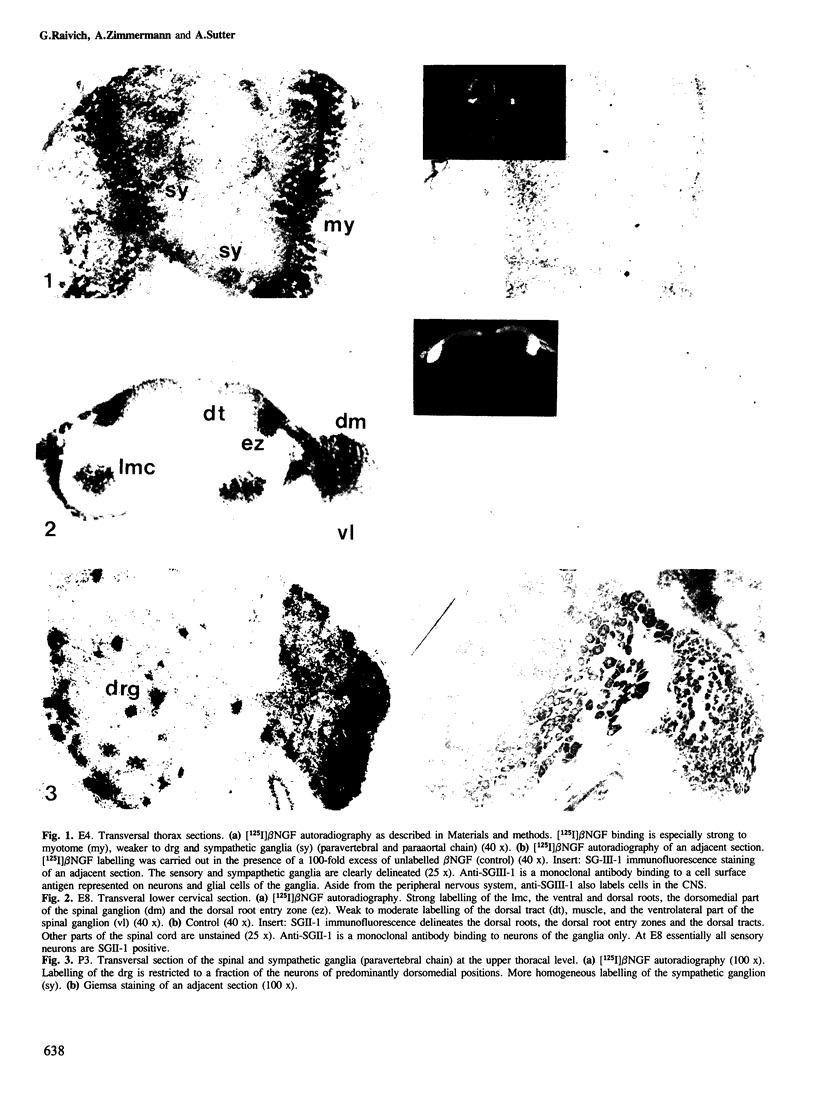
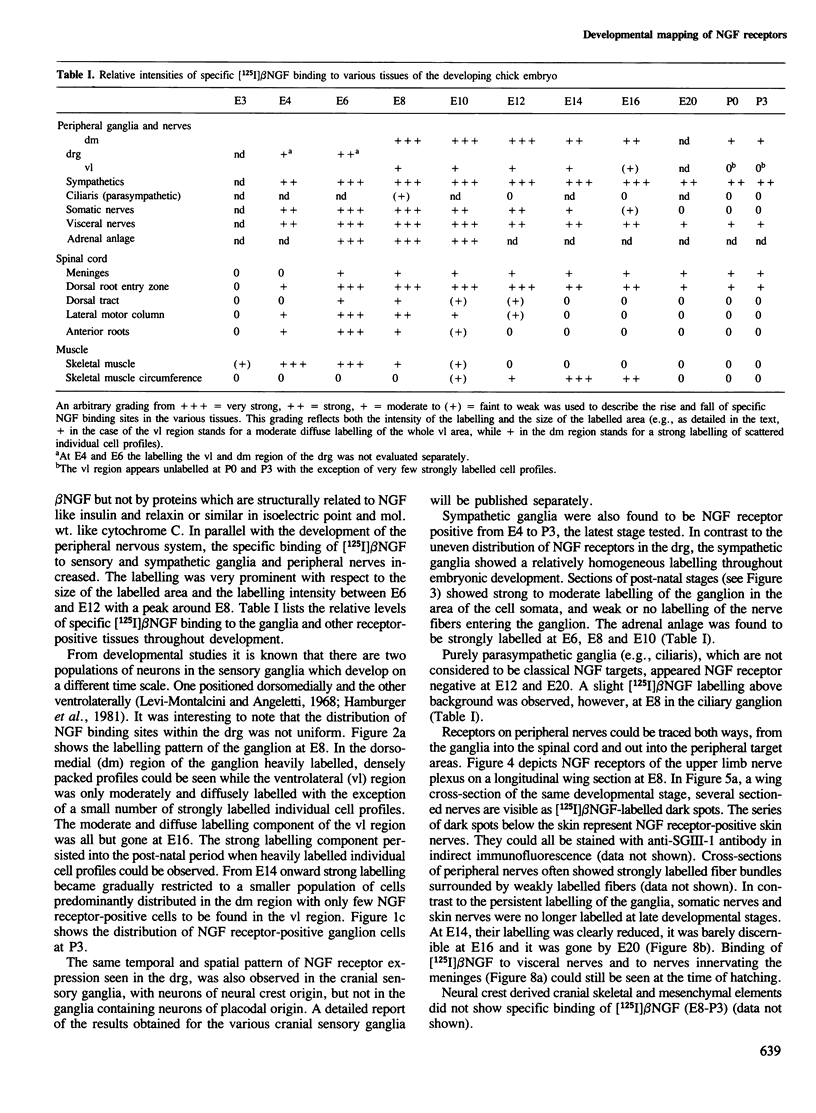
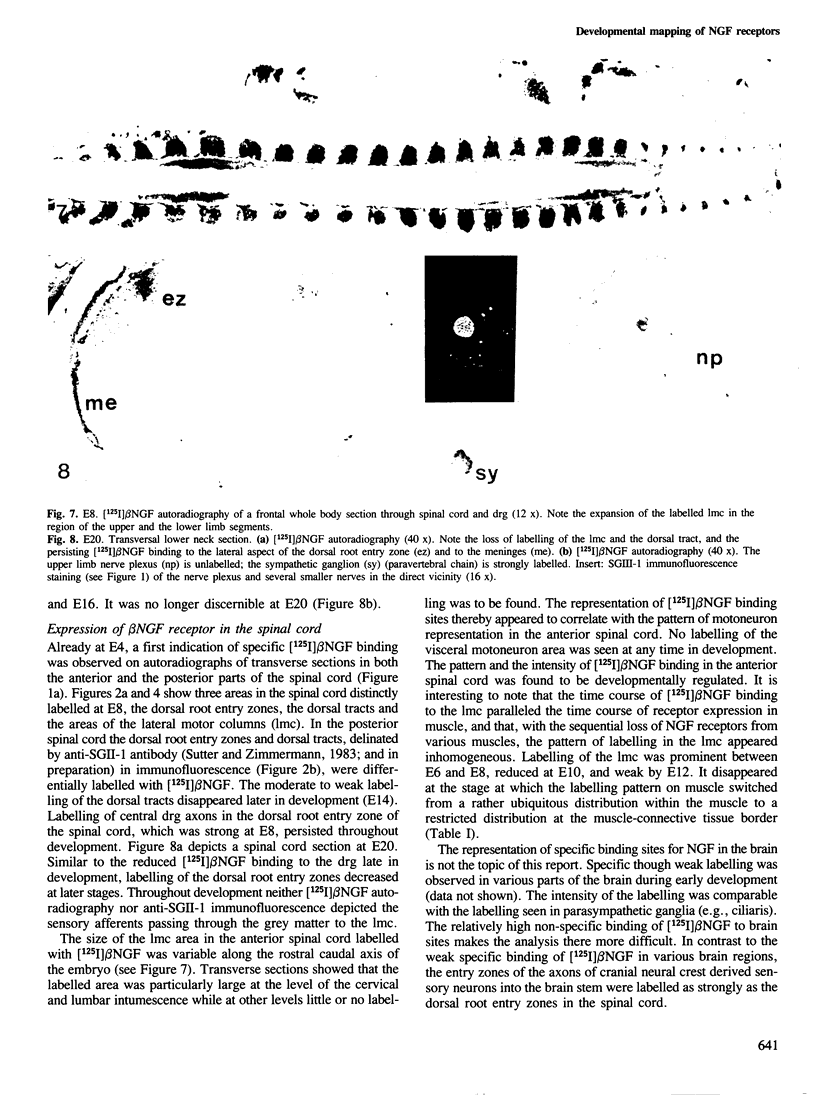
To gain insight into the developmental program of nerve growth factor (NGF) receptor expression, the binding of [125I] beta NGF to frozen chick sections was investigated autorradiographically between embryonic day 3 (E3) and post-hatching day 3. Strong NGF receptor expression was observed as early as E4, throughout embryonic development and in the post-hatching period at the classical NGF target sites: the paravertebral sensory and sympathetic ganglia, the paraaortal sympathetic ganglia as well as the cranial sensory ganglia with neurons of neural crest origin and their respective nerves. Only weak [125I] beta NGF binding was observed during a restricted time span in the parasympathetic ciliary ganglion. Clear differences were observed in the intensity and in the developmental time course of [125I] beta NGF binding to the dorsomedial and ventrolateral aspects of the dorsal root ganglia. NGF receptors were also found to be expressed on central axons of the dorsal root entry zone and the dorsal tract in the spinal cord. A transient expression of specific NGF binding sites of the same high affinity as measured at the classical NGF targets, was detected in the lateral motor column and in muscle at the time of motoneuron synapse formation and elimination.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloe L., Levi-Montalcini R. Nerve growth factor-induced transformation of immature chromaffin cells in vivo into sympathetic neurons: effect of antiserum to nerve growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1246–1250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer-Lelievre C. S., Ebendal T., Olson L., Seiger A. Localization of nerve growth factor-like immunoreactivity in rat nervous tissue. Med Biol. 1983;61(6):296–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barde Y. A., Edgar D., Thoenen H. Sensory neurons in culture: changing requirements for survival factors during embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1199–1203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boëthius J. The development of the electromyogram in chick embryos. J Exp Zool. 1967 Aug;165(3):419–424. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401650309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruni A., Bigon E., Boarato E., Mietto L., Leon A., Toffano G. Interaction between nerve growth factor and lysophosphatidylserine on rat peritoneal mast cells. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 22;138(2):190–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80438-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunso-Bechtold J. K., Hamburger V. Retrograde transport of nerve growth factor in chicken embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1494–1496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton L. E., Wilson W. H., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor in mouse saliva. Rapid isolation procedures for and characterization of 7 S nerve growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 10;253(21):7807–7812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr V. M., Simpson S. B., Jr Proliferative and degenerative events in the early development of chick dorsal root ganglia. I. Normal development. J Comp Neurol. 1978 Dec 15;182(4):727–739. doi: 10.1002/cne.901820410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J. M., Lee K. H., Endo K., Coggeshall R. E. Activation of central neurons by ventral root afferents. Science. 1983 Nov 25;222(4626):934–935. doi: 10.1126/science.6635665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F., Dawson A. An effect of nerve growth factor on parasympathetic neurite outgrowth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2091–2094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazier W. A., Boyd L. F., Pulliam M. W., Szutowicz A., Bradshaw R. A. Properties and specificity of binding sites for 125I-nerve growth factor in embryonic heart and brain. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5918–5923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnahn H., Hefti F., Heumann R., Schwab M. E., Thoenen H. NGF-mediated increase of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) in the neonatal rat forebrain: evidence for a physiological role of NGF in the brain? Brain Res. 1983 Jul;285(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(83)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Shooter E. M. The nerve growth factor: biochemistry, synthesis, and mechanism of action. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1980;3:353–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.03.030180.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene S. L., Perry H. O. Is it skin cancer--or keratoacanthoma? Geriatrics. 1984 Sep;39(9):91-4, 98-9, 102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen R. W., Barrett J. N. Characterization of the turning response of dorsal root neurites toward nerve growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):546–554. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamburger V., Brunso-Bechtold J. K., Yip J. W. Neuronal death in the spinal ganglia of the chick embryo and its reduction by nerve growth factor. J Neurosci. 1981 Jan;1(1):60–71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-01-00060.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry I. A., Campbell J. Morphometric analysis of rat superior cervical ganglion after axotomy and nerve growth factor treatment. J Neurocytol. 1976 Jun;5(3):351–360. doi: 10.1007/BF01175120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger P., Lenoir D. Nerve growth factor (NGF) stimulation of cholinergic telencephalic neurons in aggregating cell cultures. Brain Res. 1982 Feb;255(2):229–238. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(82)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Jr, Gorin P. D., Brandeis L. D., Pearson J. Dorsal root ganglion neurons are destroyed by exposure in utero to maternal antibody to nerve growth factor. Science. 1980 Nov 21;210(4472):916–918. doi: 10.1126/science.7192014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letourneau P. C. Chemotactic response of nerve fiber elongation to nerve growth factor. Dev Biol. 1978 Sep;66(1):183–196. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90283-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Angeletti P. U. Nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jul;48(3):534–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.3.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Booker B. DESTRUCTION OF THE SYMPATHETIC GANGLIA IN MAMMALS BY AN ANTISERUM TO A NERVE-GROWTH PROTEIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Mar;46(3):384–391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.3.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludueña M. A. Nerve cell differentiation in vitro. Dev Biol. 1973 Aug;33(2):268–284. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumsden A. G., Davies A. M. Earliest sensory nerve fibres are guided to peripheral targets by attractants other than nerve growth factor. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):786–788. doi: 10.1038/306786a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim R. W., Heaton M. B. The retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase from the developing limb of the chick embryo. Brain Res. 1975 Nov 14;98(2):291–302. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim R. W., Maderdrut J. L., Wells D. J. Cell death of motoneurons in the chick embryo spinal cord. VI. Reduction of naturally occurring cell death in the thoracolumbar column of Terni by nerve growth factor. