Abstract
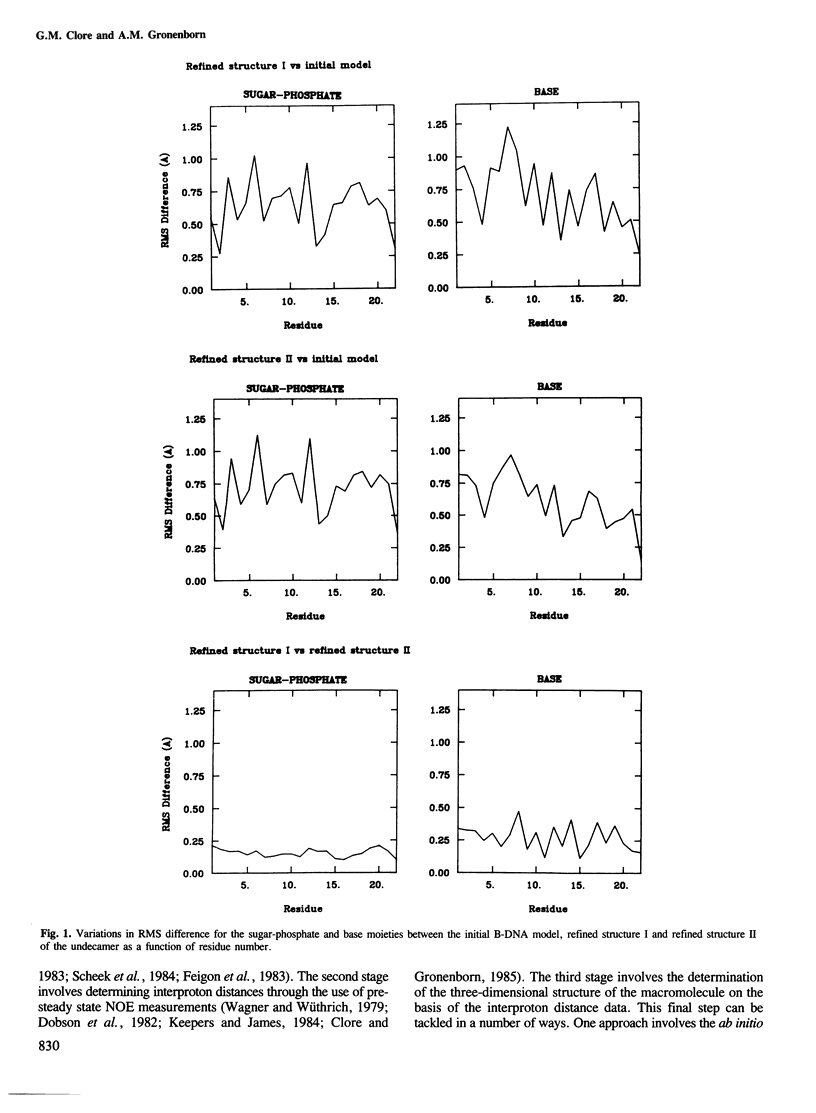
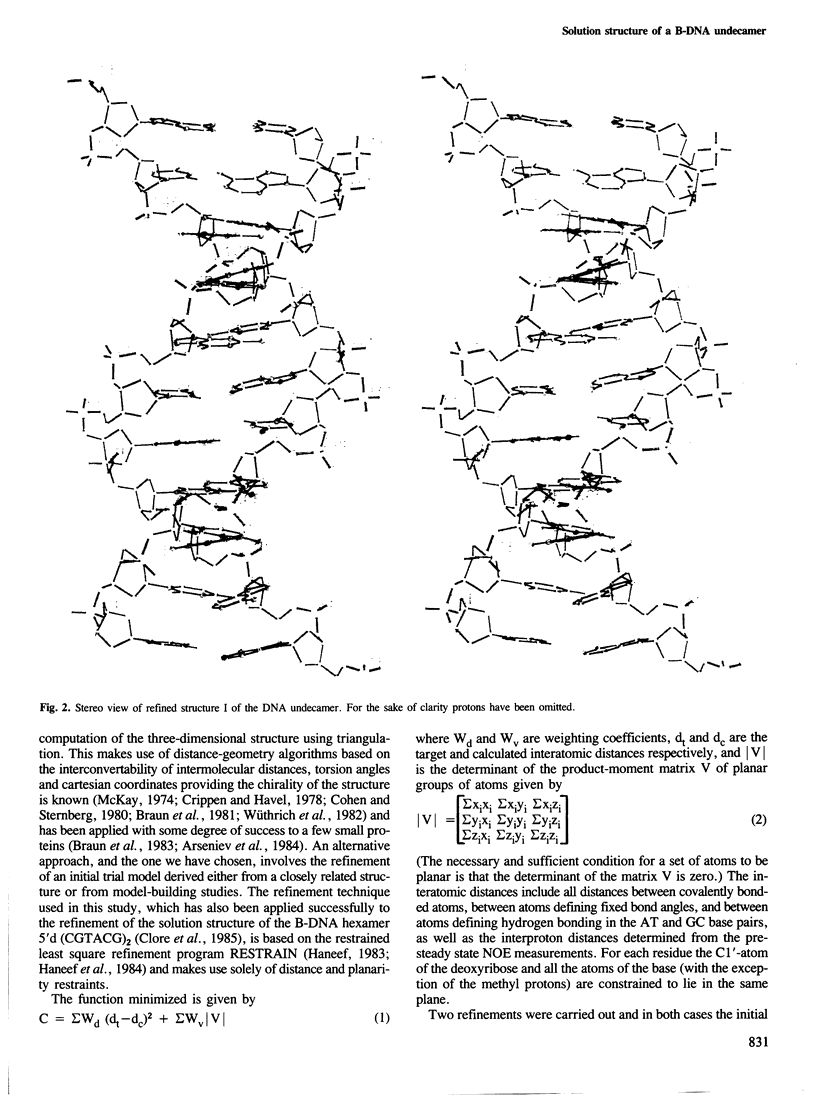
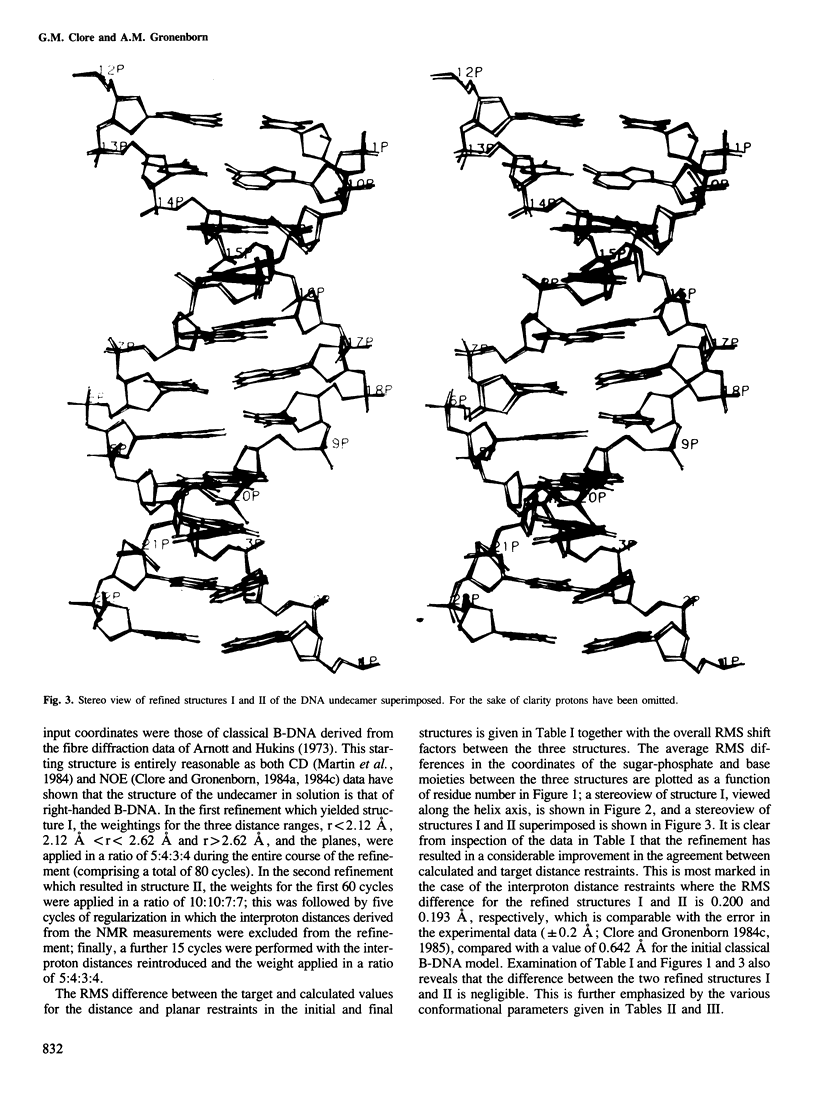
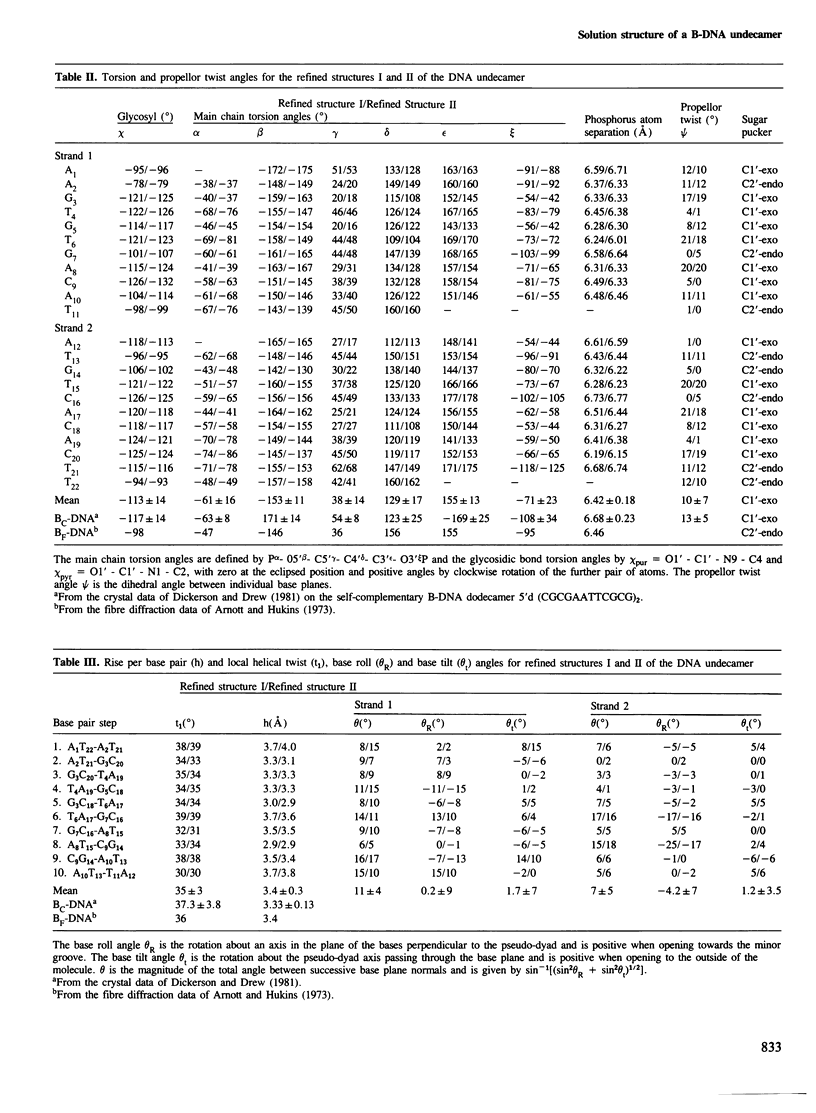
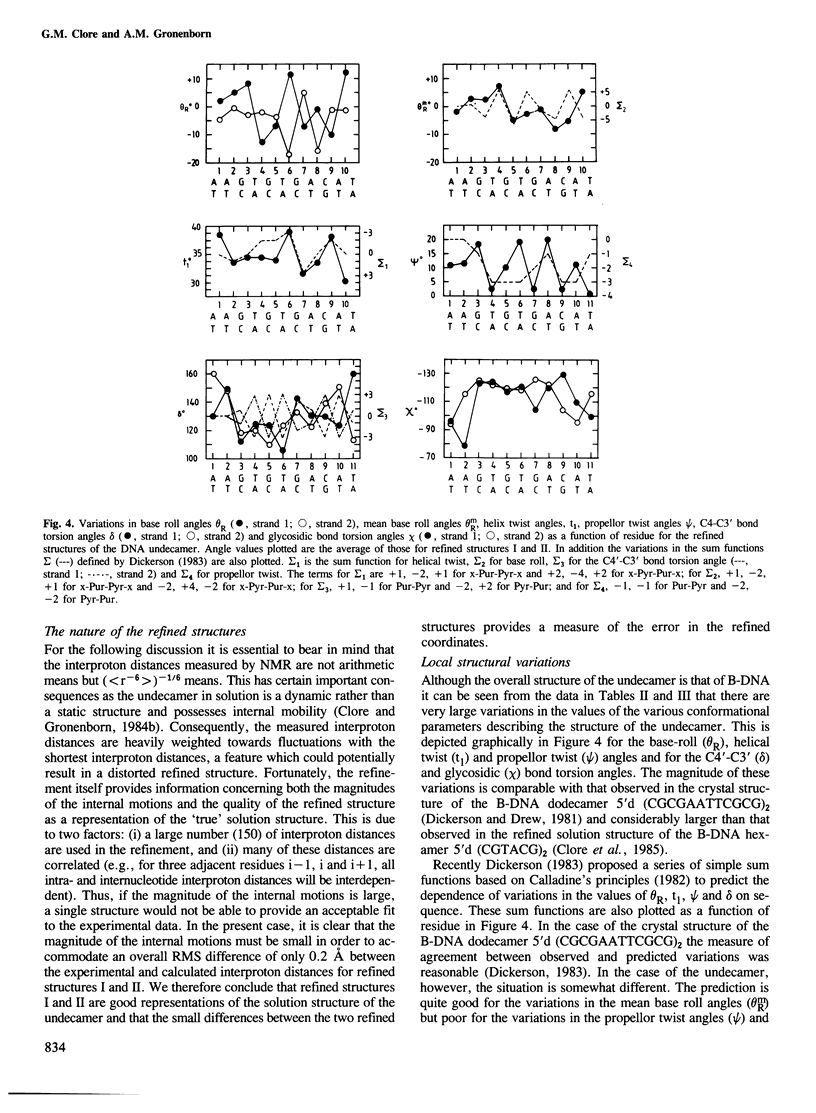
A restrained least squares refinement of the solution structure of the double-stranded DNA undecamer 5'd(AAGTGT-GACAT).5'd(ATGTCACACTT) comprising a portion of the specific target site of the cAMP receptor protein in the gal operon is presented. The structure is refined on the basis of both distance and planarity restraints, 2331 in all. The distance restraints comprise 150 interproton distances determined from pre-steady state nuclear Overhauser enhancement measurements and 2159 other interatomic distances derived from idealized geometry (i.e., distances between covalently bonded atoms, between atoms defining fixed bond angles, and between atoms defining hydrogen bonding in AT and GC base pairs). Two refinements were carried out and in both cases the final RMS difference between the experimental and calculated interproton distances was 0.2 A. The difference between the two refined structures is small (overall RMS difference of 0.23 A) and represents the error in the refined coordinates. Although the refined structures have an overall B-type conformation there are large variations in many of the local conformational parameters including backbone and glycosidic bond torsion angles, helical twist and propellor twist, base roll and base tilt angles.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. Refinement of the structure of B-DNA and implications for the analysis of x-ray diffraction data from fibers of biopolymers. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 5;81(2):93–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun W., Bösch C., Brown L. R., Go N., Wüthrich K. Combined use of proton-proton Overhauser enhancements and a distance geometry algorithm for determination of polypeptide conformations. Application to micelle-bound glucagon. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 27;667(2):377–396. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun W., Wider G., Lee K. H., Wüthrich K. Conformation of glucagon in a lipid-water interphase by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 5;169(4):921–948. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calladine C. R. Mechanics of sequence-dependent stacking of bases in B-DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 25;161(2):343–352. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M. A nuclear-Overhauser-enhancement study of the solution structure of a double-stranded DNA undecamer comprising a portion of the specific target site for the cyclic-AMP-receptor protein in the gal operon. Sequential resonance assignment. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 15;141(1):119–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M. Internal mobility in a double-stranded B DNA hexamer and undecamer. A time-dependent proton-proton nuclear Overhauser enhancement study. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jul 9;172(2):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81129-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M. Interproton distance measurements in solution for a double-stranded DNA undecamer comprising a portion of the specific target site for the cycliC AMP receptor protein in the gal operon. A nuclear Overhauser enhancement study. FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80582-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M. Sequence-dependent structural variations in two right-handed alternating pyrimidine-purine DNA oligomers in solution determined by nuclear Overhauser enhancement measurements. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2109–2115. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01710.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clore G. M., Lauble H., Frenkiel T. A., Gronenborn A. M. A two-dimensional NMR study of the solution structure of a DNA dodecamer comprising the concensus sequence for the specific DNA-binding sites of the glucocorticoid receptor protein. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 17;145(3):629–636. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen F. E., Sternberg M. J. On the prediction of protein structure: The significance of the root-mean-square deviation. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):321–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90289-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. Base sequence and helix structure variation in B and A DNA. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):419–441. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Drew H. R. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. II. Influence of base sequence on helix structure. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 15;149(4):761–786. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigon J., Leupin W., Denny W. A., Kearns D. R. Two-dimensional proton nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of the synthetic deoxyribonucleic acid decamer d(ATATCGATAT)2. Biochemistry. 1983 Dec 6;22(25):5943–5951. doi: 10.1021/bi00294a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M., Kimber B. J. An investigation into the solution structures of two self-complementary DNA oligomers, 5'-d(C-G-T-A-C-G) and 5'-d(A-C-G-C-G-C-G-T), by means of nuclear-Overhauser-enhancement measurements. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 1;221(3):723–736. doi: 10.1042/bj2210723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haasnoot C. A., Westerink H. P., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H. Conformational analysis of a hybrid DNA-RNA double helical oligonucleotide in aqueous solution: d(CG)r(CG)d(CG) studied by 1D- and 2D-1H NMR spectroscopy. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(1):131–149. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hare D. R., Wemmer D. E., Chou S. H., Drobny G., Reid B. R. Assignment of the non-exchangeable proton resonances of d(C-G-C-G-A-A-T-T-C-G-C-G) using two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance methods. J Mol Biol. 1983 Dec 15;171(3):319–336. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. R., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Specific DNA binding of the cyclic AMP receptor protein to a synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotide. A circular dichroism study. FEBS Lett. 1983 Aug 8;159(1-2):102–106. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D. G., Salisbury S. A., Bellard S., Shakked Z., Williams D. H. Proton nuclear Overhauser effect study of the structure of a deoxyoligonucleotide duplex in aqueous solution. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):2019–2025. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D. G., Salisbury S. A., Brown T., Williams D. H., Vasseur J. J., Rayner B., Imbach J. L. Use of inter-proton nuclear Overhauser effects to assign the nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of oligodeoxynucleotide and hybrid duplexes in aqueous solution. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Sep 15;135(2):307–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07654.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheek R. M., Boelens R., Russo N., van Boom J. H., Kaptein R. Sequential resonance assignments in 1H NMR spectra of oligonucleotides by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 27;23(7):1371–1376. doi: 10.1021/bi00302a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strop P., Wider G., Wüthrich K. Assignment of the 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of the proteinase inhibitor IIA from bull seminal plasma by two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance at 500 MHz. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):641–665. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80289-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., O'Neill M., de Crombrugghe B. Interaction site of Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein on DNA of galactose operon promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5090–5094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Kumar A., Wüthrich K. Systematic application of two-dimensional 1H nuclear-magnetic-resonance techniques for studies of proteins. 2. Combined use of correlated spectroscopy and nuclear Overhauser spectroscopy for sequential assignments of backbone resonances and elucidation of polypeptide secondary structures. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Feb;114(2):375–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Wüthrich K. Amide protein exchange and surface conformation of the basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor in solution. Studies with two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):343–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90180-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner G., Wüthrich K. Sequential resonance assignments in protein 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):347–366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. A., Patel D. J., Sauer R. T., Karplus M. Two-dimensional 1H NMR study of the lambda operator site OL1: a sequential assignment strategy and its application. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):130–134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson M. P., Marion D., Wüthrich K. Secondary structure in the solution conformation of the proteinase inhibitor IIA from bull seminal plasma by nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 5;173(3):341–359. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Wider G., Wagner G., Braun W. Sequential resonance assignments as a basis for determination of spatial protein structures by high resolution proton nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]