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Sep 10;210(2):174–189. doi: 10.1002/cne.902100208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten U., Goedert M., Mayer N., Lembeck F. Requirement of nerve growth factor for development of substance P-containing sensory neurones. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):158–159. doi: 10.1038/287158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radeva V. Effects of the nerve-growth factor (NGF) on certain non-neuronal elements. Agressologie. 1978;19(2):99–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. M., Riopelle R. J. Uptake of nerve growth factor along peripheral and spinal axons of primary sensory neurons. J Neurosci. 1984 Jul;4(7):1683–1689. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-07-01683.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrer H., Sommer I. Simultaneous expression of neuronal and glial properties by chick ciliary ganglion cells during development. J Neurosci. 1983 Aug;3(8):1683–1693. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-08-01683.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckel K., Schwab M., Thoenen H. Specificity of retrograde transport of nerve growth factor (NGF) in sensory neurons: a biochemical and morphological study. Brain Res. 1975 May 16;89(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutter A., Riopelle R. J., Harris-Warrick R. M., Shooter E. M. Nerve growth factor receptors. Characterization of two distinct classes of binding sites on chick embryo sensory ganglia cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):5972–5982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip H. K., Johnson E. M., Jr Developing dorsal root ganglion neurons require trophic support from their central processes: evidence for a role of retrogradely transported nerve growth factor from the central nervous system to the periphery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6245–6249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann A., Sutter A., Samuelson J., Shooter E. M. A serological assay for the detection of cell surface receptors of nerve growth factor. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(3):351–361. doi: 10.1002/jss.400090306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann A., Sutter A. beta-Nerve growth factor (beta NGF) receptors on glial cells. Cell-cell interaction between neurones and Schwann cells in cultures of chick sensory ganglia. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):879–885. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]